Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Replicate MongoDB Data to Multiple Databases
Replicate MongoDB data to disparate databases with a point-and-click configuration.
Always-on applications rely on automatic failover capabilities and real-time access to data. CData Sync integrates live MongoDB data into your mirrored databases, always-on cloud databases, and other databases such as your reporting server: Automatically synchronize with remote MongoDB data from Windows.
About MongoDB Data Integration
Accessing and integrating live data from MongoDB has never been easier with CData. Customers rely on CData connectivity to:
- Access data from MongoDB 2.6 and above, ensuring broad usability across various MongoDB versions.
- Easily manage unstructured data thanks to flexible NoSQL (learn more here: Leading-Edge Drivers for NoSQL Integration).
- Leverage feature advantages over other NoSQL drivers and realize functional benefits when working with MongoDB data (learn more here: A Feature Comparison of Drivers for NoSQL).
MongoDB's flexibility means that it can be used as a transactional, operational, or analytical database. That means CData customers use our solutions to integrate their business data with MongoDB or integrate their MongoDB data with their data warehouse (or both). Customers also leverage our live connectivity options to analyze and report on MongoDB directly from their preferred tools, like Power BI and Tableau.
For more details on MongoDB use case and how CData enhances your MongoDB experience, check out our blog post: The Top 10 Real-World MongoDB Use Cases You Should Know in 2024.
Getting Started
Configure Replication Destinations
Using CData Sync, you can replicate MongoDB data to any number of databases, both cloud-based and on-premises. To add a replication destination, navigate to the Connections tab.
For each destination database:
- Click Add Connection.
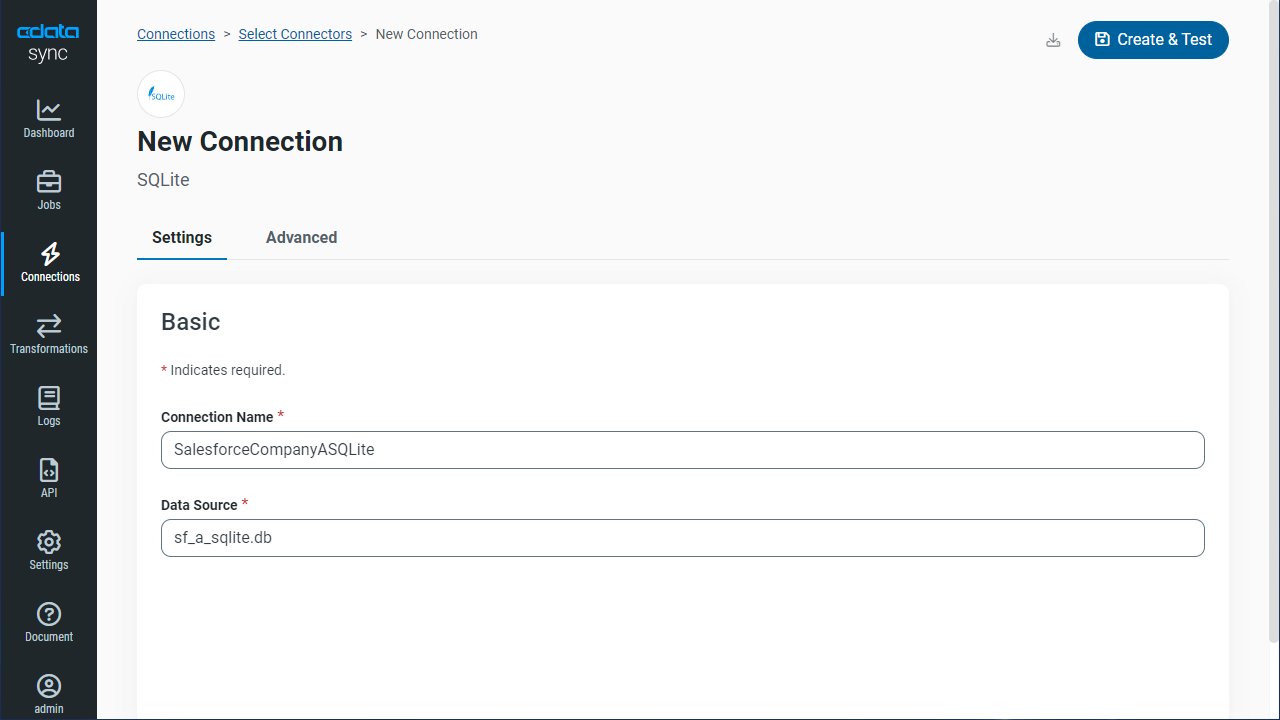
- Select a destination. In this article, we use SQLite.
![Configure a Destination connection.]()
- Enter the necessary connection properties. To replicate MongoDB to a SQLite database, enter a file path in the Data Source box.
- Click Test Connection to ensure that the connection is configured properly.
![Configure a Destination connection (SQLite is shown).]()
- Click Save Changes.
Configure the MongoDB Connection
You can configure a connection to MongoDB from the Connections tab. To add a connection to your MongoDB account, navigate to the Connections tab.
- Click Add Connection.
- Select a source (MongoDB).
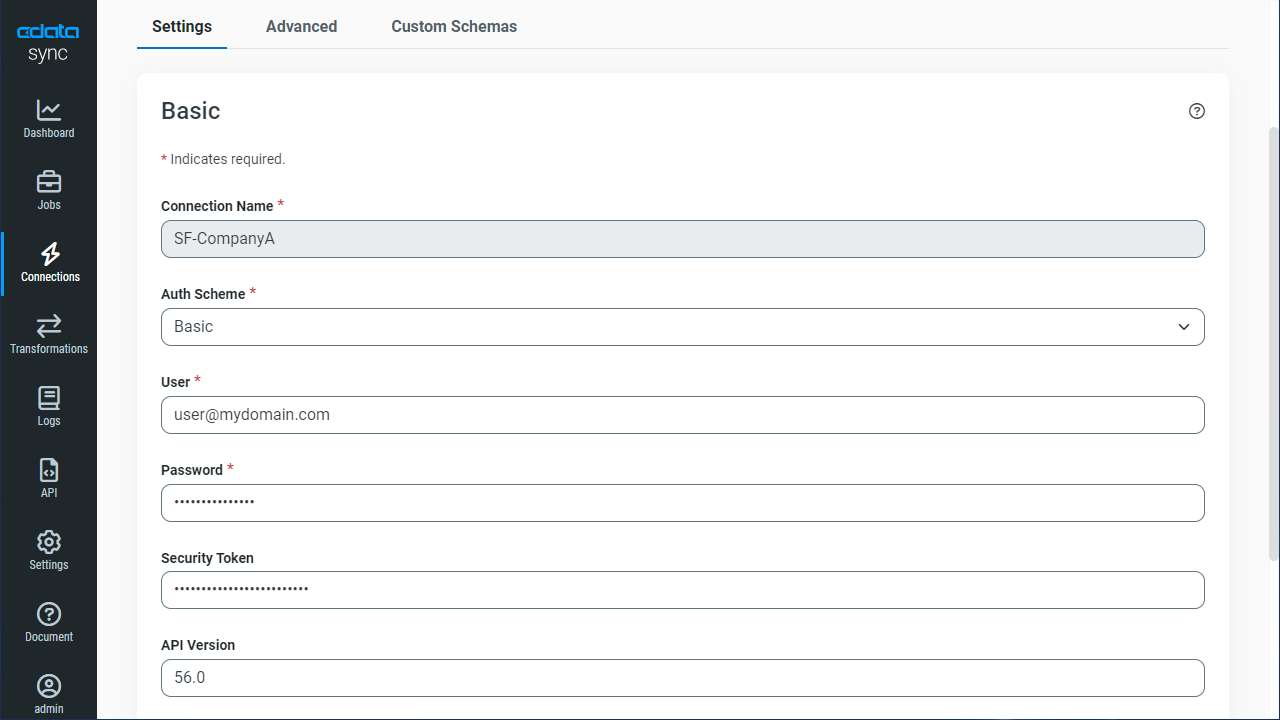
- Configure the connection properties.
Set the Server, Database, User, and Password connection properties to connect to MongoDB. To access MongoDB collections as tables you can use automatic schema discovery or write your own schema definitions. Schemas are defined in .rsd files, which have a simple format. You can also execute free-form queries that are not tied to the schema.
![Configure a Source connection (Salesforce is shown).]()
- Click Connect to ensure that the connection is configured properly.
- Click Save Changes.
Configure Replication Queries
CData Sync enables you to control replication with a point-and-click interface and with SQL queries. For each replication you wish to configure, navigate to the Jobs tab and click Add Job. Select the Source and Destination for your replication.
Replicate Entire Tables
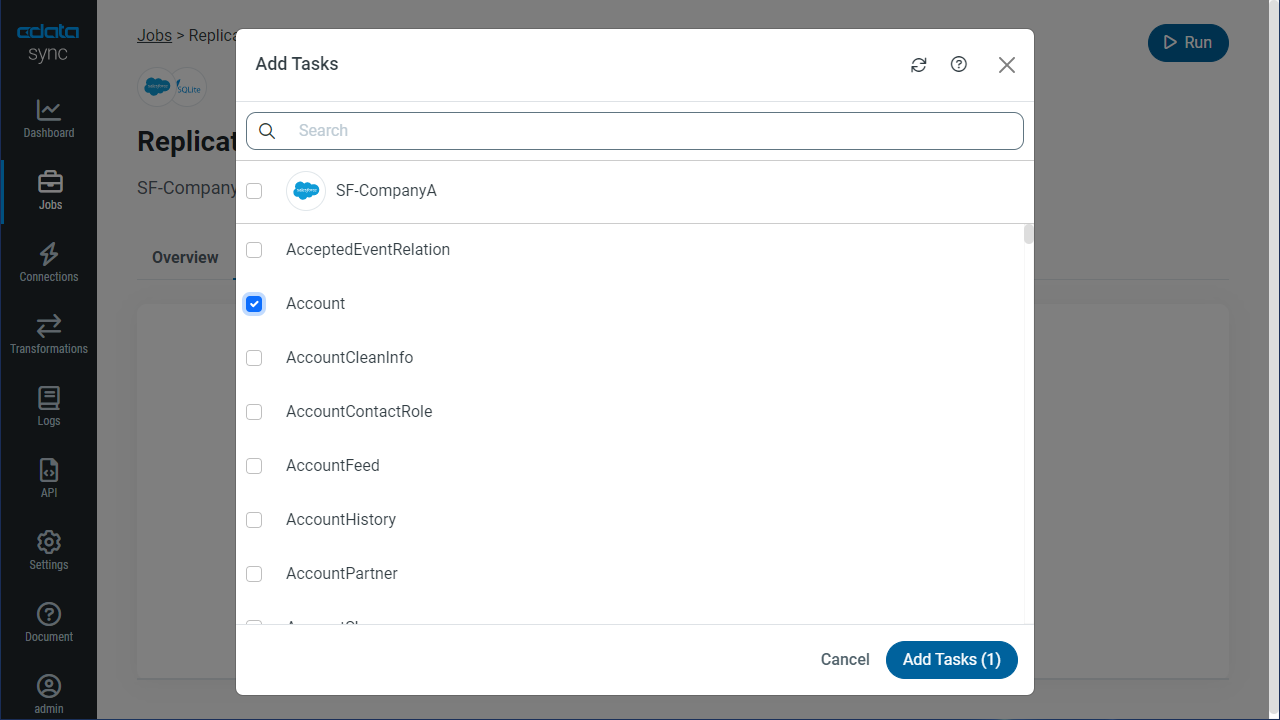
To replicate an entire table, click Add Tables in the Tables section, choose the table(s) you wish to replicate, and click Add Selected Tables.
Customize Your Replication
You can use a SQL query to customize your replication. The REPLICATE statement is a high-level command that caches and maintains a table in your database. You can define any SELECT query supported by the MongoDB API. To customize your replication, click Add Custom Query in the Tables section and define the Query Statement.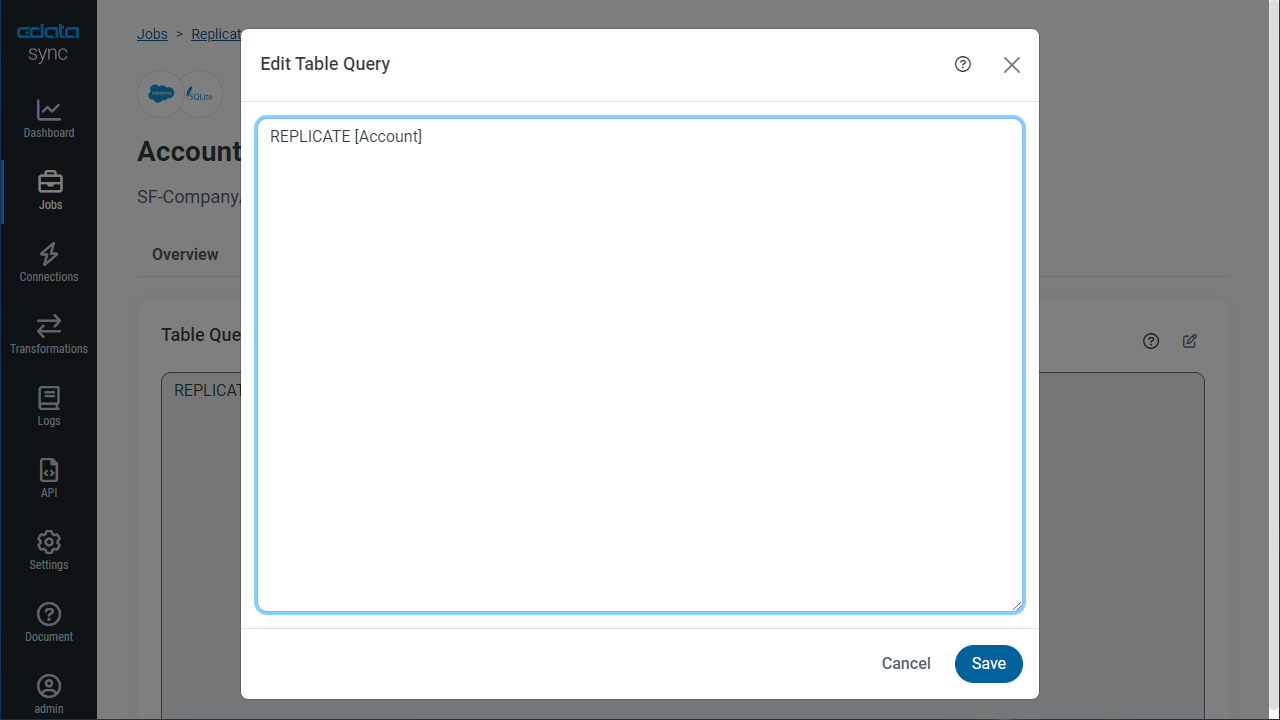
The statement below caches and incrementally updates a table of MongoDB data:
REPLICATE restaurants;
You can specify a file containing the replication queries you want to use to update a particular database. Separate replication statements with semicolons. The following options are useful if you are replicating multiple MongoDB accounts into the same database:
-
Use a different table prefix in the REPLICATE SELECT statement:
REPLICATE PROD_restaurants SELECT * FROM restaurants; -
Alternatively, use a different schema:
REPLICATE PROD.restaurants SELECT * FROM restaurants;
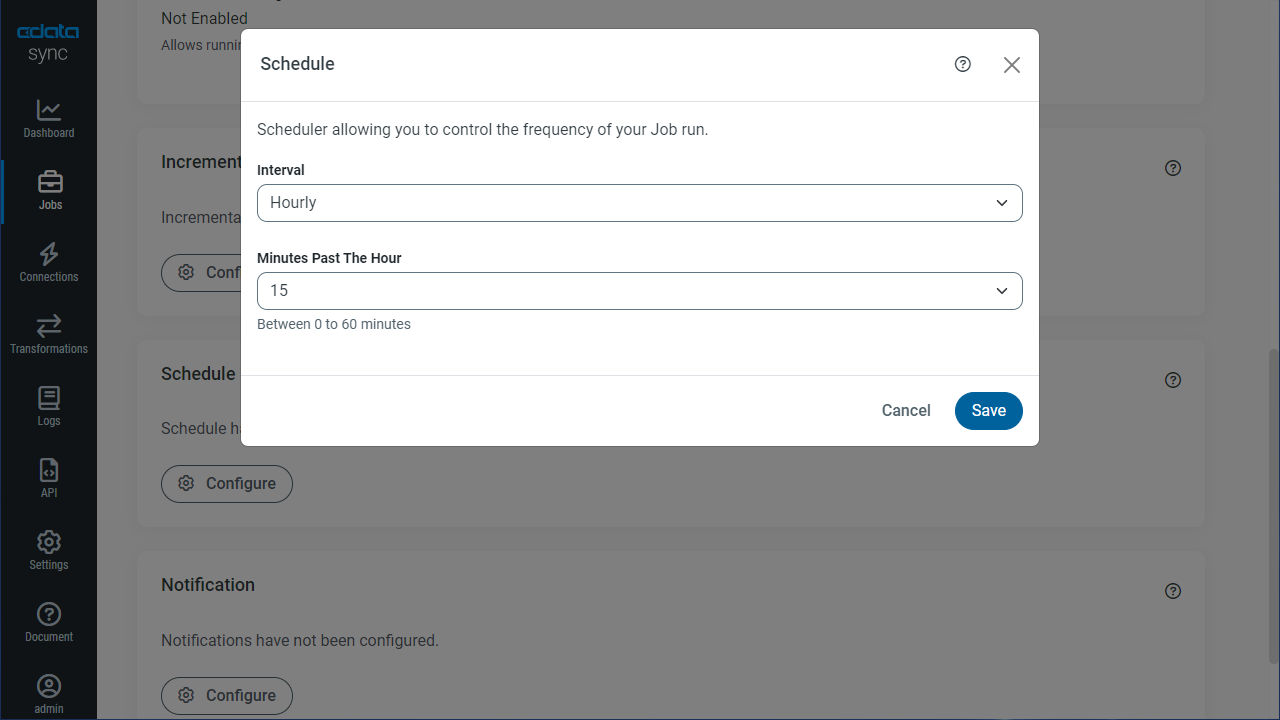
Schedule Your Replication
In the Schedule section, you can schedule a job to run automatically, configuring the job to run after specified intervals ranging from once every 10 minutes to once every month.
Once you have configured the replication job, click Save Changes. You can configure any number of jobs to manage the replication of your MongoDB data to disparate on-premises, cloud-based, and other databases.