Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →How to Build Dynamic React Applications with Database Data
React is a declarative, efficient, and flexible JavaScript library for building user interfaces. The CData API Server enables you to generate REST APIs for 80+ data sources, including both on-premises and cloud-based databases. This article walks through setting up the CData API Server to create a REST API for a SQLite database and creating a simple React Web application that has live access to the database data. The React app dynamically builds and populates an HTML table based on the database data. While the article steps through most of the code, you can download the sample React project and SQLite database to see the full source code and test the functionality for yourself.
Setting Up the API Server
If you have not already done so, download the CData API Server. Once you have installed the API Server, follow the steps below to run the application, configure the application to connect to your data (the instructions in this article are for the included sample database), and then configure the application to create a REST API for any tables you wish to access in your React app.
Enable CORS
If the React Web app and API Server are on different domains, then React will generate cross-domain requests. This means that CORS (cross-origin resource sharing) must be enabled on any servers queried by React Web apps. You can enable CORS for the API Server on the Server tab in the SETTINGS page:
- Click the checkbox to enable cross-origin resource sharing (CORS).
- Either click the checkbox to allow all domains without '*' or specify the domains that are allowed to connect in Access-Control-Allow-Origin.
- Set Access-Control-Allow-Methods to "GET,PUT,POST,OPTIONS".
- Set Access-Control-Allow-Headers to "authorization".
- Click Save Changes.
Configure Your Database Connection
Follow the steps below to configure the API Server to connect to your database:
- Navigate to the Connections tab on the SETTINGS page.
- Click Add Connection.
- Configure the connection in the resulting dialog: Name your connection, select SQLite as the database, and fill the Database field with the full path to the SQLite database (the included database is chinook.db from the SQLite Tutorial).
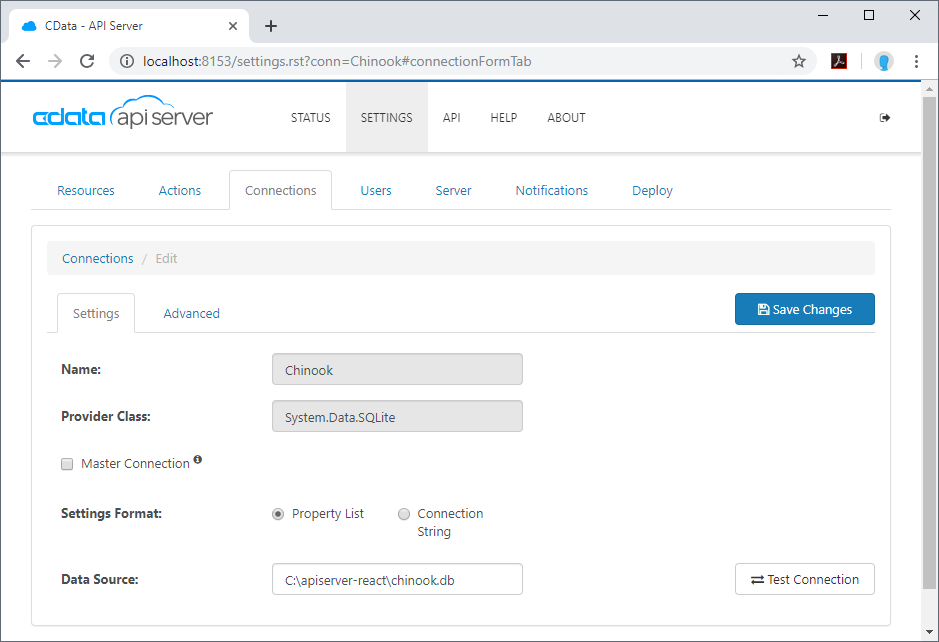
Configure a User
Next, create a user to access your database data through the API Server. You can add and configure users on the Users tab of the SETTINGS page. In this simple React app for viewing data, create a user that has read-only access: Click Add, give the user a name, select GET for the Privileges, and click Save Changes.

An authtoken is then generated for the user. You can find authtokens and other information for each user on the Users tab:
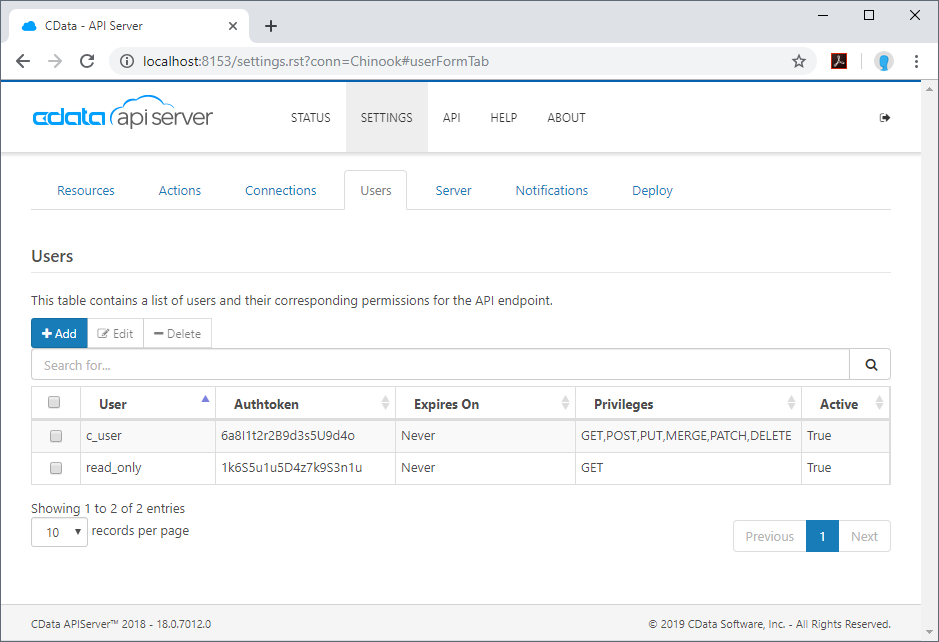
Accessing Tables
Having created a user, you are ready to enable access to the database tables:
- Click the Add Resources button on the Resources tab of the SETTINGS page.
- Select the data connection you wish to access and click Next.
- With the connection selected, enable resources by selecting each table name and clicking Next.

Sample URLs for the REST API
Having configured a connection to the database, created a user, and added resources to the API Server, you now have an easily accessible REST API based on the OData protocol for those resources. Below, you will see a list of tables and the URLs to access them. For more information on accessing the tables, you can open the API page from the navigation bar. To work with React, you can append the @json parameter to the end of URLs that do not return JSON data by default.
| Table | URL | |
|---|---|---|
| Entity (table) List | http://address:port/api.rsc/ | |
| Metadata for table albums | http://address:port/api.rsc/albums/$metadata?@json | |
| Albums data | http://address:port/api.rsc/albums | |
As with standard OData feeds, if you wish to limit the fields returned, you can add a $select parameter to the query, along with other standard URL parameters, such as $filter, $orderby, $skip, and $top.
Building a React Web Application
With the API Server setup completed, you are ready to build the sample React app. The following steps walk through the source files for the React app contained in the .zip file, making note of any relevant sections of code.
index.html
This is the home page of the sample React Web Application. It fleshes out the HTML head and body and identifies the container and the script to use to display the Web application.
main.js
This TypeScript file imports the necessary libraries, modules, and the React class. The properties, or props, for the main React class are defined here as well.
package.json
This JSON file contains the properties, including dependencies, of the React app. This file is generated automatically.
webpack.config.js
This JavaScript file defines various configurations for the React app.
App.jsx
This JavaScript XML file contains the code needed to build the React app. The class App contains all of the functions needed to retrieve data from the API Server and render the different parts of the React app. The methods are described below.
constructor
The constructor of the App class. In it, the state contains the dynamic data used to build the Web app. You can also bind other methods on this so that you can modify the state within those methods.
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
selectedTable: '',
selectedColumns: [],
tables: [],
columns: [],
tableData: [],
auth: 'Basic ' + btoa(props.user + ':' + props.pass),
};
this.onTableChange = this.onTableChange.bind(this);
this.onColumnChange = this.onColumnChange.bind(this);
this.renderTableHeaders = this.renderTableHeaders.bind(this);
this.renderTableBody = this.renderTableBody.bind(this);
this.getColumnList = this.getColumnList.bind(this);
this.getData = this.getData.bind(this);
}
componentDidMount
As per the React specification, the componentDidMount method is called before the render method and can be used to update the state variables of the app, after the constructor has run. In this method, you can send the HTTP request to the API Server for the list of tables and set the tables and selectedTable state variables.
In the sample, a call to the getColumnList method retrieves the list of available columns for the first (and currently selected) table.
componentDidMount() {
Object.assign(axios.defaults, {headers: {authorization: this.state.auth}});
axios.get(`${this.props.baseUrl}`)
.then(res => {
const tables = res.data.value;
this.setState({ tables });
this.setState({ selectedTable: tables[0].name});
})
.catch(function (error) {
if (error.response) {
alert('Code: ' + error.response.data.error.code + '\r\nMessage: ' + error.response.data.error.message);
} else {
console.log('Error', error.message);
}
});
this.getColumnList();
}
getColumnList
This function retrieves the list of columns available for the selectedTable parameter (or the table currently selected in the UI if the parameter is undefined). It performs the HTTP request and parses the response, setting the columns and selectedColumns states.
getColumnList(selectedTable) {
if (!selectedTable) {
selectedTable = this.state.selectedTable;
}
Object.assign(axios.defaults, {headers: {authorization: this.state.auth}});
axios.get(`${this.props.baseUrl}/${selectedTable}/$metadata?@json`)
.then(res => {
let columns = res.data.items[0]["odata:cname"];
this.setState({
columns,
selectedColumns: [],
});
})
.catch(error => {
if (error.response) {
alert('Code: ' + error.response.data.error.code + '\r\nMessage: ' + error.response.data.error.message);
} else {
console.log('Error', error.message);
}
});
}
renderTableList
This function uses the tables state variable to build out the options for the HTML drop-down select for selecting a table.
renderTableList() {
let tablesHTML = [];
for (let i = 0; i < this.state.tables.length; i++) {
let table = this.state.tables[i];
tablesHTML.push();
}
return tablesHTML;
}
renderColumnList
This function uses the columns state variable to build out the options for the HTML multi-select for selecting columns.
renderColumnList() {
let columnsHTML = [];
for (let i = 0; i < this.state.columns.length; i++){
let column = this.state.columns[i];
columnsHTML.push();
}
return columnsHTML;
}
renderTable
This function provides the basic framework for the HTML table based on the data retrieved from the API Server. It uses two helper functions, renderTableHeaders() and renderTableBody(), to build the table headers and data rows.
renderTable() {
return (
<table>
<thead>
{ this.renderTableHeaders() }
</thead>
{ this.renderTableBody() }
</table>
);
}
renderTableHeaders
This function uses the selectedColumns state variable to build out the headers for the HTML table used to display the data from the API Server.
renderTableHeaders() {
let headers = [];
for (let i = 0; i < this.state.selectedColumns.length; i++) {
let col = this.state.selectedColumns[i];
headers.push(<th key={col} style={{backgroundColor: '#177CB8', color: 'white', border: '1px solid grey', borderCollapse: 'collapse', padding: '5px'}}>{col}</th>)
}
return (<tr>{headers}</tr>);
}
renderTableBody
This function uses the tableData and selectedColumns state variables to build out the data rows for the HTML table used to display the data from the API Server.
renderTableBody() {
let rows = [];
this.state.tableData.forEach(function(row) {
rows.push(
<tr key={btoa('row'+rows.length)}>
{this.state.selectedColumns.map(col =>
<td key={col} style={{border: '1px solid grey', borderCollapse: 'collapse', padding: '5px'}}>{row[col]}</td>
)}
</tr>
)
}.bind(this));
return (<tbody>{rows}</tbody>);
}
getData
This function retrieves the data from the API Server, building a list for the $select parameter based on the selectedColumns state variable and using the selectedTable state variable to determine which resource to request data from. The data returned by the API Server is stored in the tableData state variable.
getData() {
let columnList = '';
columnList = this.state.selectedColumns.join(',');
Object.assign(axios.defaults, {headers: {authorization: this.state.auth}});
axios.get(`${this.props.baseUrl}/${this.state.selectedTable}/?$select=${columnList}`)
.then(res => {
const tableData = res.data.value;
this.setState({ tableData });
})
.catch(error => {
if (error.response) {
alert('Code: ' + error.response.data.error.code + '\r\nMessage: ' + error.response.data.error.message);
} else {
console.log('Error', error.message);
}
});
}
onTableChange
This function handles the change event on the HTML drop-down select for choosing a table. In the function, the selectedTable state variable is set to the selected value and the tableData state variable is cleared of all values. Also, a call to the getColumnList function updates the HTML multi-select element for choosing columns.
onTableChange(event) {
const selectedTable = event.target.value;
this.setState({
selectedTable,
tableData: [],
});
this.getColumnList(selectedTable);
}
onColumnChange
This function handles the change event on the HTML multi-select for choosing columns to retrieve and display. After determining which columns are selected, the selectedColumns state variable is updated and the tableData state variable is cleared.
onColumnChange(event) {
let options = event.target.options;
let selectedColumns = [];
for (let i = 0; i < options.length; i++){
if (options[i].selected){
selectedColumns.push(options[i].value);
}
}
this.setState({
selectedColumns,
tableData: [],
});
}
render
This function is the function that controls the layout and display of the various HTML elements. It contains all of the static HTML features, as well as function calls to those functions that render the dynamic elements.
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1 style={{fontSize: '1.2em', color: '#177CB8', marginBottom: '0'}}>CData API Server React Demo</h1>
<br/>
<label>Select a Table</label>
<br/>
<select className='tableDropDown' onChange={this.onTableChange}>
{ this.renderTableList() }
</select>
<br/>
<br/>
<label>Select {this.state.selectedTable} Columns</label>
<br/>
<select className='columnMultiSelect' onChange={this.onColumnChange} multiple>
{ this.renderColumnList() }
</select>
<br/>
<br/>
{ this.state.selectedColumns.length > 0 ? <button onClick={this.getData}>Get [{ this.state.selectedTable }] Data</button> : null }
<br/>
<br/>
{ this.state.tableData.length > 0 ? this.renderTable() : null }
</div>
);
}
Configuring the React App
With the connection to data configured and the source files for the React app reviewed, you are now ready to run the React Web application. You need to have node.js installed on your machine in order to run the React app. There are several modules that you also need to install before you can run the application.
Global Modules
In order to run the React App, install the babel and babel-cli modules globally from the command line:
- npm install -g babel
- npm install -g babel-cli
Setting Up the Project
In the next steps you will set up your React project, creating and populating your package.json file.
- In the command line,
change to the directory with the source files:
cd ./apiserver-react
-
Once in the directory, install the necessary modules using the preconfigured package.json file:
npm install
Running the React App
Now that you have created your package.json file and installed the necessary modules, you are ready to run the React app. To do so, you can simply navigate to the directory for the React app in a command-line interface and execute the following command:
npm start
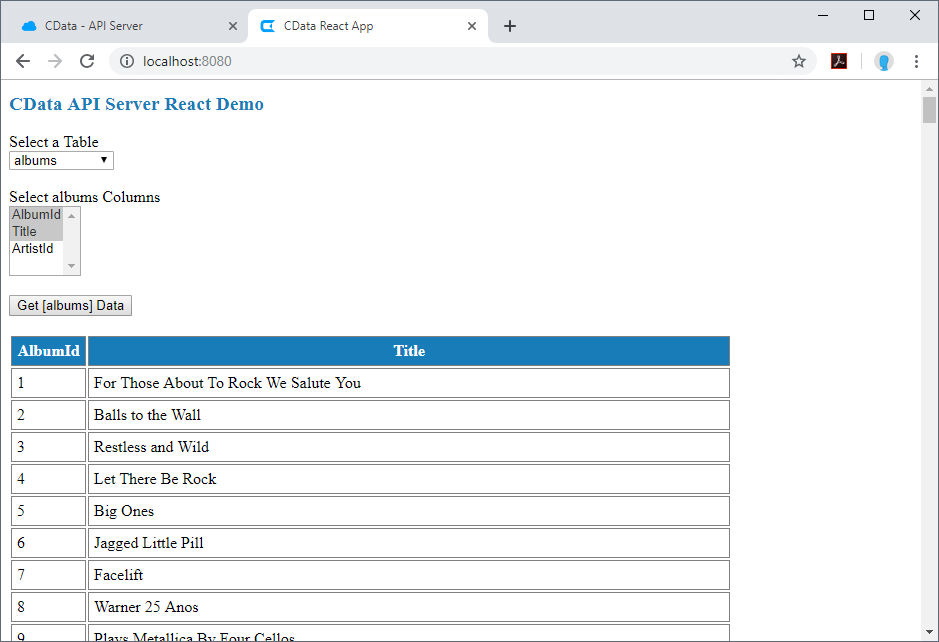
When the React app launches, the title and a drop down menu to select a table are displayed. The list of tables is retrieved from the API Server and includes all of the tables you added as resources when configuring the API Server.
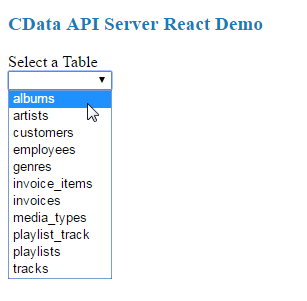
When you select a table, the drop-down, multi-select menu for columns appears, and you can then select the columns you wish to see in your table. As you select columns, the table headers appear.
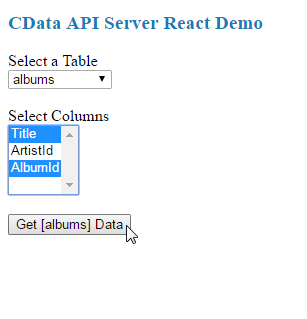
Once you select the table and columns, you can click the Get [table] Data button to retrieve data from your database via the API Server. The HTML table will be populated with data based on the table and columns you selected before clicking on the button.
Free Trial & More Information
Now that you have accomplished the steps needed to connect to your database data in dynamic Web pages, download the API Server to start building dynamic Web pages using live data from your on-premises and cloud-based databases, including SQLite, MySQL, SQL Server, Oracle, and PostgreSQL! As always, our world-class support team is ready to answer any questions you may have.






