Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Connect to Google Cloud Storage Data in RapidMiner
Integrate Google Cloud Storage data with standard components and data source configuration wizards in RapidMiner Studio.
This article shows how you can easily integrate the CData JDBC driver for Google Cloud Storage into your processes in RapidMiner. This article uses the CData JDBC Driver for Google Cloud Storage to transfer Google Cloud Storage data to a process in RapidMiner.
Connect to Google Cloud Storage in RapidMiner as a JDBC Data Source
You can follow the procedure below to establish a JDBC connection to Google Cloud Storage:
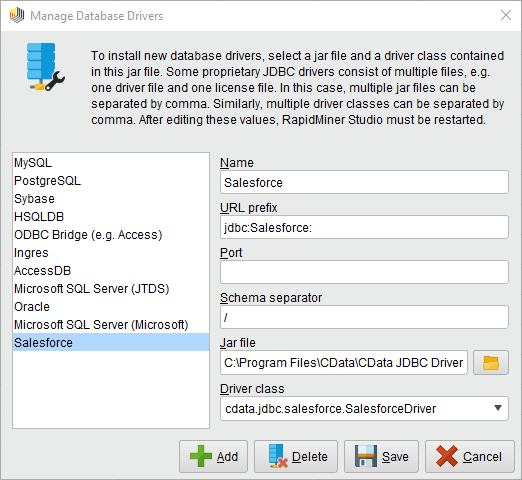
- Add a new database driver for Google Cloud Storage: Click Connections -> Manage Database Drivers.
- In the resulting wizard, click the Add button and enter a name for the connection.
- Enter the prefix for the JDBC URL:
jdbc:googlecloudstorage: - Enter the path to the cdata.jdbc.googlecloudstorage.jar file, located in the lib subfolder of the installation directory.
- Enter the driver class:
cdata.jdbc.googlecloudstorage.GoogleCloudStorageDriver![The JDBC driver configuration. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
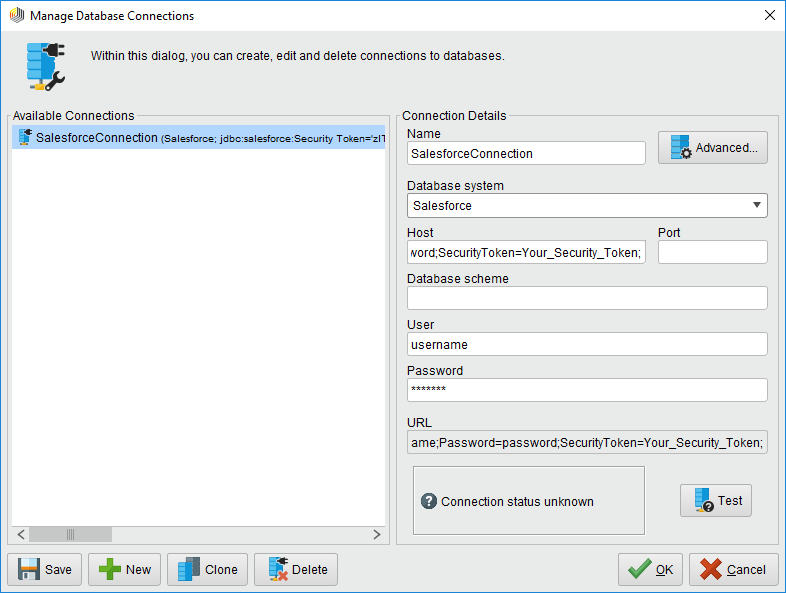
- Create a new Google Cloud Storage connection: Click Connections -> Manage Database Connections.
- Enter a name for your connection.
- For Database System, select the Google Cloud Storage driver you configured previously.
- Enter your connection string in the Host box.
Authenticate with a User Account
You can connect without setting any connection properties for your user credentials. After setting InitiateOAuth to GETANDREFRESH, you are ready to connect.
When you connect, the Google Cloud Storage OAuth endpoint opens in your default browser. Log in and grant permissions, then the OAuth process completes
Authenticate with a Service Account
Service accounts have silent authentication, without user authentication in the browser. You can also use a service account to delegate enterprise-wide access scopes.
You need to create an OAuth application in this flow. See the Help documentation for more information. After setting the following connection properties, you are ready to connect:
- InitiateOAuth: Set this to GETANDREFRESH.
- OAuthJWTCertType: Set this to "PFXFILE".
- OAuthJWTCert: Set this to the path to the .p12 file you generated.
- OAuthJWTCertPassword: Set this to the password of the .p12 file.
- OAuthJWTCertSubject: Set this to "*" to pick the first certificate in the certificate store.
- OAuthJWTIssuer: In the service accounts section, click Manage Service Accounts and set this field to the email address displayed in the service account Id field.
- OAuthJWTSubject: Set this to your enterprise Id if your subject type is set to "enterprise" or your app user Id if your subject type is set to "user".
- ProjectId: Set this to the Id of the project you want to connect to.
The OAuth flow for a service account then completes.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Google Cloud Storage JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.googlecloudstorage.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
A typical connection string is below:
ProjectId='project1';InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH - Enter your username and password if necessary.
![The connection to the JDBC data source. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
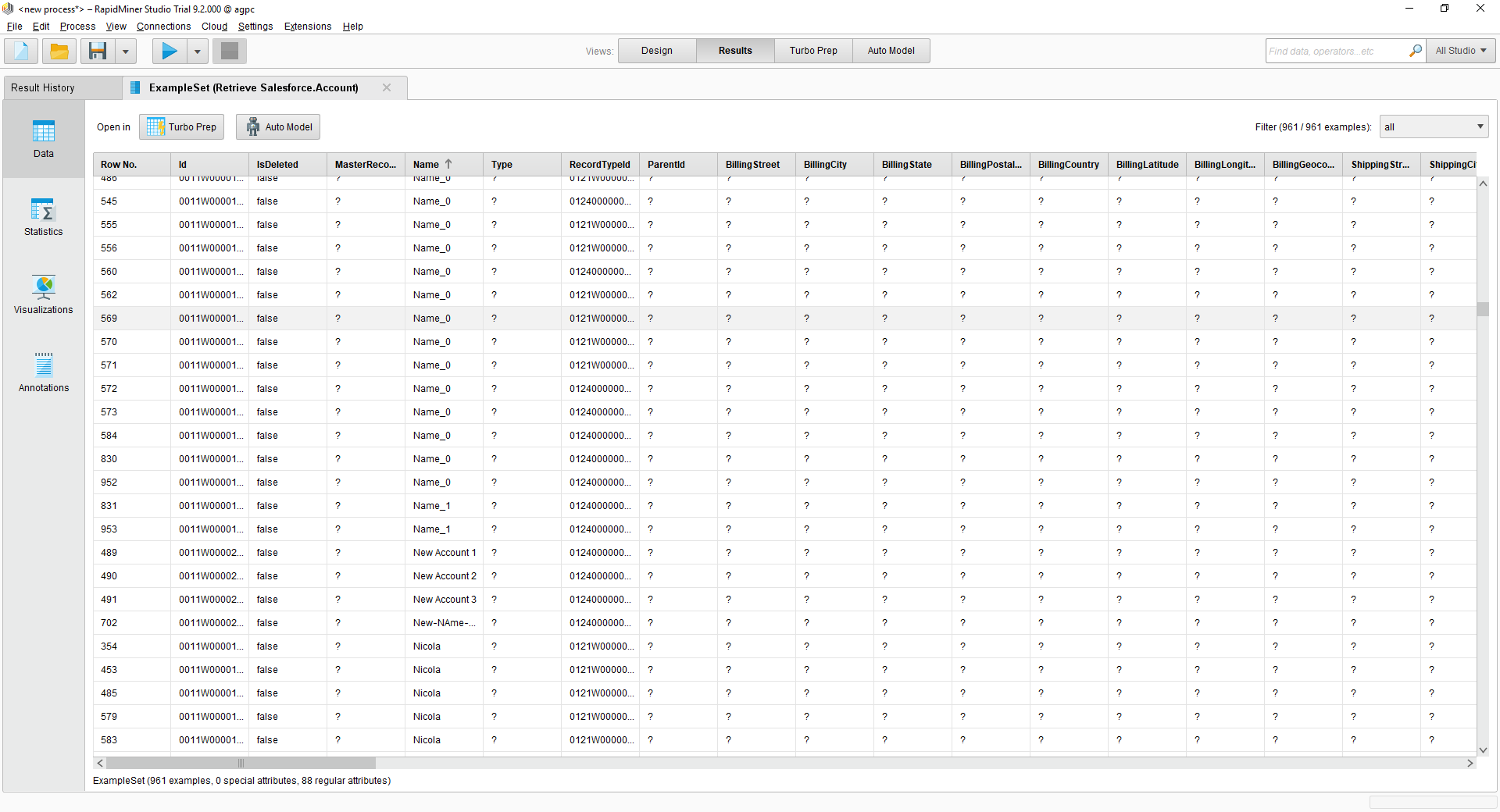
You can now use your Google Cloud Storage connection with the various RapidMiner operators in your process. To retrieve Google Cloud Storage data, drag the Retrieve operator from the Operators view.
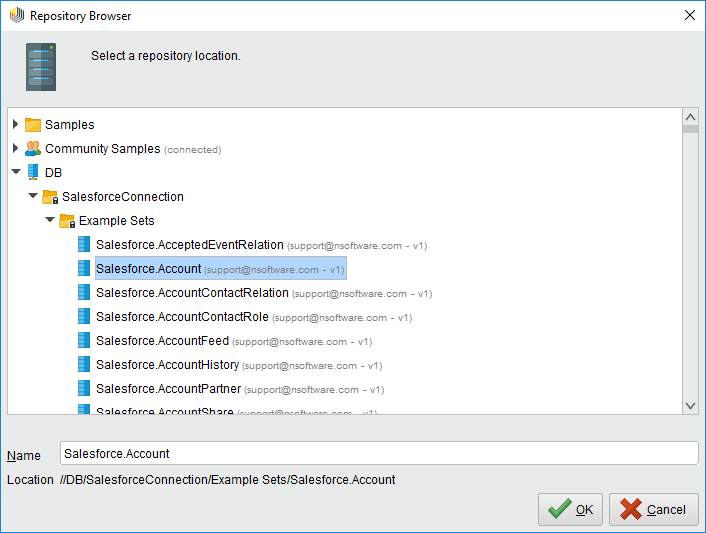 With the Retrieve operator selected, you can then define which table to retrieve in the Parameters view by clicking the folder icon next to the "repository entry." In the resulting Repository Browser, you can expand your connection node to select the desired example set.
With the Retrieve operator selected, you can then define which table to retrieve in the Parameters view by clicking the folder icon next to the "repository entry." In the resulting Repository Browser, you can expand your connection node to select the desired example set.
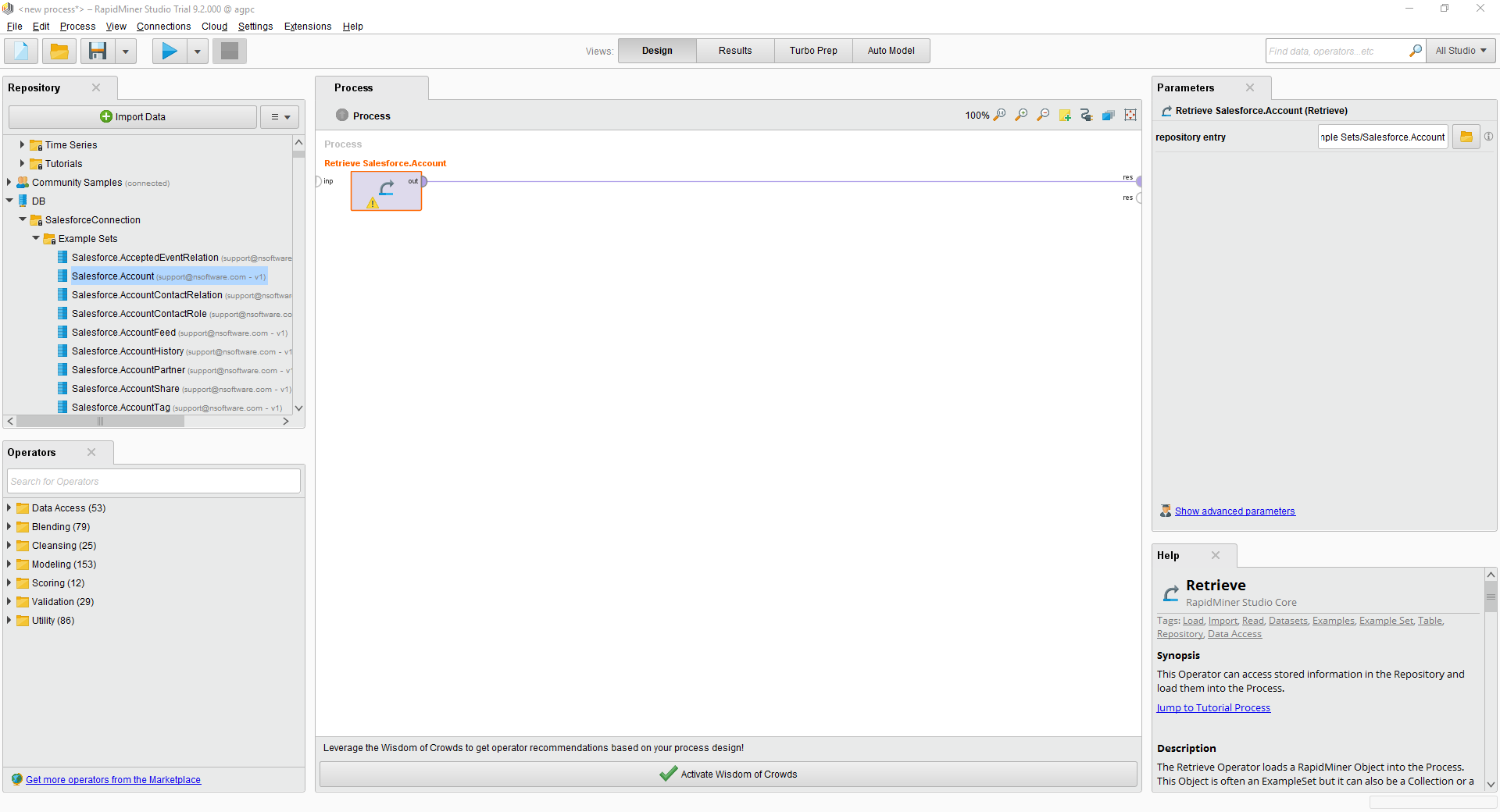
Finally, wire the output to the Retrieve process to a result, and run the process to see the Google Cloud Storage data.