Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Use the CData JDBC Driver for Google Sheets in MicroStrategy Web
Connect to Google Sheets data in MicroStrategy Web using the CData JDBC Driver for Google Sheets.
MicroStrategy is an analytics and mobility platform that enables data-driven innovation. When you pair MicroStrategy with the CData JDBC Driver for Google Sheets, you gain database-like access to live Google Sheets data from MicroStrategy, expanding your reporting and analytics capabilities. In this article, we walk through adding Google Sheets as an external data source in MicroStrategy Web and creating a simple visualization of Google Sheets data.
The CData JDBC driver offers unmatched performance for interacting with live Google Sheets data in MicroStrategy due to optimized data processing built into the driver. When you issue complex SQL queries from MicroStrategy to Google Sheets, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to Google Sheets and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations (often SQL functions and JOIN operations) client-side. With built-in dynamic metadata querying, you can visualize and analyze Google Sheets data using native MicroStrategy data types.
Connect to and Visualize Google Sheets Data using MicroStrategy Web
You can connect to Google Sheets in MicroStrategy Web by adding a data source based on the CData JDBC Driver for Google Sheets.* Before you begin, you will need install the JDBC Driver for Google Sheets on the machine hosting the MicroStrategy Intelligence Server that your instance of MicroStrategy Web is connected to. Once you have created a data source you can build dynamic visualizations of Google Sheets data in MicroStrategy Web.
- Open MicroStrategy Web and select your project.
- Click Add External Data, select Databases, and use Select Tables as the Import Option.
![Adding External Data]()
- In the Import from Tables wizard, click to add a new Data Source.
- Select Generic in the Database menu and select Generic DBMS in the Version menu.
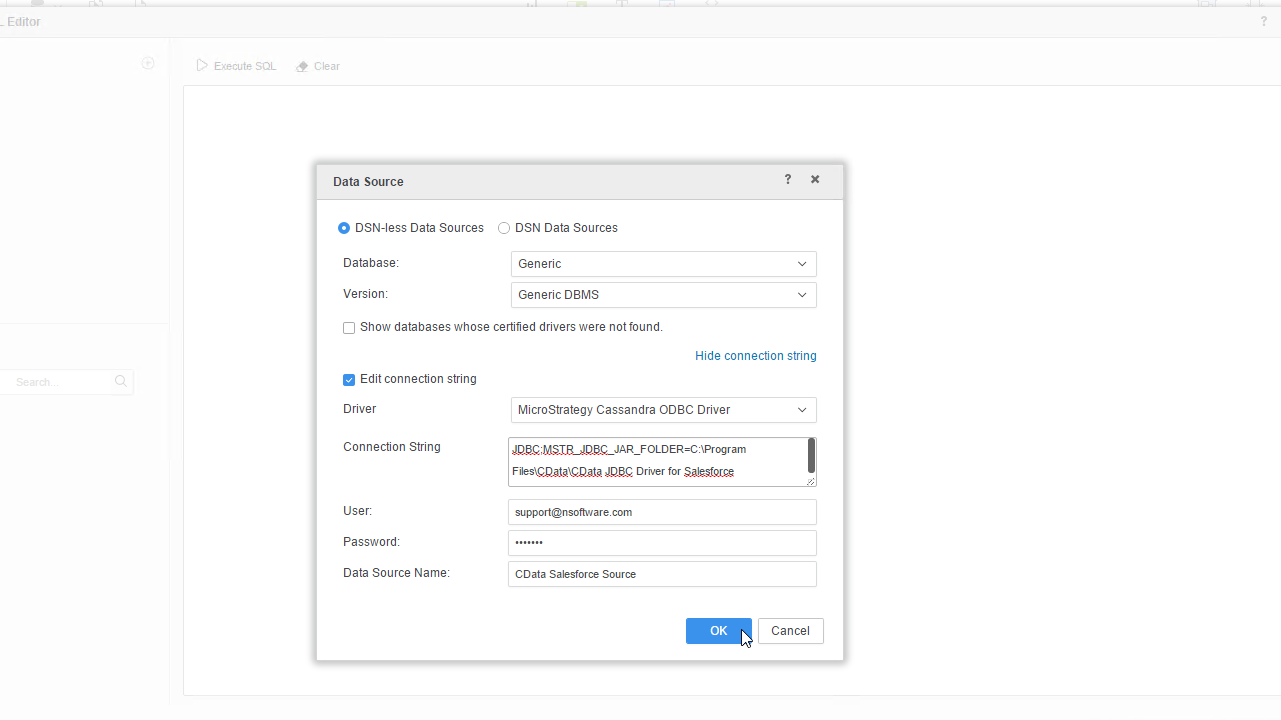
- Click the link to show the connection string and opt to edit the connection string. In the Driver menu, select MicroStrategy Cassandra ODBC Driver (MicroStrategy requires a certified driver to interface through JDBC, the actual driver will not be used).
- Set the connection string to the following:
JDBC;MSTR_JDBC_JAR_FOLDER=PATH\TO\JAR\;DRIVER=cdata.jdbc.googlesheets.GoogleSheetsDriver;URL={jdbc:googlesheets:Spreadsheet=MySheet;};![Configure the data source.]()
You can connect to a spreadsheet by providing authentication to Google and then setting the Spreadsheet connection property to the name or feed link of the spreadsheet. If you want to view a list of information about the spreadsheets in your Google Drive, execute a query to the Spreadsheets view after you authenticate.
ClientLogin (username/password authentication) has been officially deprecated since April 20, 2012 and is now no longer available. Instead, use the OAuth 2.0 authentication standard. To access Google APIs on behalf on individual users, you can use the embedded credentials or you can register your own OAuth app.
OAuth also enables you to use a service account to connect on behalf of users in a Google Apps domain. To authenticate with a service account, you will need to register an application to obtain the OAuth JWT values.
See the Getting Started chapter in the help documentation to connect to Google Sheets from different types of accounts: Google accounts, Google Apps accounts, and accounts using two-step verification.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Google Sheets JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.googlesheets.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
When you configure the JDBC URL, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
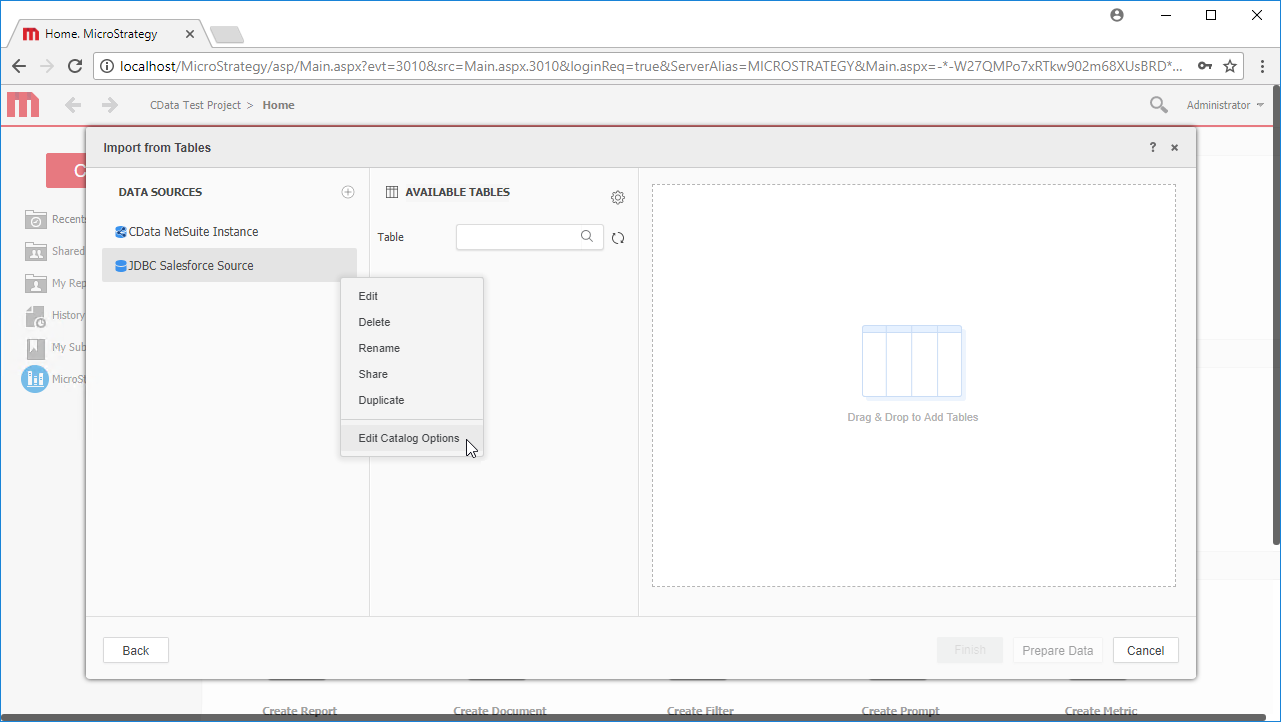
- Right-click on the new data source, and choose Edit catalog options.
![Edit the catalog options.]()
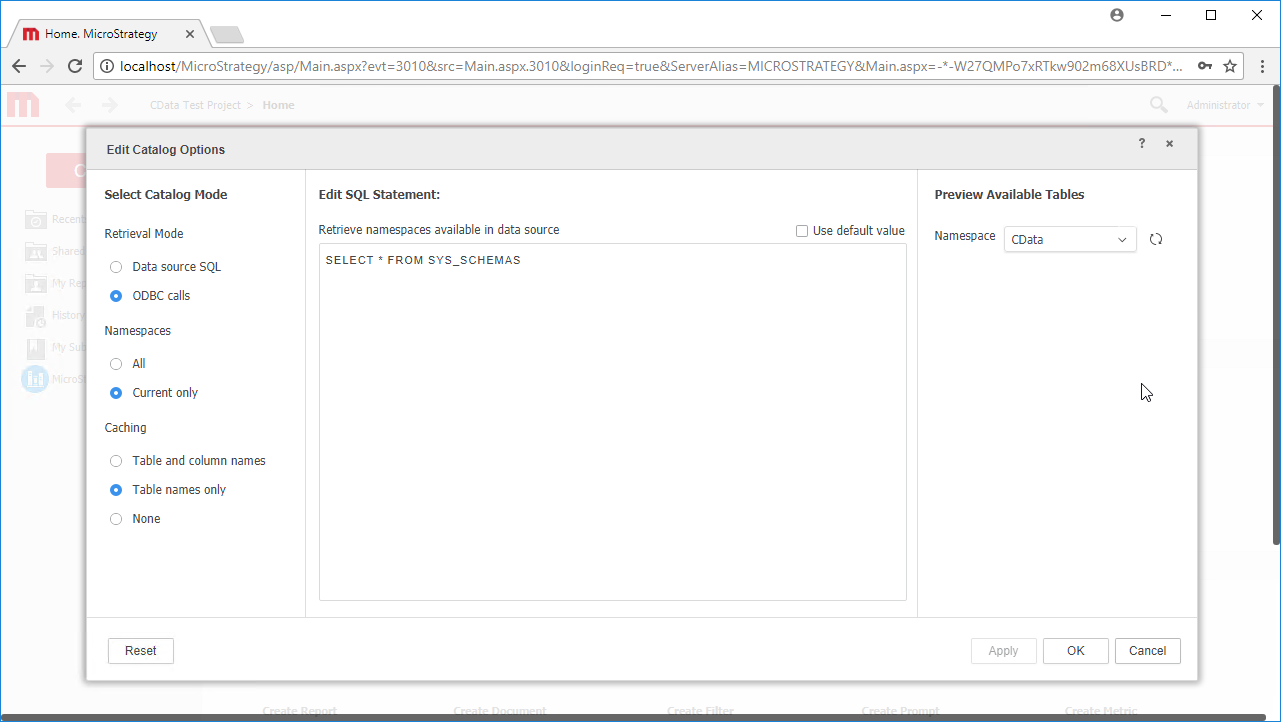
- Edit the SQL Statement to SELECT * FROM SYS_SCHEMAS to read the metadata from the JDBC Driver.
![Configuring the Catalog Options.]()
- Select the new data source to view the available tables. You may need to manually click the search icon in the Available Tables section to see the tables.
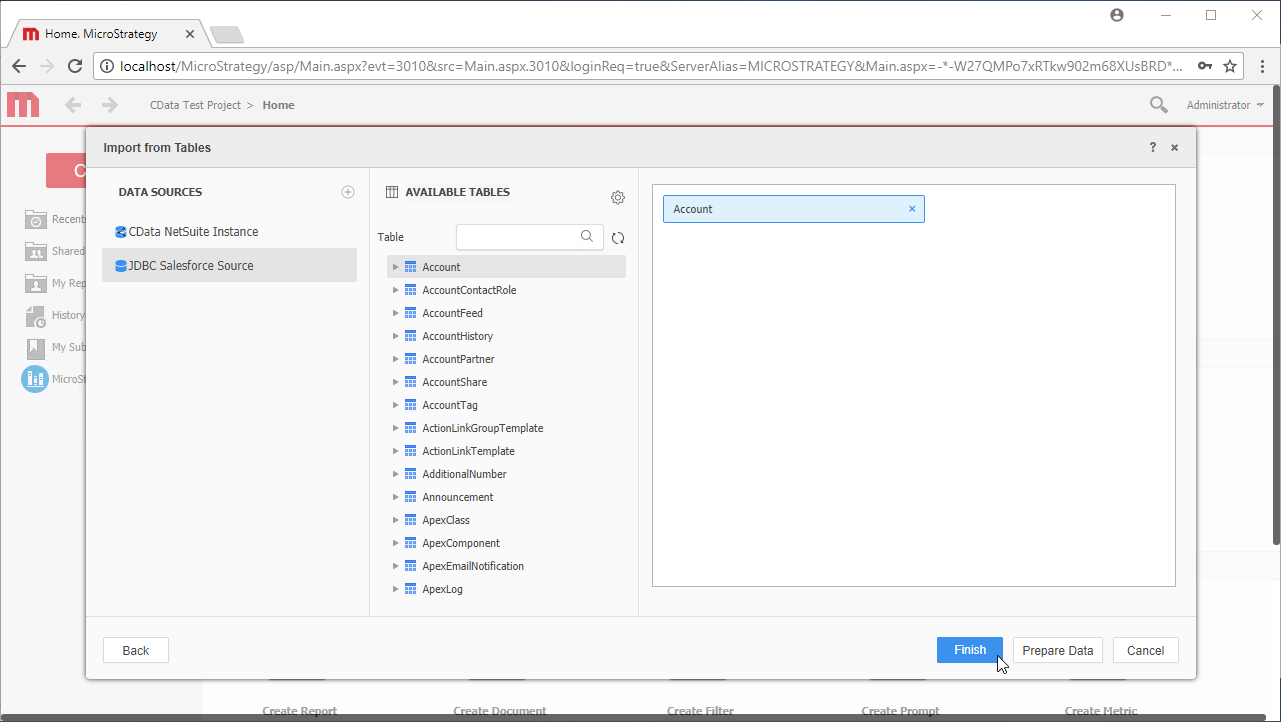
- Drag tables into the pane to import them.
![Select tables to import.]() Note: Since we create a live connection, we can import whole tables and utilize the filtering and aggregation features native to the MicroStrategy products to customize our datasets.
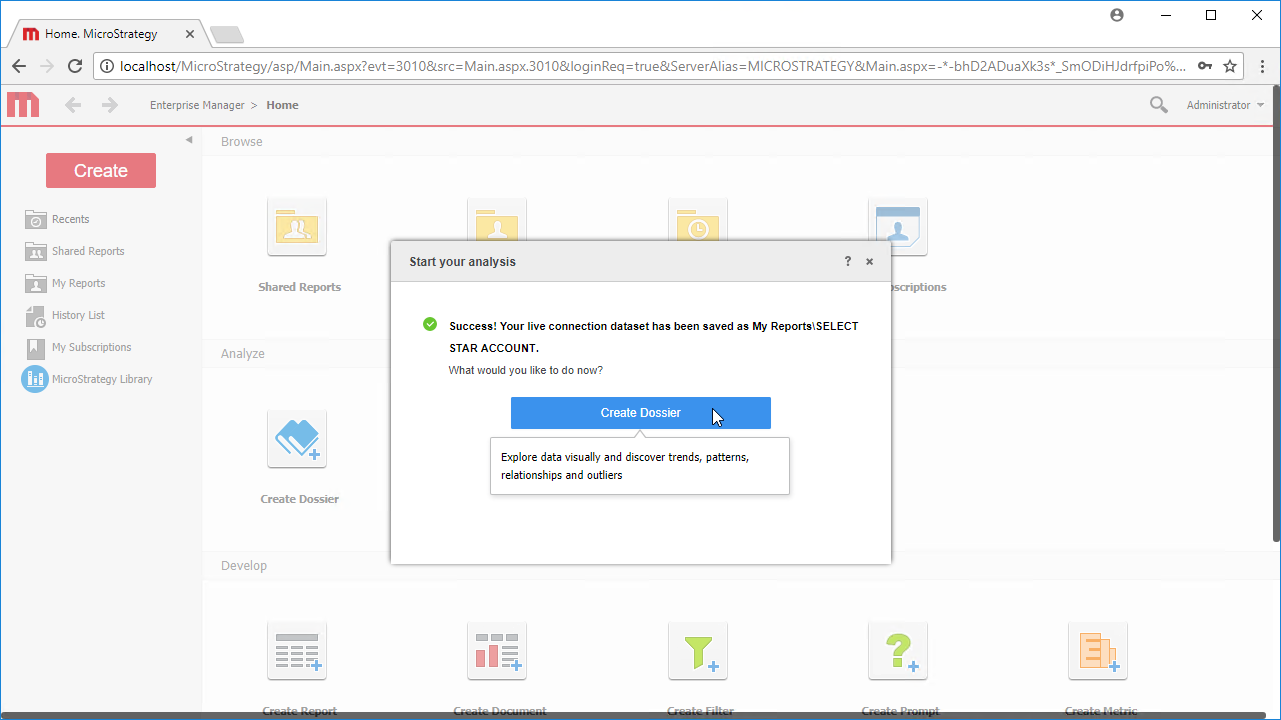
Note: Since we create a live connection, we can import whole tables and utilize the filtering and aggregation features native to the MicroStrategy products to customize our datasets. - Click Finish, choose to the option to connect live, save the query, and choose the option to create a new dossier. Live connections are possible and effective, thanks to high-performance data processing native to CData JDBC drivers.
![Save the query and create a new dossier.]()
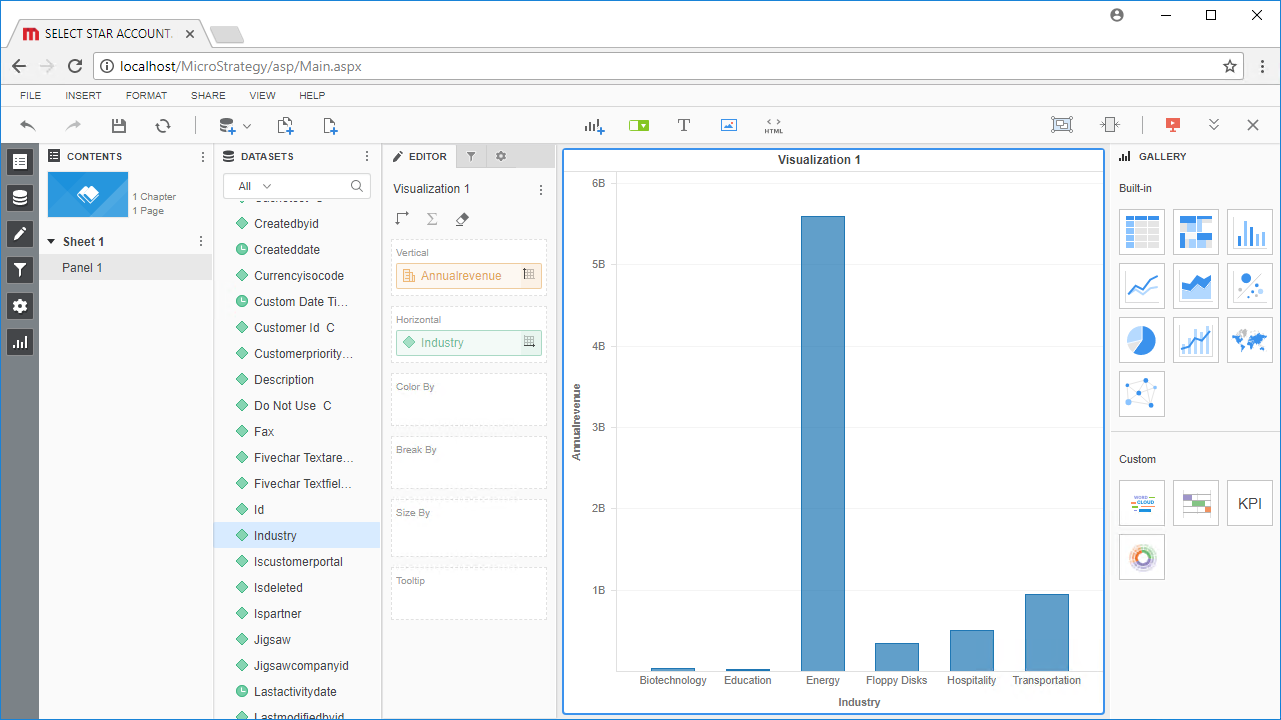
- Choose a visualization, choose fields to display and apply any filters to create a new visualization of Google Sheets data. Data types are discovered automatically through dynamic metadata discovery. Where possible, the complex queries generated by the filters and aggregations will be pushed down to Google Sheets, while any unsupported operations (which can include SQL functions and JOIN operations) will be managed client-side by the CData SQL engine embedded in the driver.
![Visualize Google Sheets data.]()
- Once you have finished configuring the dossier, click File -> Save.
Using the CData JDBC Driver for Google Sheets in MicroStrategy Web, you can easily create robust visualizations and reports on Google Sheets data. Read our other articles on connecting to Google Sheets in MicroStrategy and connecting to Google Sheets in MicroStrategy Desktop for more examples.
Note: Connecting using a JDBC Driver requires a 3- or 4-Tier Architecture.








 Note: Since we create a live connection, we can import whole tables and utilize the filtering and aggregation features native to the MicroStrategy products to customize our datasets.
Note: Since we create a live connection, we can import whole tables and utilize the filtering and aggregation features native to the MicroStrategy products to customize our datasets.