Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →How to connect to Microsoft Planner Data in DBVisualizer
Integrate Microsoft Planner data with visual data analysis tools and data connection wizards in DBVisualizer
The CData JDBC Driver for Microsoft Planner implements JDBC standards to provide connectivity to Microsoft Planner data in applications ranging from business intelligence tools to IDEs. This article shows how to establish a connection to Microsoft Planner data in DBVisualizer and use the table editor to edit and save Microsoft Planner data.
Create a New Driver Definition for Microsoft Planner Data
Follow the steps below to use the Driver Manager to provide connectivity to Microsoft Planner data from DBVisualizer tools.
- In DBVisualizer, click Tools -> Driver Manager.
- Click the plus sign "" to create a new driver.
- Select "Custom" as the template.
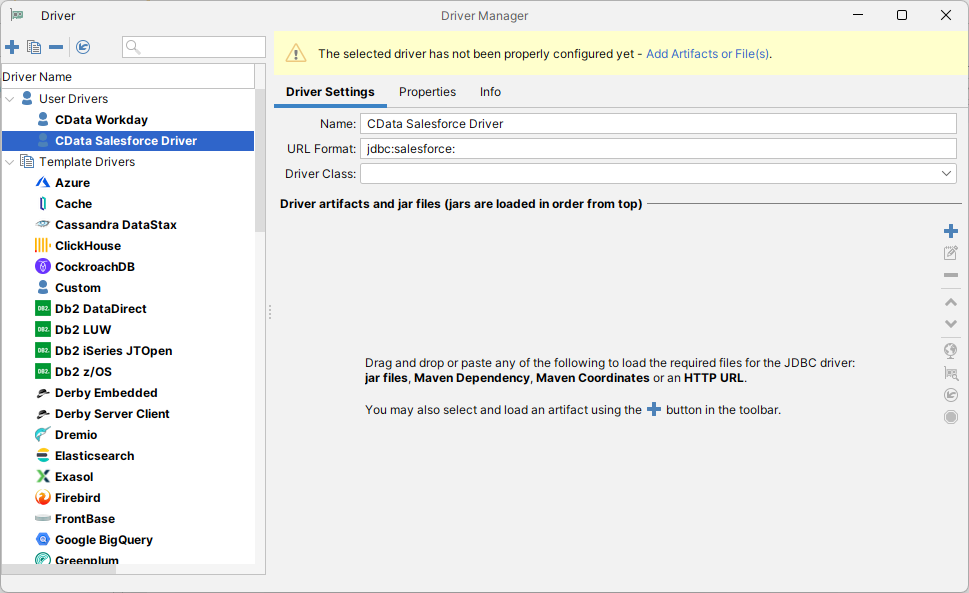
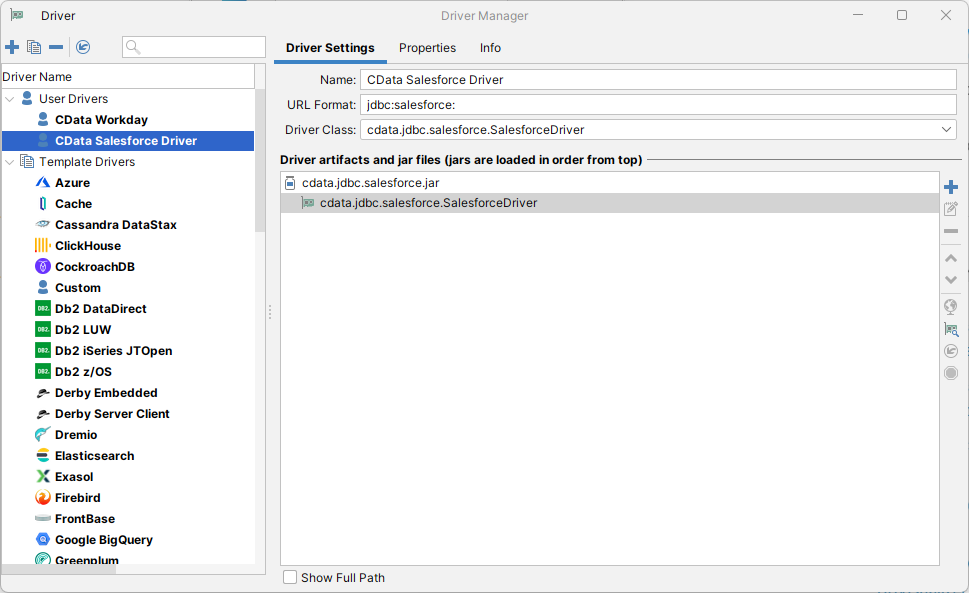
- On the Driver Settings tab:
- Set Name to a user-friendly name (e.g. "CData Microsoft Planner Driver")
- Set URL Format to jdbc:microsoftplanner:
![Setting the Driver Settings (Salesforce is shown).]()
- In Driver artifacts and jar files (jars are loaded in order from top):
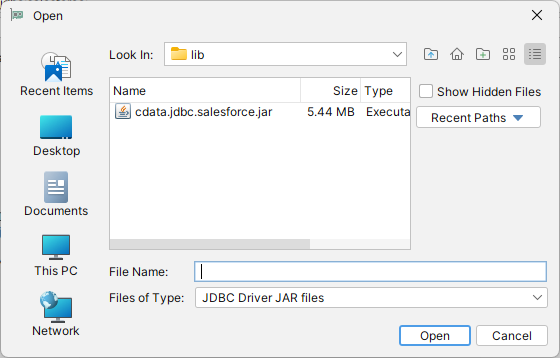
- Click the plus sign "" -> "Add Files"
- Navigate to the "lib" folder in the installation directory (C:\Program Files\CData[product_name] XXXX\)
- Select the JAR file (cdata.jdbc.MicrosoftPlanner.jar) and click "Open"
![Loading the driver JAR file.]()
- The Driver Class should populate automatically. If not, select class (cdata.jdbc.microsoftplanner.MicrosoftPlannerDriver).
Define the Connection to the JDBC Data Source
Close the "Driver Manager" and follow the steps below to save connection properties in the JDBC URL.
- In the "Databases" tab, click the plus sign "" and select the driver you just created.
In the "Connection" section, set the following options:
- Database Type: If you selected the wizard option, the database type is automatically detected. If you selected the "No Wizard" option, select the Generic or Auto Detect option in the Database Type menu.
- Driver Type: Select the driver you just created.
Database URL: Enter the full JDBC URL. The syntax of the JDBC URL is jdbc:microsoftplanner: followed by the connection properties in a semicolon-separated list of name-value pairs.
You can connect without setting any connection properties for your user credentials. Below are the minimum connection properties required to connect.
- InitiateOAuth: Set this to GETANDREFRESH. You can use InitiateOAuth to avoid repeating the OAuth exchange and manually setting the OAuthAccessToken.
- Tenant (optional): Set this if you wish to authenticate to a different tenant than your default. This is required to work with an organization not on your default Tenant.
When you connect the Driver opens the MS Planner OAuth endpoint in your default browser. Log in and grant permissions to the Driver. The Driver then completes the OAuth process.
- Extracts the access token from the callback URL and authenticates requests.
- Obtains a new access token when the old one expires.
- Saves OAuth values in OAuthSettingsLocation to be persisted across connections.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Microsoft Planner JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.microsoftplanner.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
When you configure the JDBC URL, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
A typical connection string is below:
jdbc:microsoftplanner:OAuthClientId=MyApplicationId;OAuthClientSecret=MySecretKey;CallbackURL=http://localhost:33333;InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH- NOTE: Since Microsoft Planner does not require a User or Password to authenticate, you may use whatever values you wish for Database Userid and Database Password.
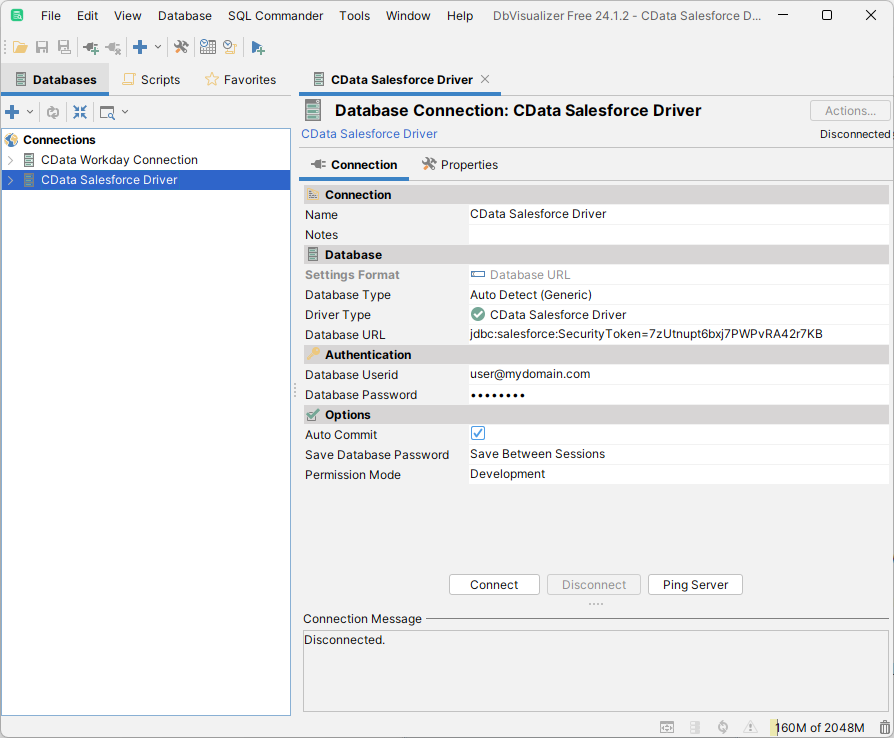
- On the Connection tab, click Connect.
![A newly configured Database Connection. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
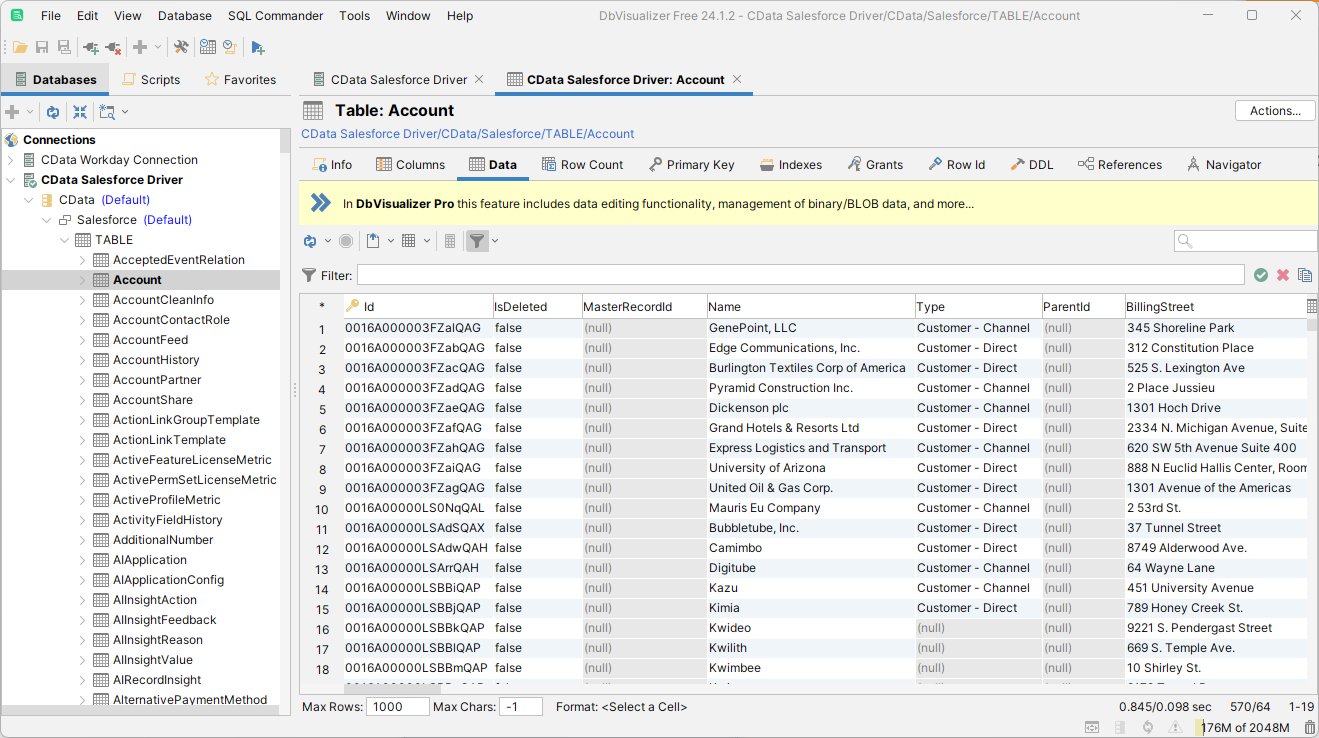
To browse through tables exposed by the Microsoft Planner JDBC Driver, right-click a table and click "Open in New Tab."
To execute SQL queries, use the SQL Commander tool: Click SQL Commander -> New SQL Commander. Select the Database Connection, Database, and Schema from the available menus.
See the "Supported SQL" chapter in the help documentation for more information on the supported SQL. See the "Data Model" chapter for table-specific information.