Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Connect to and Query JSON Services in QlikView over ODBC
Create data visualizations with JSON services in QlikView.
The CData ODBC drivers expand your ability to work with data from more than 200 data sources. QlikView is a business discovery platform that provides self-service BI for all business users in an organization. This article outlines simple steps to connect to JSON services using the CData ODBC driver and create data visualizations in QlikView.
The CData ODBC drivers offer unmatched performance for interacting with live JSON services in QlikView due to optimized data processing built into the driver. When you issue complex SQL queries from QlikView to JSON, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to JSON and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations (often SQL functions and JOIN operations) client-side. With built-in dynamic metadata querying, you can visualize and analyze JSON services using native QlikView data types.
Connect to JSON as an ODBC Data Source
If you have not already, first specify connection properties in an ODBC DSN (data source name). This is the last step of the driver installation. You can use the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure ODBC DSNs.
See the Getting Started chapter in the data provider documentation to authenticate to your data source: The data provider models JSON APIs as bidirectional database tables and JSON files as read-only views (local files, files stored on popular cloud services, and FTP servers). The major authentication schemes are supported, including HTTP Basic, Digest, NTLM, OAuth, and FTP. See the Getting Started chapter in the data provider documentation for authentication guides.
After setting the URI and providing any authentication values, set DataModel to more closely match the data representation to the structure of your data.
The DataModel property is the controlling property over how your data is represented into tables and toggles the following basic configurations.
- Document (default): Model a top-level, document view of your JSON data. The data provider returns nested elements as aggregates of data.
- FlattenedDocuments: Implicitly join nested documents and their parents into a single table.
- Relational: Return individual, related tables from hierarchical data. The tables contain a primary key and a foreign key that links to the parent document.
See the Modeling JSON Data chapter for more information on configuring the relational representation. You will also find the sample data used in the following examples. The data includes entries for people, the cars they own, and various maintenance services performed on those cars.
When you configure the DSN, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
Populate a Chart with JSON Services
The steps below supply the results of an SQL query to a visualization in QlikView. In this article, you will create a bar chart with the query below:
SELECT [people].[personal.age] AS age, [people].[personal.gender] AS gender, [people].[personal.name.first] AS first_name, [people].[personal.name.last] AS last_name, [vehicles].[model], FROM [people] JOIN [vehicles] ON [people].[_id] = [vehicles].[people_id]
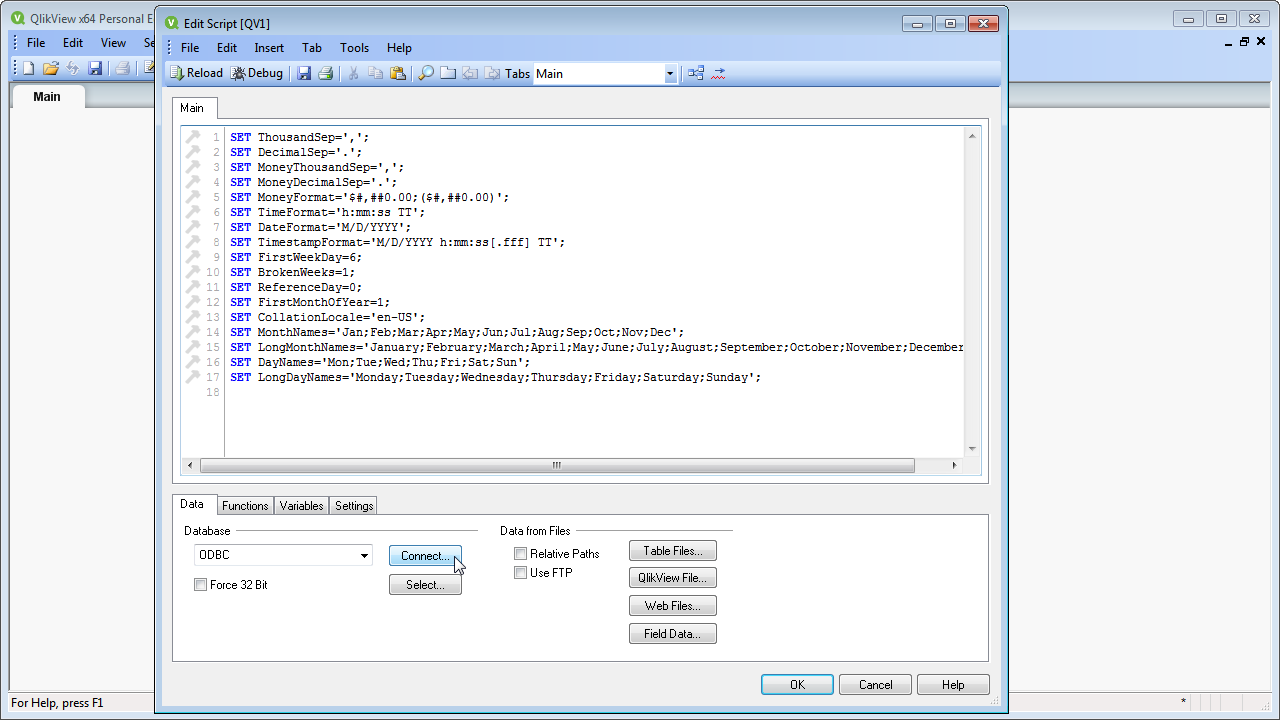
- Click File -> Edit Script (or click the Edit Script button in the Toolbar).
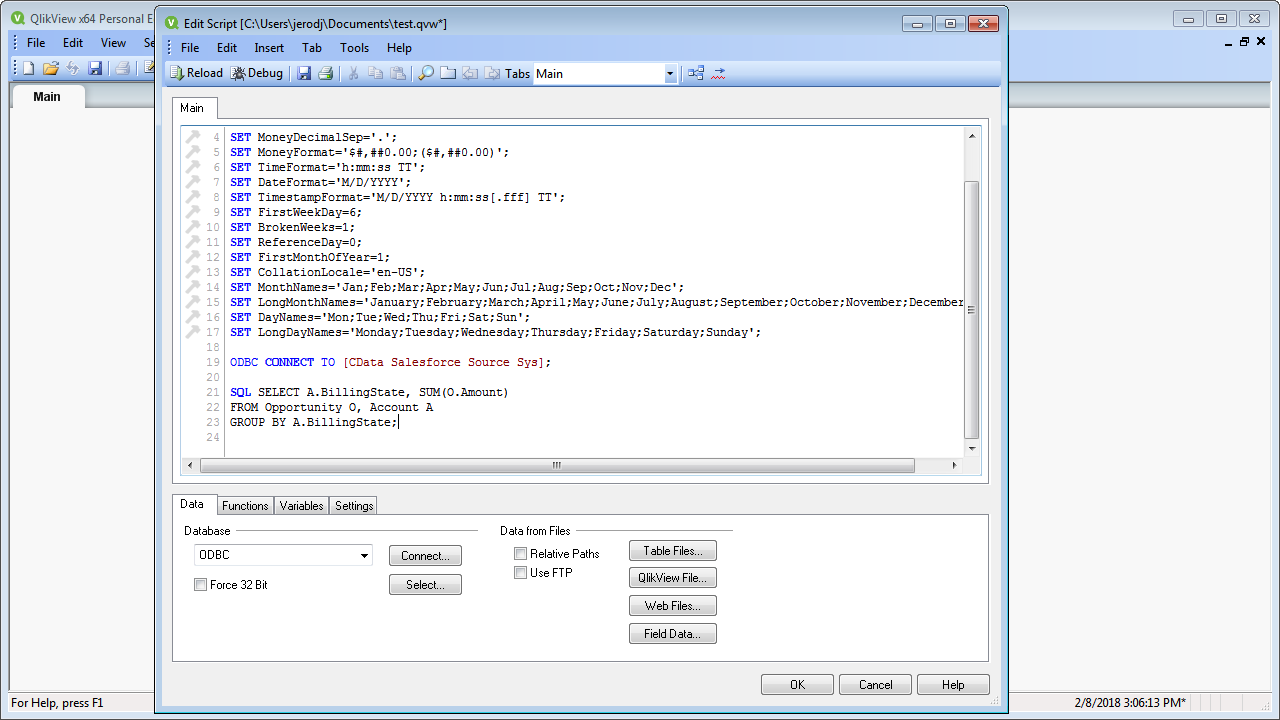
- On the Data tab, select ODBC in the Database menu and click Connect.
![Connecting to an ODBC data source.]()
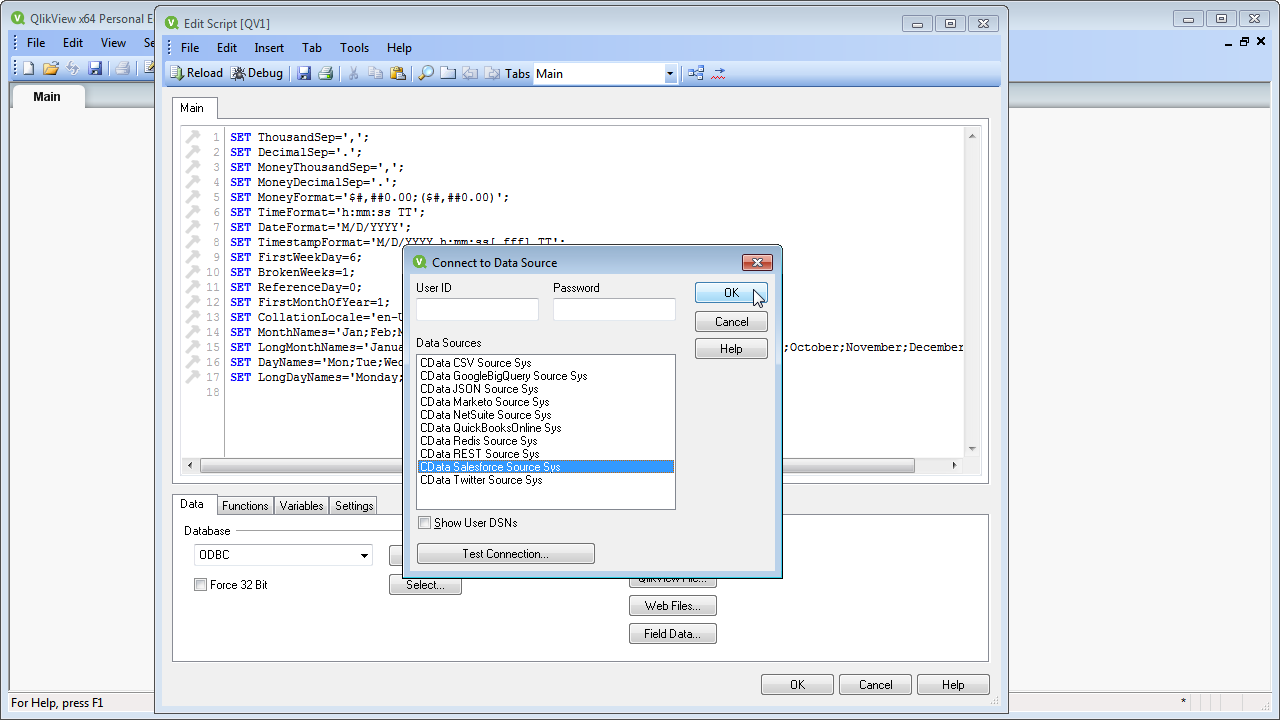
- Select the DSN (CData JSON Sys) in the resulting dialog.
![Selecting a DSN (Salesforce is shown).]() A command like the following is generated:
A command like the following is generated:
ODBC CONNECT TO [CData JSON Sys]; - Enter the SQL query directly into the script with the SQL command (or click Select to build the query in the SELECT statement wizard).
SQL SELECT [people].[personal.age] AS age, [people].[personal.gender] AS gender, [people].[personal.name.first] AS first_name, [people].[personal.name.last] AS last_name, [vehicles].[model], FROM [people] JOIN [vehicles] ON [people].[_id] = [vehicles].[people_id];Where possible, the SQL operations in the query, like filters and aggregations, will be pushed down to JSON, while any unsupported operations (which can include SQL functions and JOIN operations) will be managed client-side by the CData SQL engine embedded in the driver.
![A script that connects and executes an SQL query. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
- Close the script editor and reload the document to execute the script.
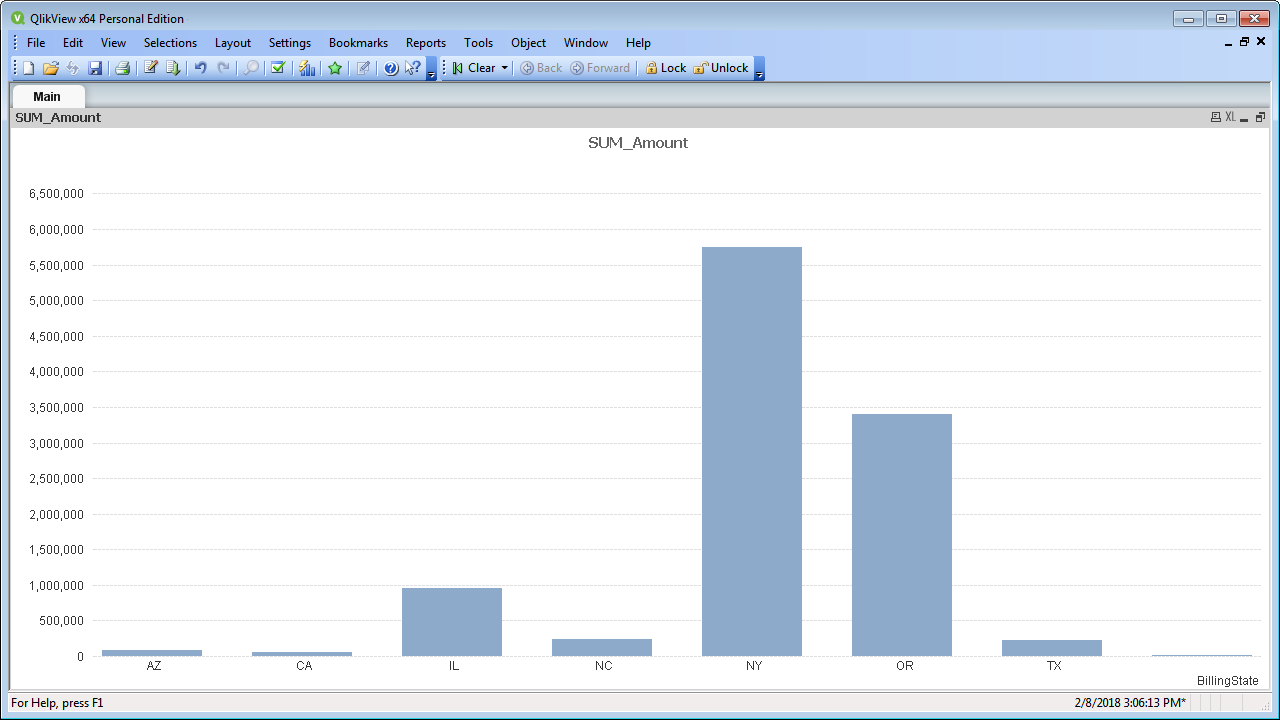
- Click Tools -> Quick Chart Wizard. In the wizard, select the chart type. This example uses a bar chart. When building the chart, you have access to the fields from JSON, typed appropriately for QlikView, thanks to built-in dynamic metadata querying.
- When defining Dimensions, select [ personal.name.first ] in the First Dimension menu.
- When defining Expressions, click the summary function you want and select [ personal.name.last ] in the menu.
Finish the wizard to generate the chart. The CData ODBC Driver for JSON connects to live JSON services, so the chart can be refreshed to see real-time changes. Live connections are possible and effective, thanks to the high-performance data processing native to CData ODBC Drivers.
![A chart populated with the results of a query. (Salesforce is shown.)]()






 A command like the following is generated:
A command like the following is generated: