Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Manage Excel Data in DBArtisan as a JDBC Source
Use wizards in DBArtisan to create a JDBC data source for Excel.
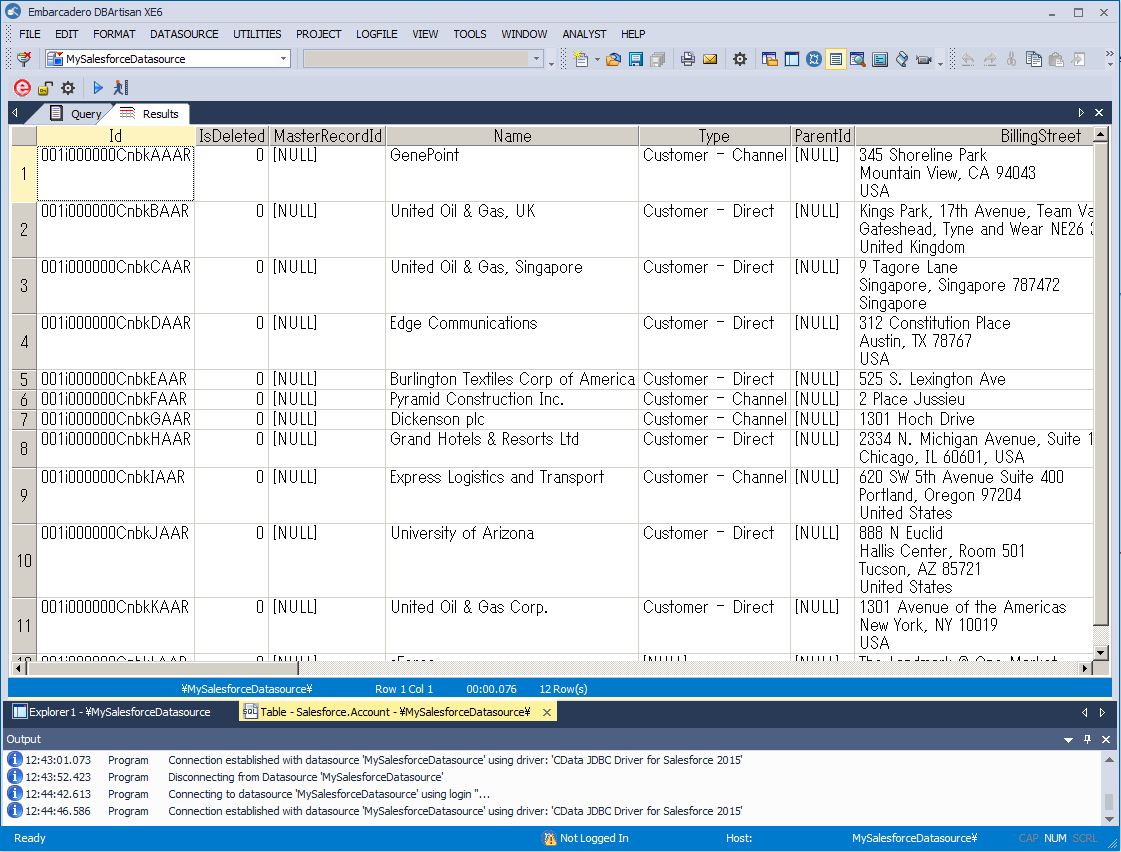
The CData JDBC Driver for Excel seamlessly integrates Excel data into database management tools like DBArtisan by enabling you to access Excel data as a database. This article shows how to create a JDBC source for Excel in DBArtisan. You can then edit data visually and execute standard SQL.
Integrate Excel Data into DBArtisan Projects
Follow the steps below to register Excel data as a database instance in your project:
- In DBArtisan, click Data Source -> Register Datasource.
- Select Generic JDBC.
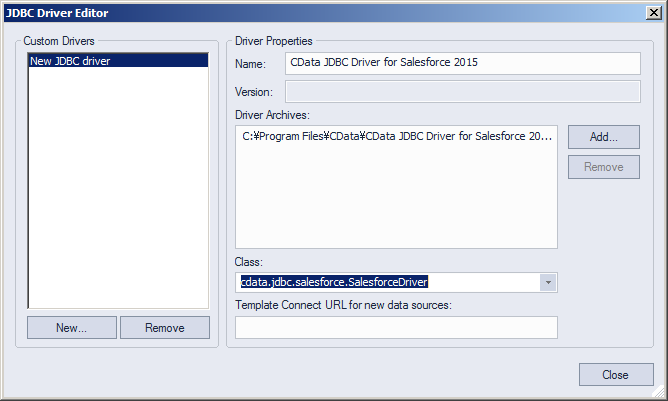
- Click Manage.
- In the resulting dialog, click New. Enter a name for the driver and click Add. In the resulting dialog, navigate to the driver JAR. The driver JAR is located in the lib subfolder of the installation directory.
![The JDBC driver definition in the Register Datasource wizard. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
-
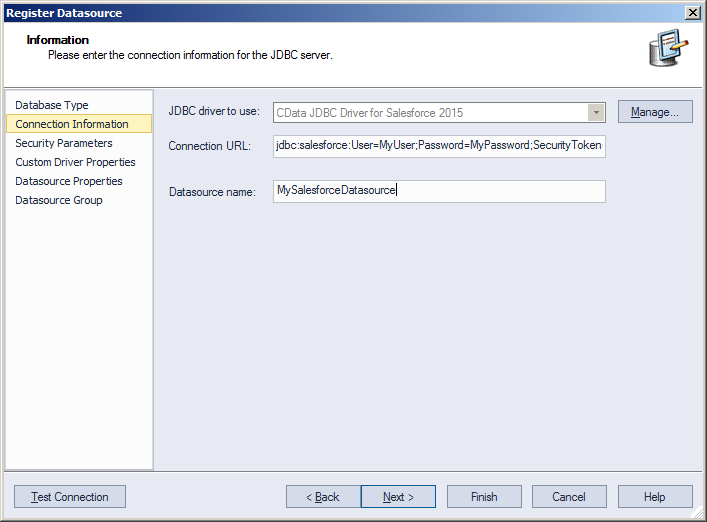
In the Connection URL box, enter credentials and other required connection properties in the JDBC URL.
The ExcelFile, under the Authentication section, must be set to a valid Excel File.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Excel JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.excel.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Required JDBC connection properties in the Register Datasource wizard. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
Below is a typical connection string:
jdbc:excel:Excel File='C:/MyExcelWorkbooks/SampleWorkbook.xlsx'; - Finish the wizard to connect to Excel data. Excel entities are displayed in the Datasource Explorer.
You can now work with Excel data as you work with any other database. See the driver help documentation for more information on the queries supported by the Excel API.