Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Build Charts with AlloyDB Data in Clear Analytics
Create dynamic charts and perform analytics based on AlloyDB data in Clear Analytics.
The CData ODBC Driver for AlloyDB enables access to live data from AlloyDB under the ODBC standard, allowing you work with AlloyDB data in a wide variety of BI, reporting, and ETL tools and directly, using familiar SQL queries. This article shows how to use Clear Analytics, a Microsoft Excel Add-In, to connect to AlloyDB as an ODBC source and create queries, tables, and charts (including PivotTables) based on AlloyDB data.
Connect to AlloyDB Data
Configure the ODBC Data Source Name
If you have not already done so, provide values for the required connection properties in the data source name (DSN). You can use the built-in Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to configure the DSN. This is also the last step of the driver installation. See the "Getting Started" chapter in the help documentation for a guide to using the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure a DSN.
The following connection properties are usually required in order to connect to AlloyDB.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the AlloyDB database.
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
You can also optionally set the following:
- Database: The database to connect to when connecting to the AlloyDB Server. If this is not set, the user's default database will be used.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the AlloyDB database. This property is set to 5432 by default.
Authenticating with Standard Authentication
Standard authentication (using the user/password combination supplied earlier) is the default form of authentication.
No further action is required to leverage Standard Authentication to connect.
Authenticating with pg_hba.conf Auth Schemes
There are additional methods of authentication available which must be enabled in the pg_hba.conf file on the AlloyDB server.
Find instructions about authentication setup on the AlloyDB Server here.
Authenticating with MD5 Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to md5.
Authenticating with SASL Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to scram-sha-256.
Authenticating with Kerberos
The authentication with Kerberos is initiated by AlloyDB Server when the ∏ is trying to connect to it. You should set up Kerberos on the AlloyDB Server to activate this authentication method. Once you have Kerberos authentication set up on the AlloyDB Server, see the Kerberos section of the help documentation for details on how to authenticate with Kerberos.
When you configure the DSN, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
Configure the Data Source in Clear Analytics
- Open Excel and navigate to the CLEAR ANALYTICS ribbon. Once there, open the Data Manager.
- Select Database as the data source.
- In the Set Connection section, click the option to create a new database.
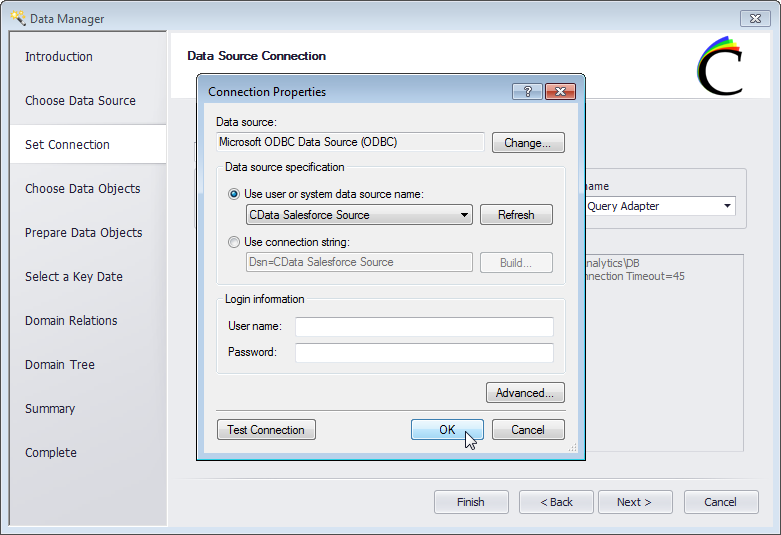
- Select Microsoft ODBC Data Source as the data source and click OK.
- Select the DSN you already configured from the drop-down menu.
![Selecting the DSN.]()
- Back on the Set Connection section, select Standard (ANSI ODBC) Query Builder as the SQL Builder Provider and click Next.
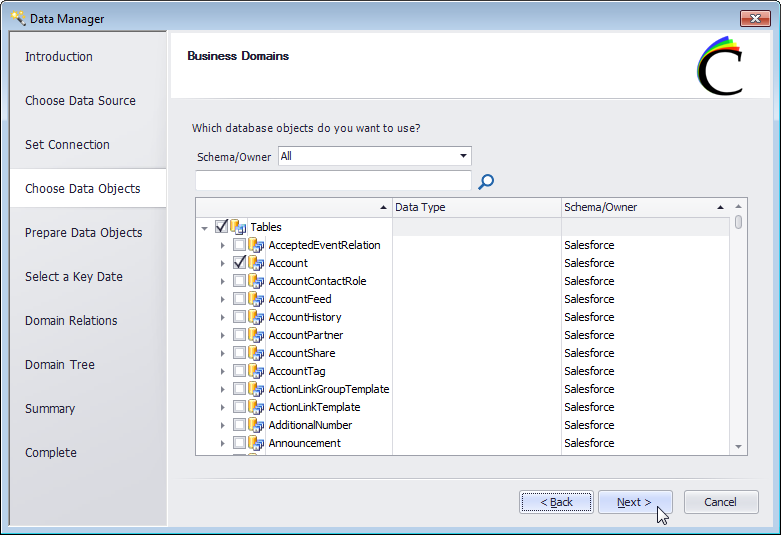
- Select the Schema/Owner and choose the domains (tables) that you wish to use in Clear Analytics.
![Selecting data tables (called Domains in Clear Analytics).]()
- Prepare your data objects as needed by customizing the display names and descriptions of the tables and columns.
- For the vast majority of the CData ODBC Drivers, you will not set a key date for your domains.
- In the Domain Relations section, add any relational information between tables.
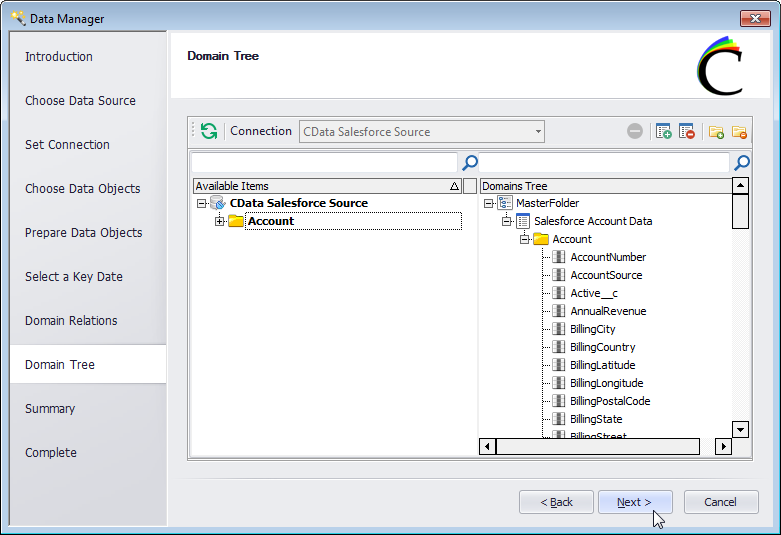
- In the Domain Tree section, create groups for your data and add the available items to the groups.
![Adding Domains (tables) to Groups in the Domain Tree.]()
- Review the summary of your data and click Finish.
Create a Chart with AlloyDB Data
You are now ready to create a chart with AlloyDB data.
Create a New Query
- Click Repository in the CLEAR ANALYTICS ribbon.
- Create a new query.
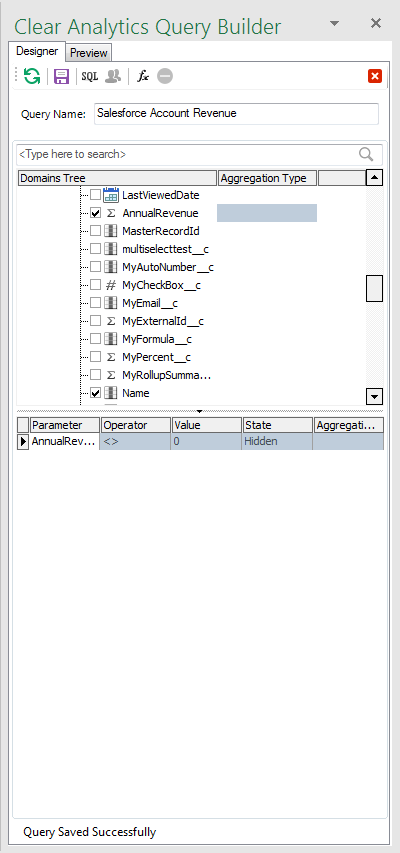
- Select the columns you wish to retrieve.
- Set the aggregation type for your data (use the blank entry if you do not wish to aggregate the data).
- Set filters and formulas by dragging columns to the lower window.
- Name your query and click Save.
![Creating a New Query.]()
Build a Chart Based on a Query Report
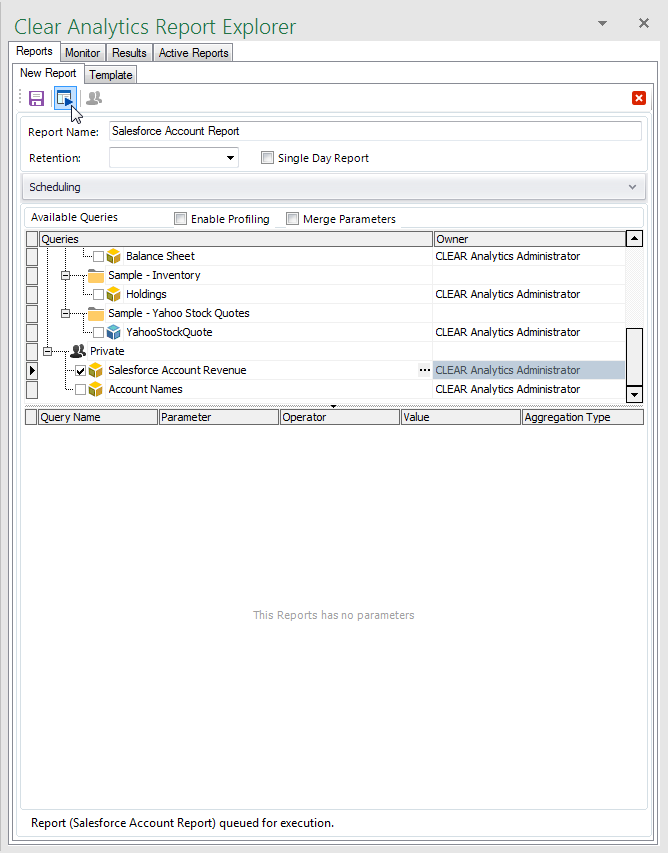
With the query created, you are now ready to execute a report and display a chart.- Click Report Explorer in the CLEAR ANALYTICS ribbon.
- In the Report Explorer pane, click the 'New Report' icon in the toolbar.
- Select the query you just created.
- Name the report and click 'Save and Execute'.
![Creating and Executing a Report.]()
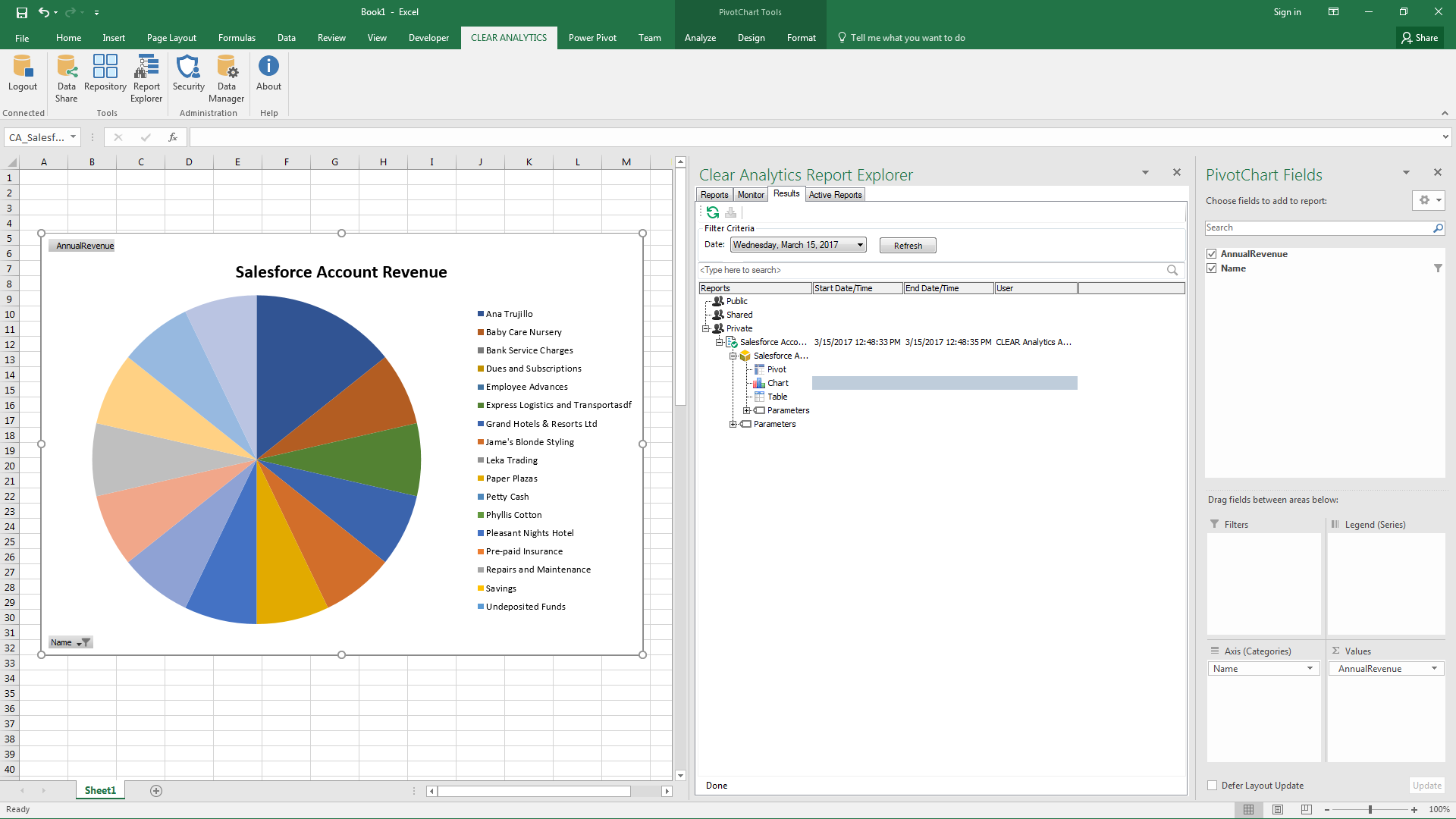
- Click the Results tab within the Report Explorer
- Expand your report and drag the chart to the Excel spreadsheet.
- In the resulting PivotChart window, drag the fields (columns) to the Filters, Legends, Axis (Categories), and Values windows.
![Building a PivotChart.]()
With a new data source in Clear Analytics established and a chart created, you are ready to begin analysis of AlloyDB data. With the ODBC Driver for AlloyDB and Clear Analytics, you can perform self-service analytics in Excel with live data, directly from AlloyDB.