Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →How to Access Live EnterpriseDB Data in Power Automate Desktop via ODBC
The CData ODBC Driver for EnterpriseDB enables you to integrate EnterpriseDB data into workflows built using Microsoft Power Automate Desktop.
The CData ODBC Driver for EnterpriseDB enables you to access live EnterpriseDB data in workflow automation tools like Power Automate. This article shows how to integrate EnterpriseDB data into a simple workflow, moving EnterpriseDB data into a CSV file.
Through optimized data processing, CData ODBC Drivers offer unmatched performance for interacting with live EnterpriseDB data in Microsoft Power Automate. When you issue complex SQL queries from Power Automate to EnterpriseDB, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to EnterpriseDB and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations client-side (e.g. SQL functions and JOIN operations).
Connect to EnterpriseDB as an ODBC Data Source
If you have not already, first specify connection properties in an ODBC DSN (data source name). This is the last step of the driver installation. You can use the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure ODBC DSNs.
The following connection properties are required in order to connect to data.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the EnterpriseDB database.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the EnterpriseDB database.
You can also optionally set the following:
- Database: The default database to connect to when connecting to the EnterpriseDB Server. If this is not set, the user's default database will be used.
Connect Using Standard Authentication
To authenticate using standard authentication, set the following:
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the EnterpriseDB server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the EnterpriseDB server.
Connect Using SSL Authentication
You can leverage SSL authentication to connect to EnterpriseDB data via a secure session. Configure the following connection properties to connect to data:
- SSLClientCert: Set this to the name of the certificate store for the client certificate. Used in the case of 2-way SSL, where truststore and keystore are kept on both the client and server machines.
- SSLClientCertPassword: If a client certificate store is password-protected, set this value to the store's password.
- SSLClientCertSubject: The subject of the TLS/SSL client certificate. Used to locate the certificate in the store.
- SSLClientCertType: The certificate type of the client store.
- SSLServerCert: The certificate to be accepted from the server.
When you configure the DSN, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing workflows.
Integrate EnterpriseDB Data into Power Automate Workflows
After configuring the DSN for EnterpriseDB, you are ready to integrate EnterpriseDB data into your Power Automate workflows. Open Microsoft Power Automate, add a new flow, and name the flow.
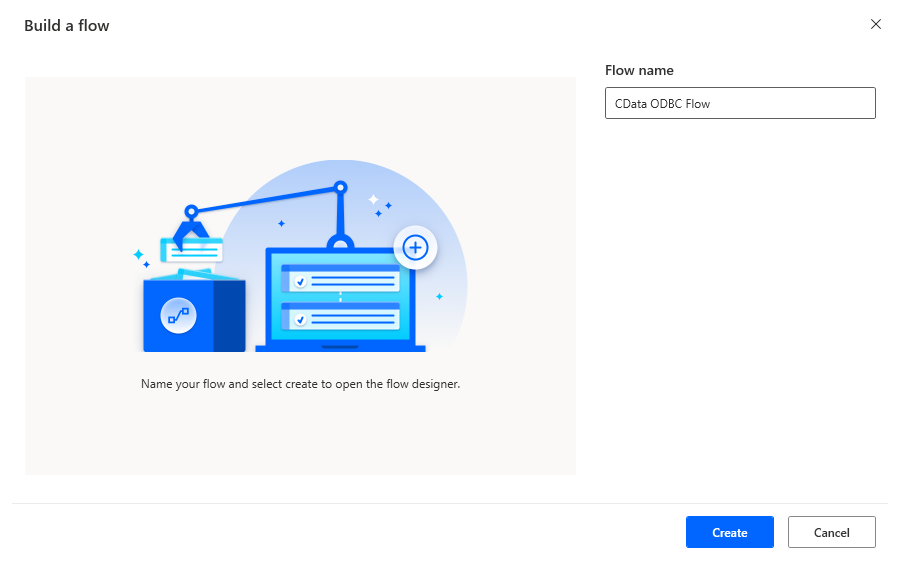
In the flow editor, you can add the actions to connect to EnterpriseDB, query EnterpriseDB using SQL, and write the query results to a CSV document.
Add an Open SQL Connection Action
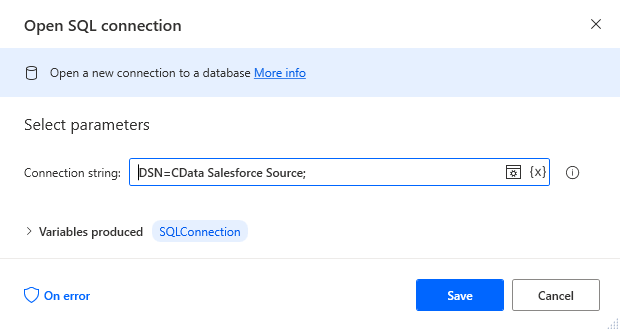
Add an "Open SQL connection" action (Actions -> Database) and configure the properties.
- Connection string: DSN=CData EnterpriseDB Source
After configuring the action, click Save.
Add an Execute SQL Statement Action
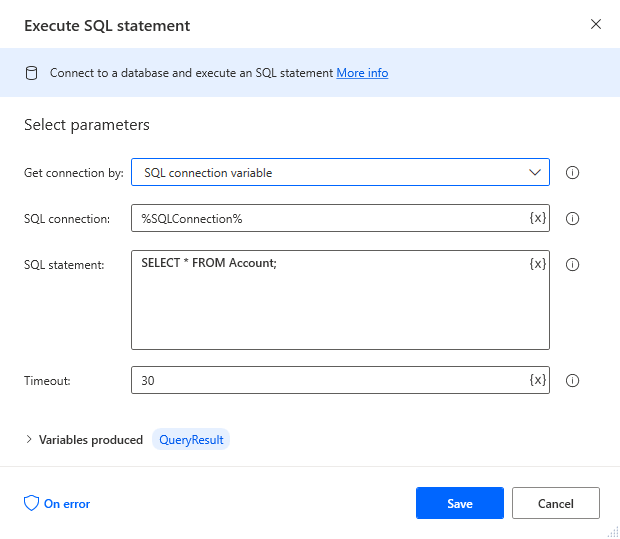
Add an "Execute SQL statement" action (Actions -> Database) and configure the properties.
- Get connection by: SQL connection variable
- SQL connection: %SQLConnection% (the variable from the "Open SQL connection" action above)
- SQL statement: SELECT * FROM Orders
After configuring the action, click Save.
Add a Write to CSV File Action
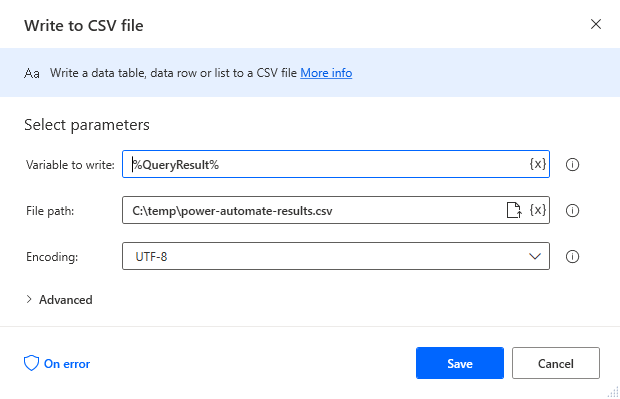
Add a "Write to CSV file" action (Actions -> File) and configure the properties.
- Variable to write to: %QueryResult% (the variable from the "Execute SQL statement" action above)
- File path: set to a file on disk
- Configure Advanced settings as needed.
After configuring the action, click Save.
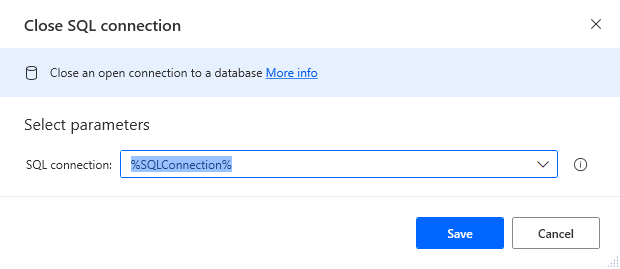
Add a Close SQL Connection Action
Add a "Close SQL connection" action (Actions -> Database) and configure the properties.
- SQL Connection: %SQLConnection% (the variable from the "Open SQL connection" action above)
After configuring the action, click Save.
Save & Run the Flow
Once you have configured all the actions for the flow, click the disk icon to save the flow. Click the play icon to run the flow.
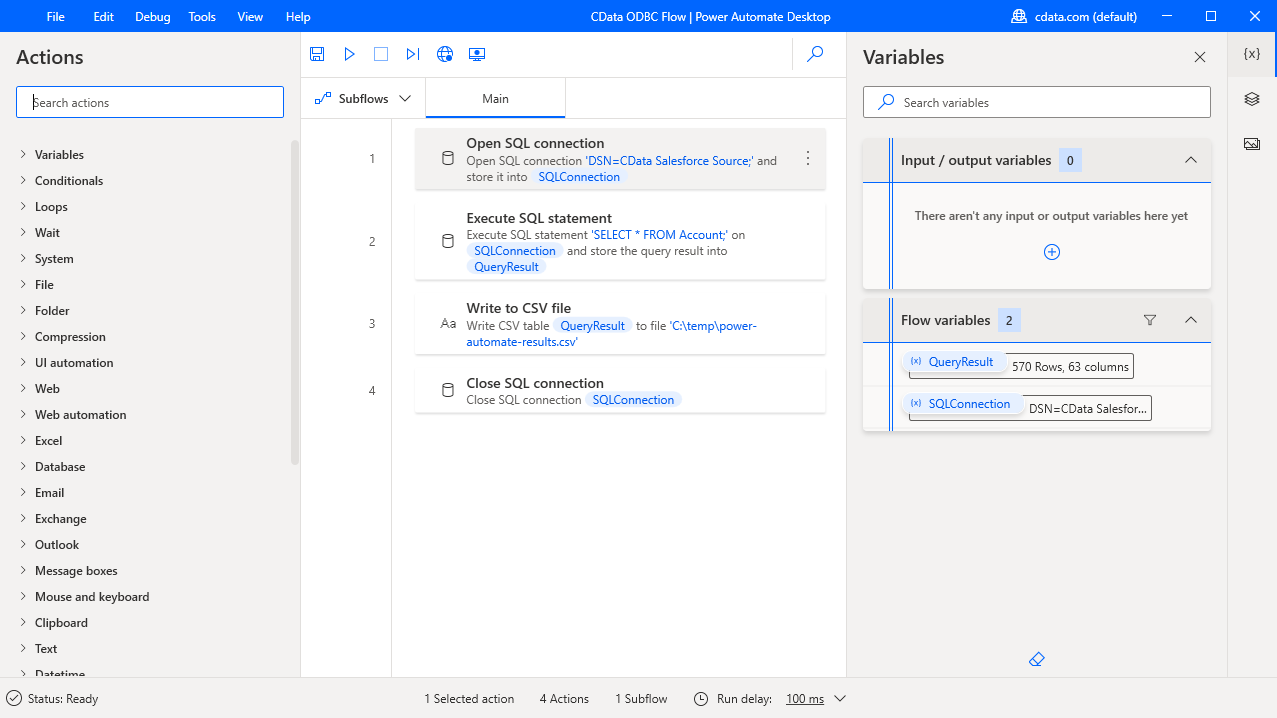
Now you have a workflow to move EnterpriseDB data into a CSV file.
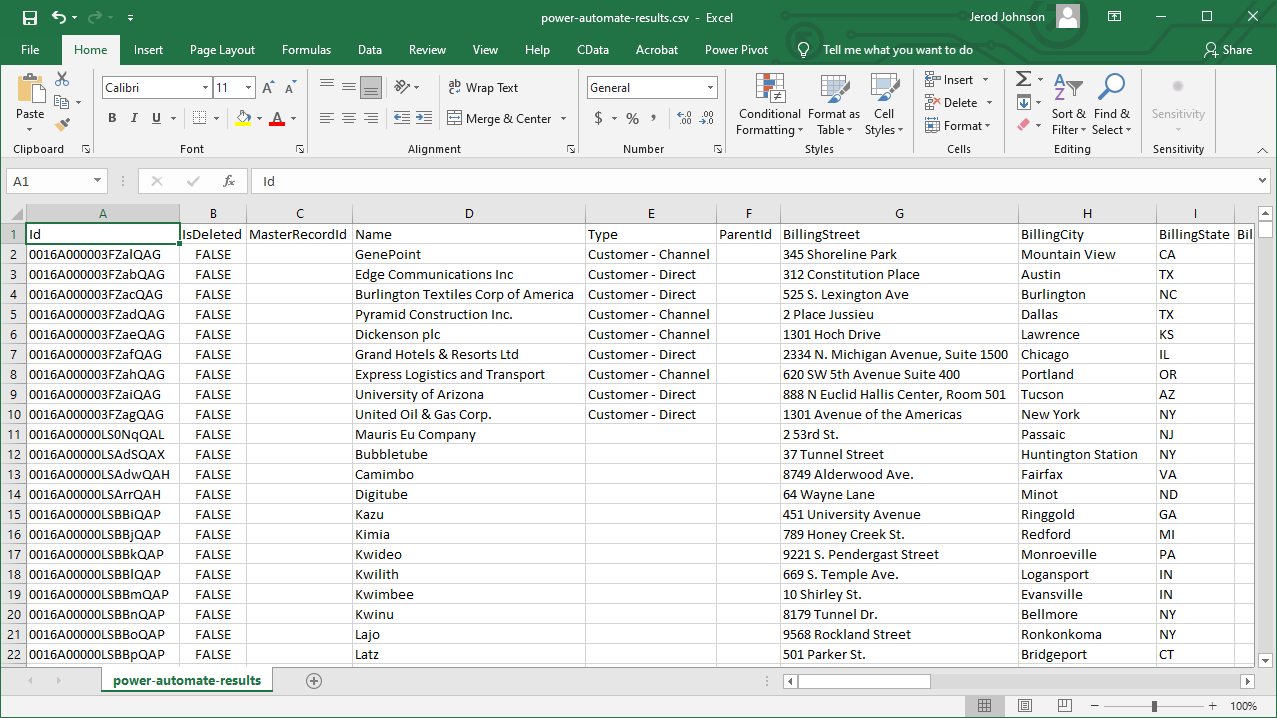
With the CData ODBC Driver for EnterpriseDB, you get live connectivity to EnterpriseDB data within your Microsoft Power Automate workflows.
Related Power Automate Articles
This article walks through using the CData ODBC Driver for EnterpriseDB with Power Automate Desktop. Check out our other articles for more ways to work with Power Automate (Desktop & Online):






