Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Explore Geographical Relationships in Impala Data with Power Map
Create data visualizations with Impala data in Power Map.
The CData ODBC Driver for Impala is easy to set up and use with self-service analytics solutions like Power BI: Microsoft Excel provides built-in support for the ODBC standard. This article shows how to load the current Impala data into Excel and start generating location-based insights on Impala data in Power Map.
Create an ODBC Data Source for Impala
If you have not already, first specify connection properties in an ODBC DSN (data source name). This is the last step of the driver installation. You can use the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure ODBC DSNs.
In order to connect to Apache Impala, set the Server, Port, and ProtocolVersion. You may optionally specify a default Database. To connect using alternative methods, such as NOSASL, LDAP, or Kerberos, refer to the online Help documentation.
When you configure the DSN, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
When you configure the DSN, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
Import Impala Data into Excel
You can import data into Power Map either from an Excel spreadsheet or from Power Pivot. For a step-by-step guide to use either method to import Impala data, see the "Using the ODBC Driver" section in the help documentation.
Geocode Impala Data
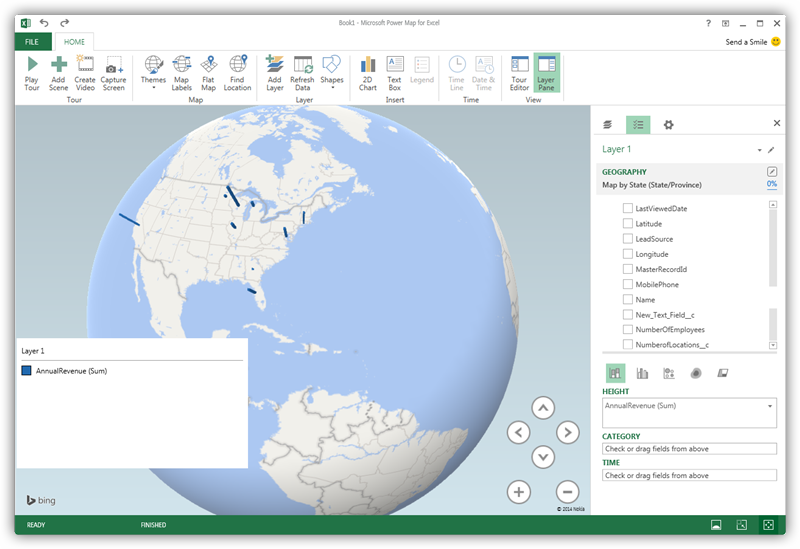
After importing the Impala data into an Excel spreadsheet or into PowerPivot, you can drag and drop Impala entities in Power Map. To open Power Map, click any cell in the spreadsheet and click Insert -> Map.
In the Choose Geography menu, Power Map detects the columns that have geographic information. In the Geography and Map Level menu in the Layer Pane, you can select the columns you want to work with. Power Map then plots the data. A dot represents a record that has this value. When you have selected the geographic columns you want, click Next.
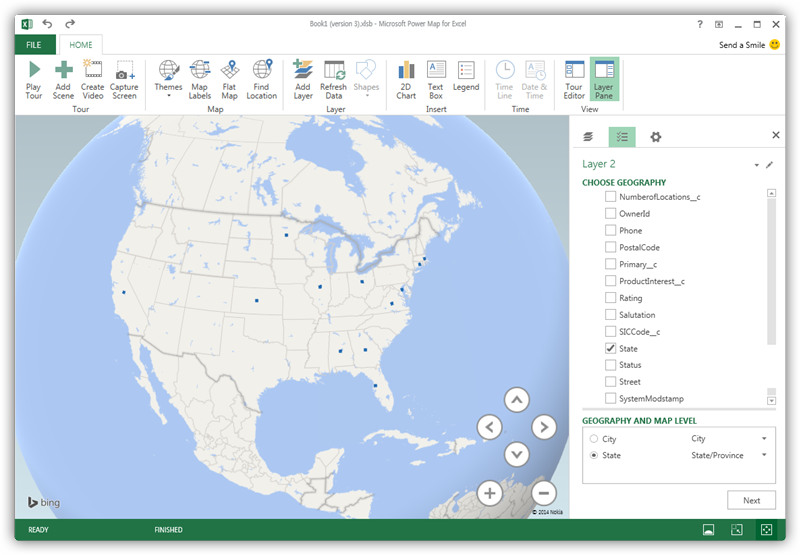
Select Measures and Categories
You can then simply select columns: Measures and categories are automatically detected. The available chart types are Stacked Column, Clustered Column, Bubble, Heat Map, and Region.