Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Create Data Visualizations in Cognos BI with Amazon Athena Data
Access Amazon Athena data as an ODBC data source in Cognos Business Intelligence and create data visualizations in Cognos Report Studio.
You can use the CData ODBC driver for Amazon Athena to integrate Amazon Athena data with the drag-and-drop style of Cognos Report Studio. This article describes both a graphical approach to create data visualizations, with no SQL required, as well as how to execute any SQL query supported by Amazon Athena.
About Amazon Athena Data Integration
CData provides the easiest way to access and integrate live data from Amazon Athena. Customers use CData connectivity to:
- Authenticate securely using a variety of methods, including IAM credentials, access keys, and Instance Profiles, catering to diverse security needs and simplifying the authentication process.
- Streamline their setup and quickly resolve issue with detailed error messaging.
- Enhance performance and minimize strain on client resources with server-side query execution.
Users frequently integrate Athena with analytics tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Excel for in-depth analytics from their preferred tools.
To learn more about unique Amazon Athena use cases with CData, check out our blog post: https://www.cdata.com/blog/amazon-athena-use-cases.
Getting Started
Configure and Publish the Data Source
If you have not already, first specify connection properties in an ODBC DSN (data source name). This is the last step of the driver installation. You can use the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure ODBC DSNs.
Authenticating to Amazon Athena
To authorize Amazon Athena requests, provide the credentials for an administrator account or for an IAM user with custom permissions: Set AccessKey to the access key Id. Set SecretKey to the secret access key.
Note: Though you can connect as the AWS account administrator, it is recommended to use IAM user credentials to access AWS services.
Obtaining the Access Key
To obtain the credentials for an IAM user, follow the steps below:
- Sign into the IAM console.
- In the navigation pane, select Users.
- To create or manage the access keys for a user, select the user and then select the Security Credentials tab.
To obtain the credentials for your AWS root account, follow the steps below:
- Sign into the AWS Management console with the credentials for your root account.
- Select your account name or number and select My Security Credentials in the menu that is displayed.
- Click Continue to Security Credentials and expand the Access Keys section to manage or create root account access keys.
Authenticating from an EC2 Instance
If you are using the CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 from an EC2 Instance and have an IAM Role assigned to the instance, you can use the IAM Role to authenticate. To do so, set UseEC2Roles to true and leave AccessKey and SecretKey empty. The CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 will automatically obtain your IAM Role credentials and authenticate with them.
Authenticating as an AWS Role
In many situations it may be preferable to use an IAM role for authentication instead of the direct security credentials of an AWS root user. An AWS role may be used instead by specifying the RoleARN. This will cause the CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 to attempt to retrieve credentials for the specified role. If you are connecting to AWS (instead of already being connected such as on an EC2 instance), you must additionally specify the AccessKey and SecretKey of an IAM user to assume the role for. Roles may not be used when specifying the AccessKey and SecretKey of an AWS root user.
Authenticating with MFA
For users and roles that require Multi-factor Authentication, specify the MFASerialNumber and MFAToken connection properties. This will cause the CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 to submit the MFA credentials in a request to retrieve temporary authentication credentials. Note that the duration of the temporary credentials may be controlled via the TemporaryTokenDuration (default 3600 seconds).
Connecting to Amazon Athena
In addition to the AccessKey and SecretKey properties, specify Database, S3StagingDirectory and Region. Set Region to the region where your Amazon Athena data is hosted. Set S3StagingDirectory to a folder in S3 where you would like to store the results of queries.
If Database is not set in the connection, the data provider connects to the default database set in Amazon Athena.
When you configure the DSN, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
If you are running Cognos from a 64-bit machine and want to modify the DSN or create other Amazon Athena DSNs, you must use a system DSN. You will also need to open the 32-bit ODBC Data Source Administrator. You can open it with the following command:
C:\Windows\sysWOW64\odbcad32.exe
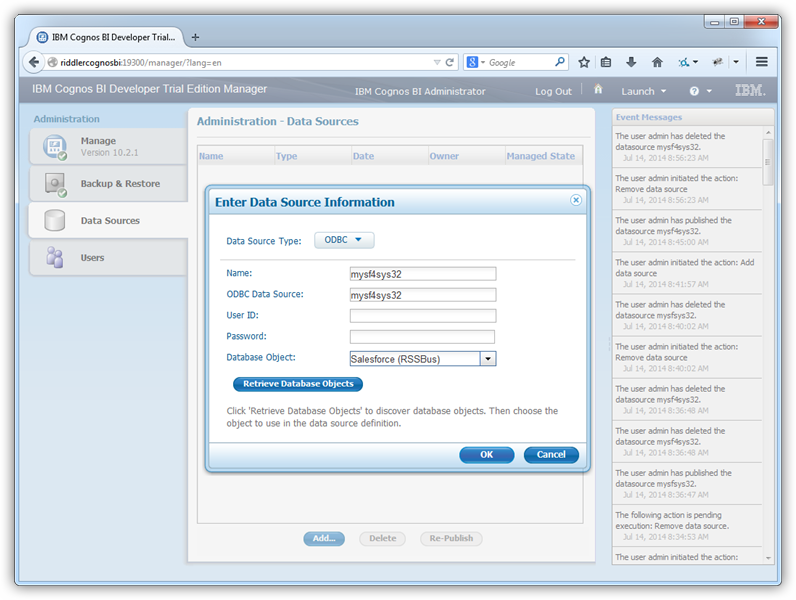
After creating a DSN, you can then publish the data source:
- Open Cognos Administration and click Data Source Connections to add a new data source:
-
Select the ODBC option and enter the DSN, CData AmazonAthena Sys, and a user-friendly name.
- Click Retrieve Objects and choose the CData Amazon Athena database object.
![The DSN used to add the data source. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
Add Data Visualizations to a Report
You can now create reports on Amazon Athena data in Cognos Report Studio by dragging and dropping table columns from the Source Explorer onto report objects. The sections below show how to create a simple report with a chart that shows up-to-date data.
As you build the report, Cognos Report Studio will generate SQL queries and rely on the driver to execute them. The driver will convert queries into requests to the Amazon Athena API. To execute queries to the live Amazon Athena data, the driver depends on the capabilities of the underlying API.
Create a Chart Based on an Aggregate
You can populate almost any report object in Cognos with Amazon Athena data by simply dragging and dropping columns from the Source Explorer onto the dimensions of the object. The column in the Series dimension of the chart is automatically grouped.
Additionally, Cognos sets a logical default aggregate function for the measure dimension based on the data type. For this example, override the default by clicking the TotalDue column in the Data Items tab and set the Aggregate Function property to Not Applicable. The Rollup Aggregate Function property must be set to Automatic.
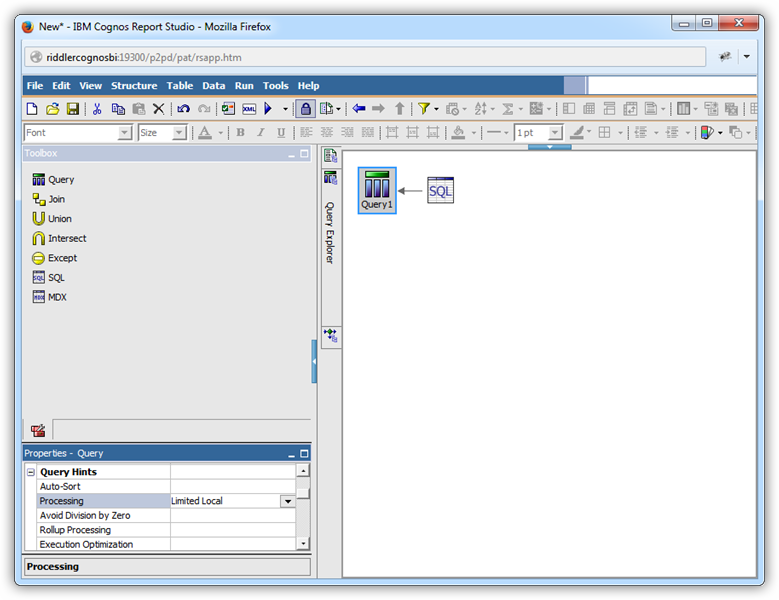
Convert a Query Object to SQL
When you know the query you need, or if you want to adjust the generated query, convert a query object into an SQL statement. After a query has been converted to SQL, the UI controls are not available for the query object. Follow the procedure below to populate a chart with user-defined SQL.
Cognos will rely on the driver to execute the user-defined query. Using the driver's SQL engine ensures that queries will always return up-to-date results, as there is no cached copy of the data.
- Hover over the Query Explorer and click the Queries folder to display the query objects in your report.
-
If you want to edit the autogenerated query, click the button in the Generated SQL property for the query object. In the resulting dialog, click Convert.
If you want to enter a new SQL statement, drop an SQL object in-line with the query object.
- Modify the properties for the SQL object: Select the Amazon Athena data source in the SQL properties and set the SQL Syntax property to Native.
Click the button in the SQL property and enter the SQL query in the resulting dialog. This example uses the query below:
SELECT Name, TotalDue FROM CustomersModify the properties for the query object: Set the Processing property to "Limited Local". This value is required to convert a query object to SQL.
![A query object created from an SQL statement.]()
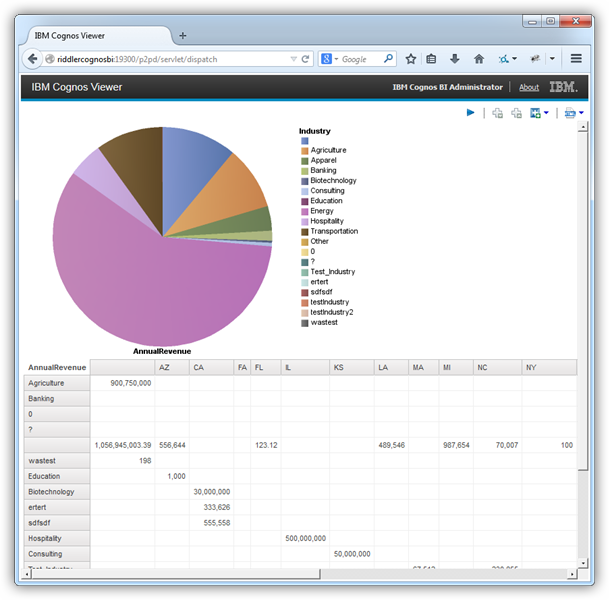
Fill a Chart with the Results of a Query
You can now access the results of the SQL query as objects in the Data Items tab. Follow the procedure below to create a chart with the results; for example, the TotalDue for each Name from the Customers table.
- Return to the page by hovering over the Page Explorer and then clicking the page object.
- Drag a pie chart from the toolbox onto the workspace.
- In the properties for the chart, set the Query property to the name of the query you created above.
- Click the Data Items tab and drag columns onto the x- and y-axes. In this example, drag the Name column to the Series (pie slices) box and the TotalDue column to the Default Measure box.
-
Modify the default properties for the Default Measure (the TotalDue values): In the Aggregate Function box, select the Total option.
Run the report to add the results of the query.