Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Use the CData ODBC Driver for Microsoft Planner in MicroStrategy Desktop
Connect to Microsoft Planner data in MicroStrategy Desktop using the CData ODBC Driver for Microsoft Planner.
MicroStrategy is an analytics and mobility platform that enables data-driven innovation. When paired with the CData ODBC Driver for Microsoft Planner, you gain database-like access to live Microsoft Planner data from MicroStrategy, expanding your reporting and analytics capabilities. In this article, we walk through adding Microsoft Planner as a data source in MicroStrategy Desktop and creating a simple visualization of Microsoft Planner data.
The CData ODBC Driver offers unmatched performance for interacting with live Microsoft Planner data in MicroStrategy due to optimized data processing built into the driver. When you issue complex SQL queries from MicroStrategy to Microsoft Planner, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to Microsoft Planner and utilizes the embedded SQL Engine to process unsupported operations (often SQL functions and JOIN operations) client-side. With built-in dynamic metadata querying, you can visualize and analyze Microsoft Planner data using native MicroStrategy data types.
Connect to Microsoft Planner as an ODBC Data Source
Information for connecting to Microsoft Planner follows, along with different instructions for configuring a DSN in Windows and Linux environments.
You can connect without setting any connection properties for your user credentials. Below are the minimum connection properties required to connect.
- InitiateOAuth: Set this to GETANDREFRESH. You can use InitiateOAuth to avoid repeating the OAuth exchange and manually setting the OAuthAccessToken.
- Tenant (optional): Set this if you wish to authenticate to a different tenant than your default. This is required to work with an organization not on your default Tenant.
When you connect the Driver opens the MS Planner OAuth endpoint in your default browser. Log in and grant permissions to the Driver. The Driver then completes the OAuth process.
- Extracts the access token from the callback URL and authenticates requests.
- Obtains a new access token when the old one expires.
- Saves OAuth values in OAuthSettingsLocation to be persisted across connections.
When you configure the DSN, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
Windows
If you have not already, first specify connection properties in an ODBC DSN (data source name). This is the last step of the driver installation. You can use the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure ODBC DSNs.
Linux
If you are installing the CData ODBC Driver for Microsoft Planner in a Linux environment, the driver installation predefines a system DSN. You can modify the DSN by editing the system data sources file (/etc/odbc.ini) and defining the required connection properties.
/etc/odbc.ini
[CData MicrosoftPlanner Sys]
Driver = CData ODBC Driver for Microsoft Planner
Description = My Description
OAuthClientId = MyApplicationId
OAuthClientSecret = MySecretKey
CallbackURL = http://localhost:33333
For specific information on using these configuration files, please refer to the help documentation (installed and found online).
Connect to and Visualize Microsoft Planner Data using MicroStrategy Desktop
In addition to connecting Microsoft Planner in MicroStrategy enterprise products, you can connect to Microsoft Planner in MicroStrategy Desktop. Follow the steps below to add Microsoft Planner data as a dataset and create visualizations and reports of Microsoft Planner data.
- Open MicroStrategy Desktop and create a new dossier.
- In the datasets panel, click New Data, select Databases, and select Type a Query as the Import Option.
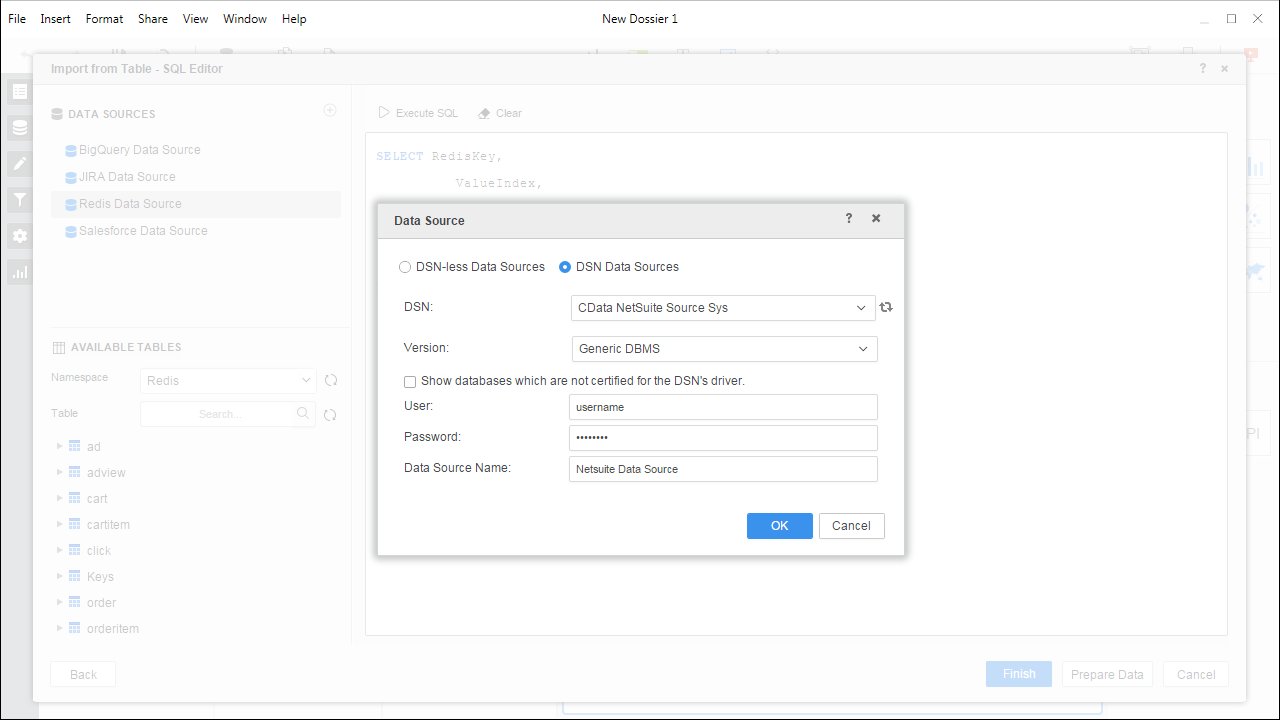
- Add a new data source and choose DSN data sources.
- Choose the DSN you previously configured (likely CData MicrosoftPlanner Sys) and select Generic DBMS in the Version menu.
- Set the User and Password properties for the DSN (or use placeholder values) and name the data source.
- Select the new database instance to view the tables. You may need to manually click the search icon in the Available Tables section to see the tables.
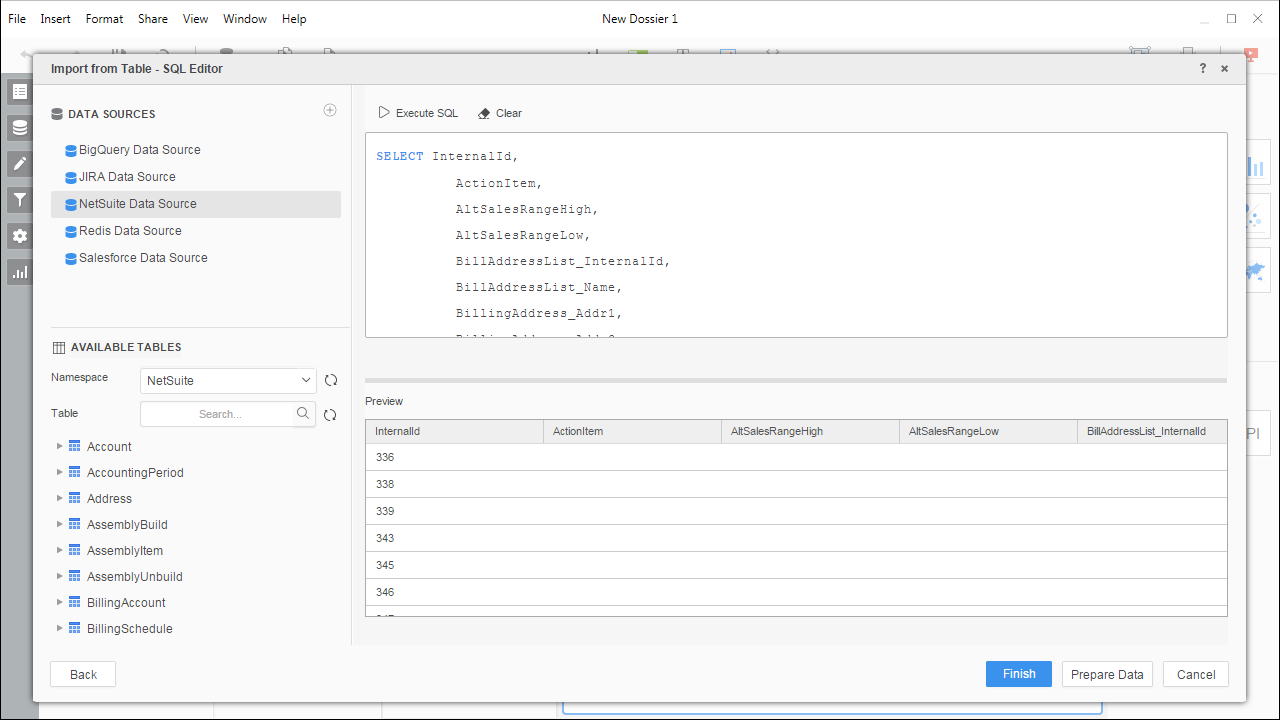
- Create a SQL query for the Microsoft Planner data (see below) and click Execute SQL to test the query.
SELECT * FROM Tasks![Querying Microsoft Planner for data.]() NOTE: Since we create a live connection, we can execute a SELECT * query and utilize the filtering and aggregation features native to the MicroStrategy products.
NOTE: Since we create a live connection, we can execute a SELECT * query and utilize the filtering and aggregation features native to the MicroStrategy products. - Click Finish and choose to connect live.
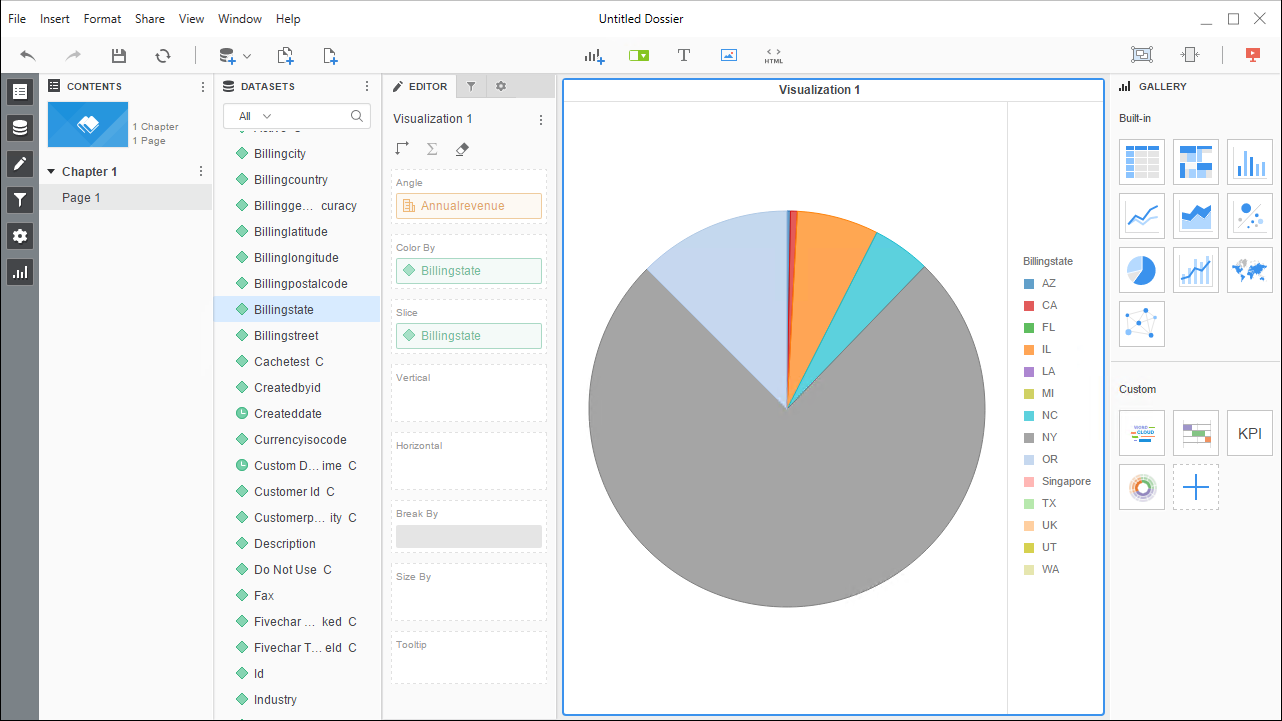
- Choose a visualization, choose fields to display (data types are discovered automatically through dynamic metadata discovery) and apply any filters to create a new visualization of Microsoft Planner data. Where possible, the complex queries generated by the filters and aggregations will be pushed down to Microsoft Planner, while any unsupported operations (which can include SQL functions and JOIN operations) will be managed client-side by the CData SQL Engine embedded in the driver.
![Visualize Microsoft Planner data.]()
- Once you are finished configuring the dossier, click File -> Save.
Using the CData ODBC Driver for Microsoft Planner in MicroStrategy Desktop, you can easily create robust visualizations and reports on Microsoft Planner data. Read our other articles on connecting to Microsoft Planner in MicroStrategy and connecting to Microsoft Planner in MicroStrategy Web for more examples.






 NOTE: Since we create a live connection, we can execute a SELECT * query and utilize the filtering and aggregation features native to the MicroStrategy products.
NOTE: Since we create a live connection, we can execute a SELECT * query and utilize the filtering and aggregation features native to the MicroStrategy products.