Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →How to connect and process Oracle Service Cloud Data from Azure Databricks
Use CData, Azure, and Databricks to perform data engineering and data science on live Oracle Service Cloud Data
Databricks is a cloud-based service that provides data processing capabilities through Apache Spark. When paired with the CData JDBC Driver, customers can use Databricks to perform data engineering and data science on live Oracle Service Cloud data. This article walks through hosting the CData JDBC Driver in Azure, as well as connecting to and processing live Oracle Service Cloud data in Databricks.
With built-in optimized data processing, the CData JDBC Driver offers unmatched performance for interacting with live Oracle Service Cloud data. When you issue complex SQL queries to Oracle Service Cloud, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to Oracle Service Cloud and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations client-side (often SQL functions and JOIN operations). Its built-in dynamic metadata querying allows you to work with and analyze Oracle Service Cloud data using native data types.
Install the CData JDBC Driver in Azure
To work with live Oracle Service Cloud data in Databricks, install the driver on your Azure cluster.
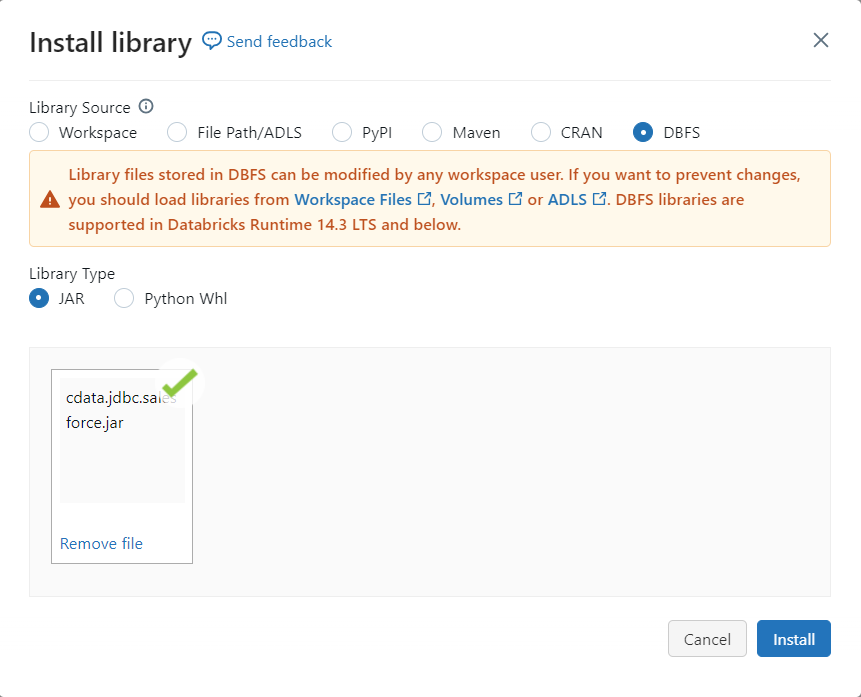
- Navigate to your Databricks administration screen and select the target cluster.
- On the Libraries tab, click "Install New."
- Select "Upload" as the Library Source and "Jar" as the Library Type.
- Upload the JDBC JAR file (cdata.jdbc.oracleservicecloud.jar) from the installation location (typically C:\Program Files\CData[product_name]\lib).
Connect to Oracle Service Cloud from Databricks
With the JAR file installed, we are ready to work with live Oracle Service Cloud data in Databricks. Start by creating a new notebook in your workspace. Name the notebook, select Python as the language (though Scala is available as well), and choose the cluster where you installed the JDBC driver. When the notebook launches, we can configure the connection, query Oracle Service Cloud, and create a basic report.
Configure the Connection to Oracle Service Cloud
Connect to Oracle Service Cloud by referencing the class for the JDBC Driver and constructing a connection string to use in the JDBC URL. Additionally, you will need to set the RTK property in the JDBC URL (unless you are using a Beta driver). You can view the licensing file included in the installation for information on how to set this property.
driver = "cdata.jdbc.oracleservicecloud.OracleServiceCloudDriver" url = "jdbc:oracleservicecloud:RTK=5246...;Url=https://abc.rightnowdemo.com;User=user;Password=password;"
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Oracle Service Cloud JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.oracleservicecloud.jar
Fill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
Using Basic Authentication
You must set the following to authenticate to Oracle Service Cloud:
- Url: The Url of the account to connect to.
- User: The username of the authenticating account.
- Password: The password of the authenticating account.

Load Oracle Service Cloud Data
Once the connection is configured, you can load Oracle Service Cloud data as a dataframe using the CData JDBC Driver and the connection information.
remote_table = spark.read.format ( "jdbc" ) \ .option ( "driver" , driver) \ .option ( "url" , url) \ .option ( "dbtable" , "Accounts") \ .load ()
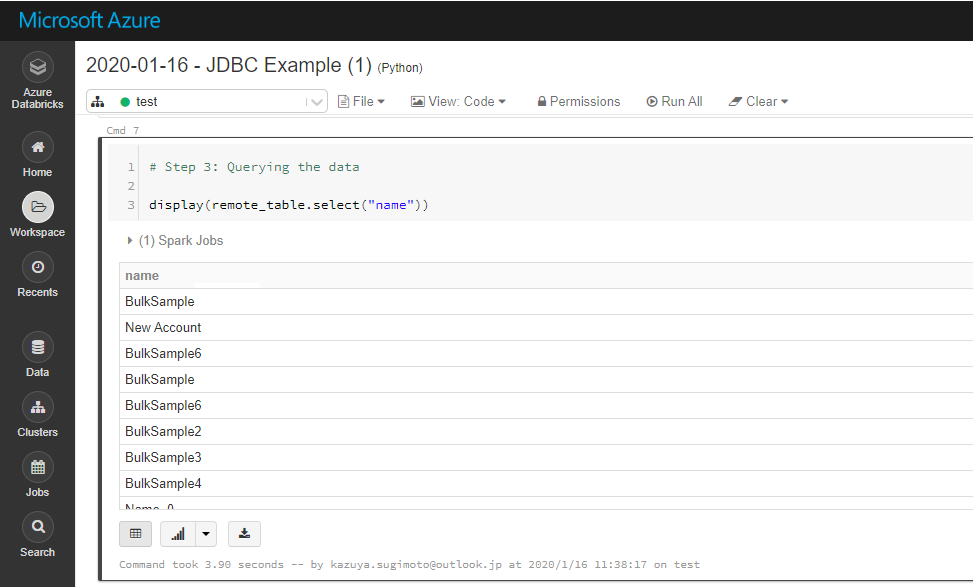
Display Oracle Service Cloud Data
Check the loaded Oracle Service Cloud data by calling the display function.
display (remote_table.select ("Id"))
Analyze Oracle Service Cloud Data in Azure Databricks
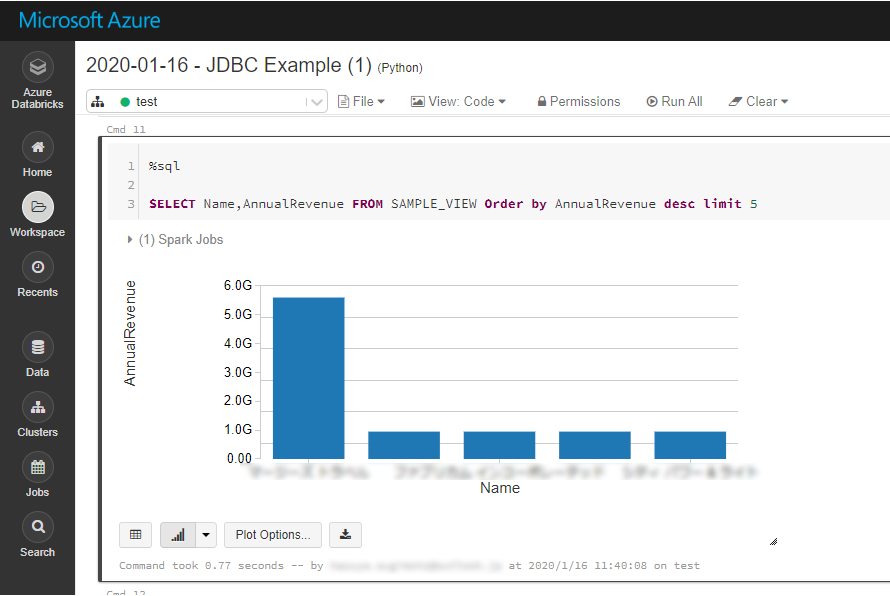
If you want to process data with Databricks SparkSQL, register the loaded data as a Temp View.
remote_table.createOrReplaceTempView ( "SAMPLE_VIEW" )
The SparkSQL below retrieves the Oracle Service Cloud data for analysis.
% sql SELECT Id, LookupName FROM Accounts WHERE DisplayOrder = 12
The data from Oracle Service Cloud is only available in the target notebook. If you want to use it with other users, save it as a table.
remote_table.write.format ( "parquet" ) .saveAsTable ( "SAMPLE_TABLE" )
Download a free, 30-day trial of the CData JDBC Driver for Oracle Service Cloud and start working with your live Oracle Service Cloud data in Azure Databricks. Reach out to our Support Team if you have any questions.






