Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →How to Visualize Phoenix Data in Python with pandas
Use pandas and other modules to analyze and visualize live Phoenix data in Python.
The rich ecosystem of Python modules lets you get to work quickly and integrate your systems more effectively. With the CData Python Connector for Phoenix, the pandas & Matplotlib modules, and the SQLAlchemy toolkit, you can build Phoenix-connected Python applications and scripts for visualizing Phoenix data. This article shows how to use the pandas, SQLAlchemy, and Matplotlib built-in functions to connect to Phoenix data, execute queries, and visualize the results.
With built-in optimized data processing, the CData Python Connector offers unmatched performance for interacting with live Phoenix data in Python. When you issue complex SQL queries from Phoenix, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to Phoenix and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations client-side (often SQL functions and JOIN operations).
Connecting to Phoenix Data
Connecting to Phoenix data looks just like connecting to any relational data source. Create a connection string using the required connection properties. For this article, you will pass the connection string as a parameter to the create_engine function.
Connect to Apache Phoenix via the Phoenix Query Server. Set the Server and Port (if different from the default port) properties to connect to Apache Phoenix. The Server property will typically be the host name or IP address of the server hosting Apache Phoenix.
Authenticating to Apache Phoenix
By default, no authentication will be used (plain). If authentication is configured for your server, set AuthScheme to NEGOTIATE and set the User and Password properties (if necessary) to authenticate through Kerberos.
Follow the procedure below to install the required modules and start accessing Phoenix through Python objects.
Install Required Modules
Use the pip utility to install the pandas & Matplotlib modules and the SQLAlchemy toolkit:
pip install pandas pip install matplotlib pip install sqlalchemy
Be sure to import the module with the following:
import pandas import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sqlalchemy import create_engine
Visualize Phoenix Data in Python
You can now connect with a connection string. Use the create_engine function to create an Engine for working with Phoenix data.
engine = create_engine("apachephoenix:///?Server=localhost&Port=8765")
Execute SQL to Phoenix
Use the read_sql function from pandas to execute any SQL statement and store the resultset in a DataFrame.
df = pandas.read_sql("SELECT Id, Column1 FROM MyTable WHERE Id = '123456'", engine)
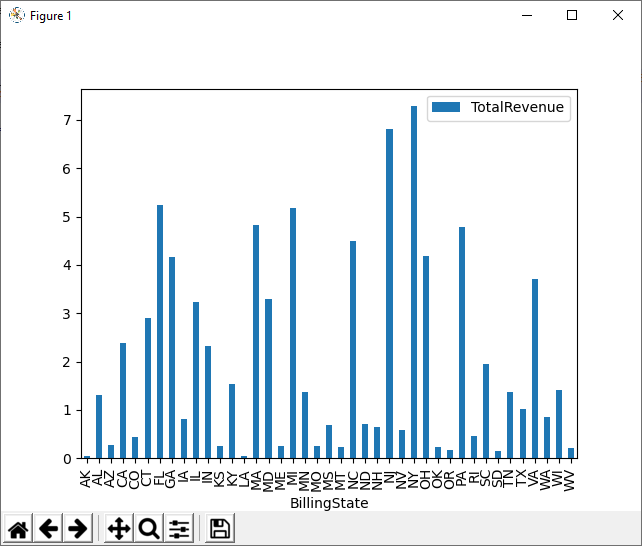
Visualize Phoenix Data
With the query results stored in a DataFrame, use the plot function to build a chart to display the Phoenix data. The show method displays the chart in a new window.
df.plot(kind="bar", x="Id", y="Column1") plt.show()
Free Trial & More Information
Download a free, 30-day trial of the CData Python Connector for Phoenix to start building Python apps and scripts with connectivity to Phoenix data. Reach out to our Support Team if you have any questions.
Full Source Code
import pandas
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sqlalchemy import create_engin
engine = create_engine("apachephoenix:///?Server=localhost&Port=8765")
df = pandas.read_sql("SELECT Id, Column1 FROM MyTable WHERE Id = '123456'", engine)
df.plot(kind="bar", x="Id", y="Column1")
plt.show()