Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →How to Create Power BI Visual Reports with Real-Time Snowflake Data
Use CData Power BI Connectors to visualize Snowflake data in Power BI.
CData Power BI Connectors provide self-service integration with Microsoft Power BI. The CData Power BI Connector for Snowflake links your Power BI reports to real-time Snowflake data. You can monitor Snowflake data through dashboards and ensure that your analysis reflects Snowflake data in real time by scheduling refreshes or refreshing on demand. This article details how to use the Power BI Connector to create real-time visualizations of Snowflake data in Microsoft Power BI Desktop.
If you are interested in publishing reports on Snowflake data to PowerBI.com, refer to our other Knowledge Base article.
Collaborative Query Processing
The CData Power BI Connectors offer unmatched performance for interacting with live Snowflake data in Power BI due to optimized data processing built into the connector. When you issue complex SQL queries from Power BI to Snowflake, the connector pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to Snowflake and utilizes the embedded SQL Engine to process unsupported operations (often SQL functions and JOIN operations) client-side. With built-in dynamic metadata querying, you can visualize and analyze Snowflake data using native Power BI data types.
Connect to Snowflake as a Power BI Data Source
Installing the Power BI Connector creates a DSN (data source name) called CData Power BI Snowflake. This the name of the DSN that Power BI uses to request a connection to the data source. Configure the DSN by filling in the required connection properties.
You can use the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure the DSN: From the Start menu, enter "ODBC Data Sources" and select the CData PowerBI REST DSN. Ensure that you run the version of the ODBC Administrator that corresponds to the bitness of your Power BI Desktop installation (32-bit or 64-bit). You can also use run the ConfigureODBC.exe tool located in the installation folder for the connector.
To connect to Snowflake:
- Set User and Password to your Snowflake credentials and set the AuthScheme property to PASSWORD or OKTA.
- Set URL to the URL of the Snowflake instance (i.e.: https://myaccount.snowflakecomputing.com).
- Set Warehouse to the Snowflake warehouse.
- (Optional) Set Account to your Snowflake account if your URL does not conform to the format above.
- (Optional) Set Database and Schema to restrict the tables and views exposed.
See the Getting Started guide in the CData driver documentation for more information.
How to Query Snowflake Tables
Follow the steps below to build a query to pull Snowflake data into the report:
- Open Power BI Desktop and click Get Data -> Other -> CData Snowflake.
- Select CData PowerBI Snowflake in the Data Source Name menu and select a data connectivity mode:
Select Import if you want to import a copy of the data into your project. You can refresh this data on demand.
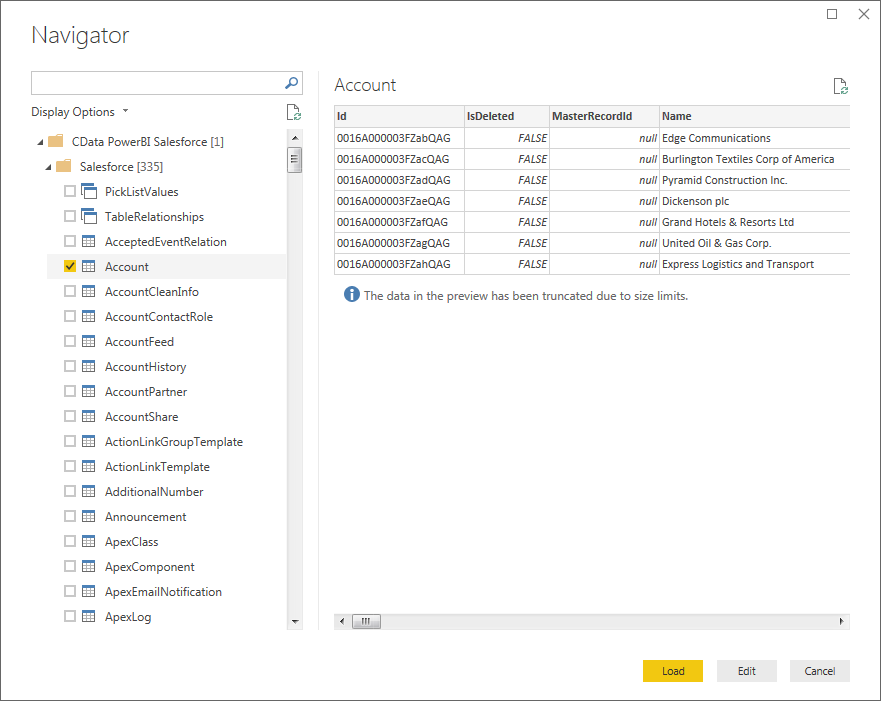
Select DirectQuery if you want to work with the remote data. - Select tables in the Navigator dialog.
![The available tables. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
In the Query Editor, you can customize your dataset by filtering, sorting, and summarizing Snowflake columns. Click Edit to open the query editor. Right-click a row to filter the rows. Right-click a column header to perform actions like the following:
- Change column data types
- Remove a column
- Group by columns
Power BI detects each column's data type from the Snowflake metadata retrieved by the connector.
Power BI records your modifications to the query in the Applied Steps section, adjusting the underlying data retrieval query that is executed to the remote Snowflake data. When you click Close and Apply, Power BI executes the data retrieval query.
Otherwise, click Load to pull the data into Power BI.
How to Create Data Visualizations in Power BI
After pulling the data into Power BI, you can create data visualizations in the Report view by dragging fields from the Fields pane onto the canvas. Follow the steps below to create a pie chart:
- Select the pie chart icon in the Visualizations pane.
- Select a dimension in the Fields pane: for example, Id.
- Select a measure in the Fields pane: for example, ProductName.
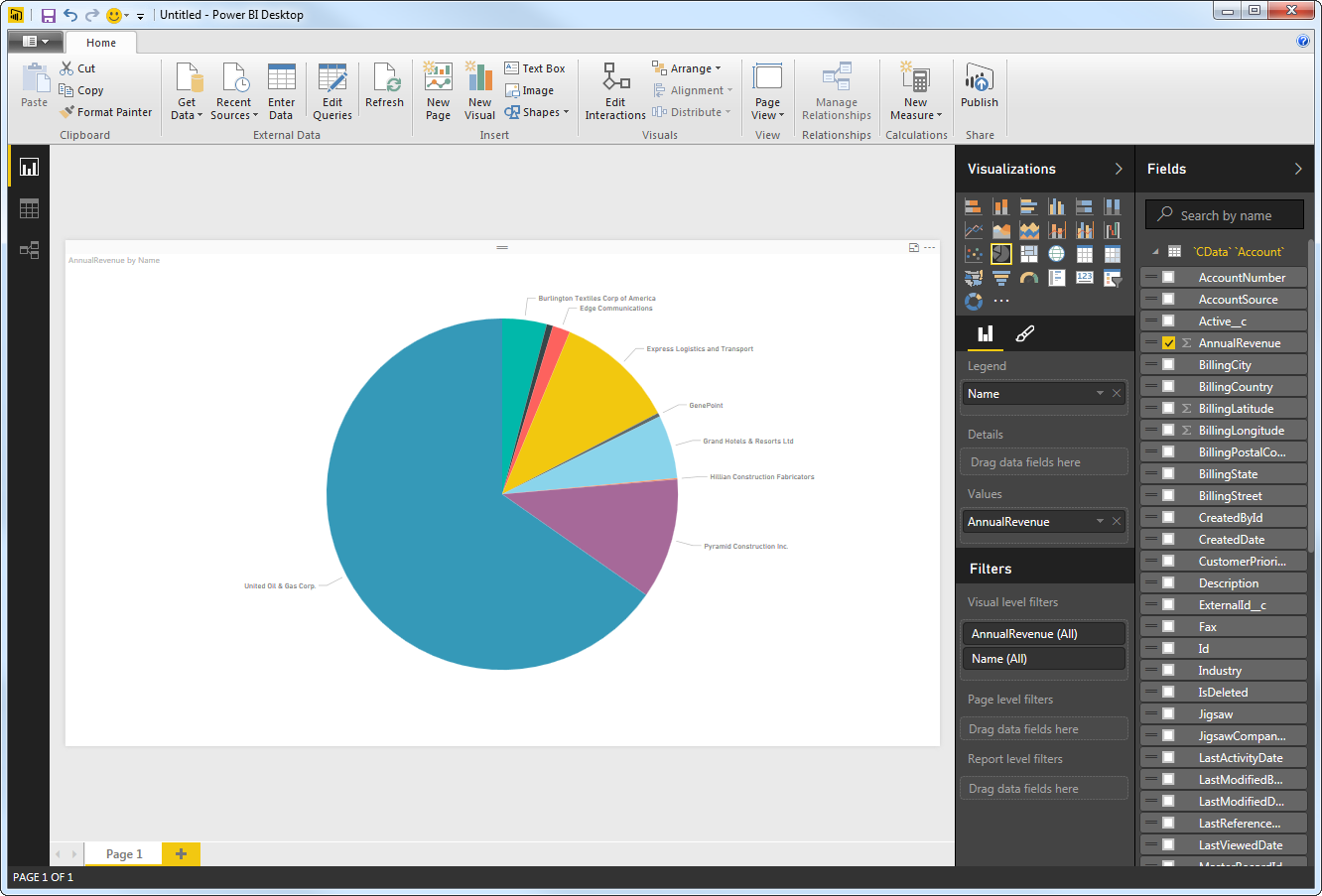
You can change sort options by clicking the ellipsis (...) button for the chart. Options to select the sort column and change the sort order are displayed.
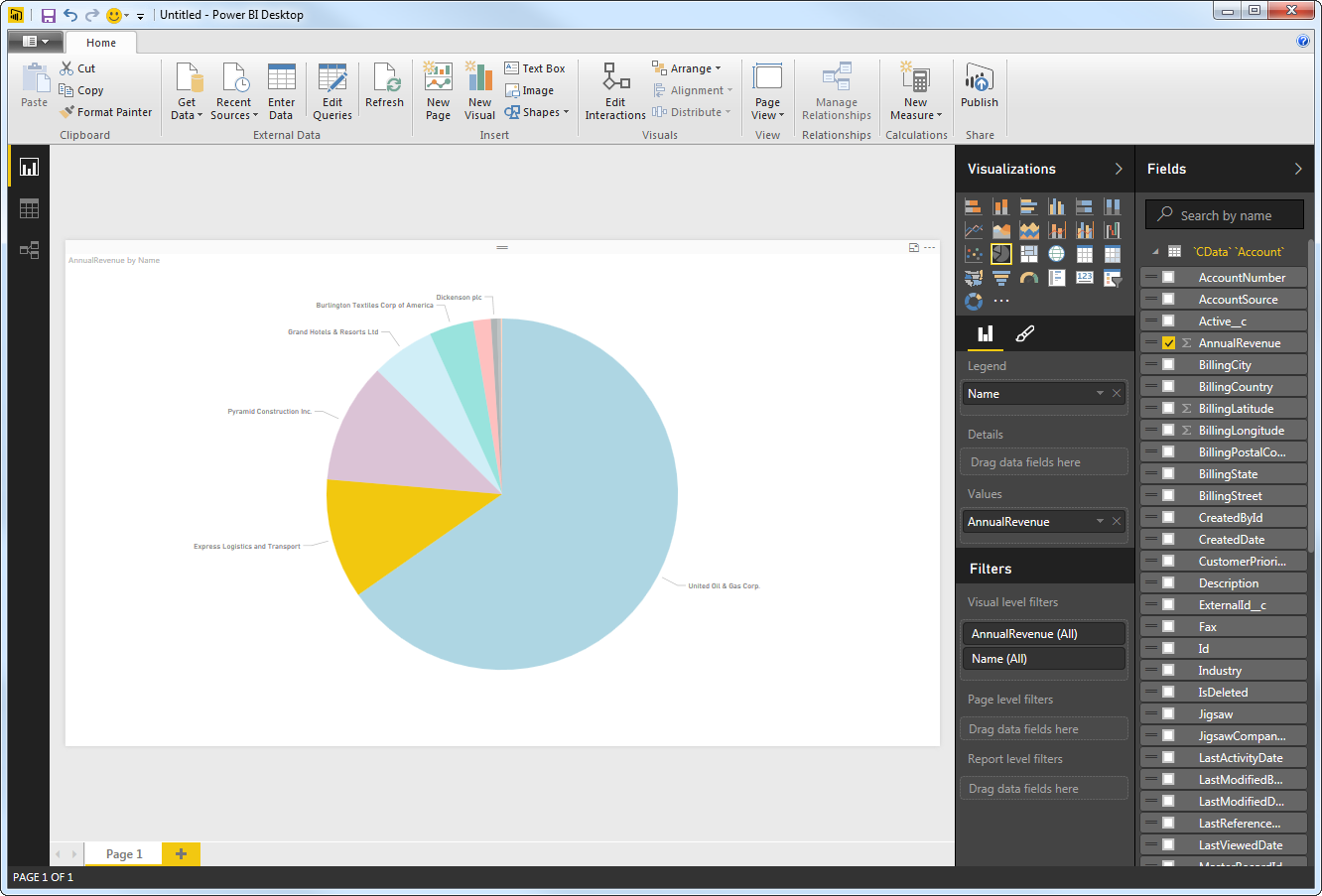
You can use both highlighting and filtering to focus on data. Filtering removes unfocused data from visualizations; highlighting dims unfocused data. You can highlight fields by clicking them:
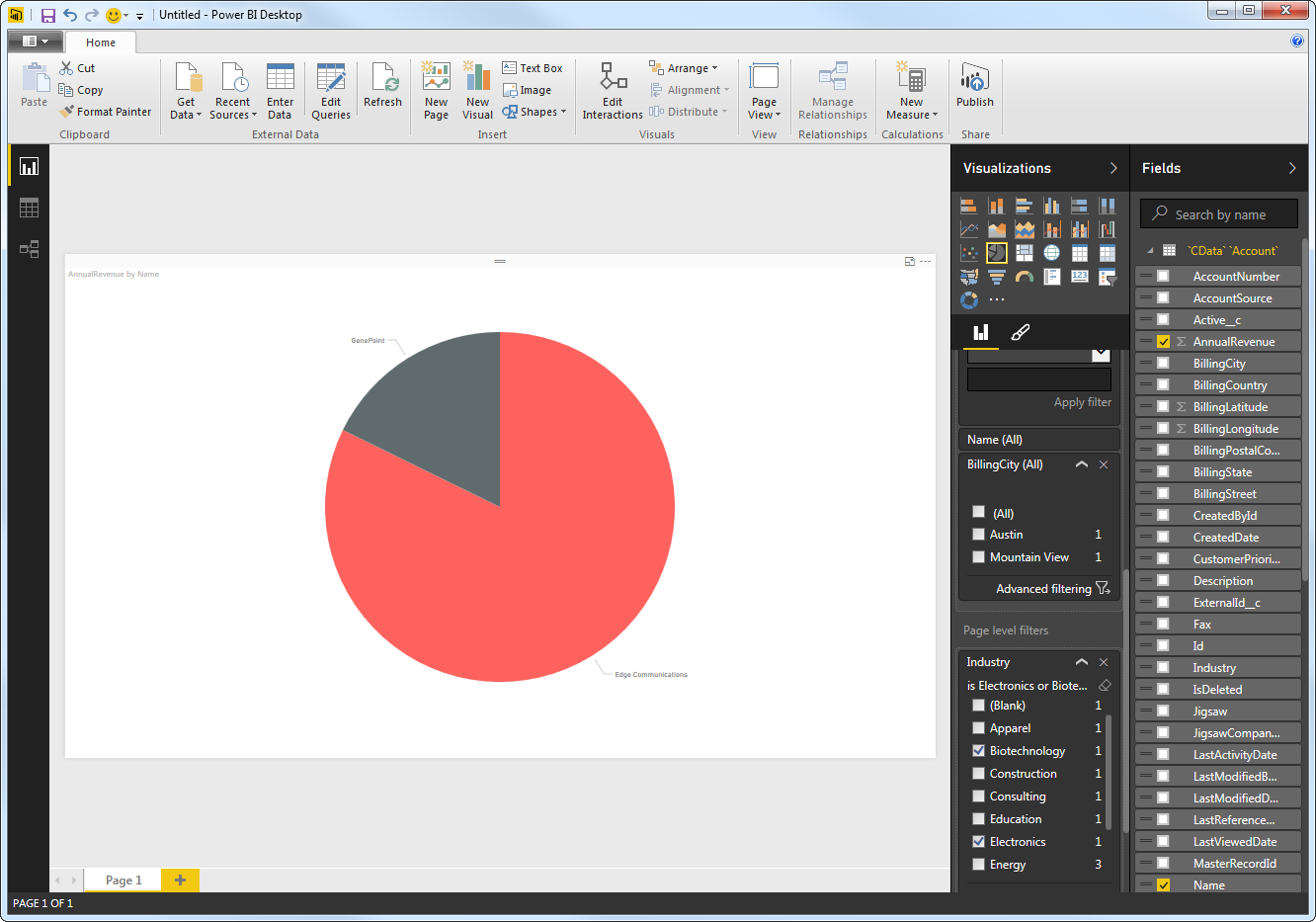
You can apply filters at the page level, at the report level, or to a single visualization by dragging fields onto the Filters pane. To filter on the field's value, select one of the values that are displayed in the Filters pane.
Click Refresh to synchronize your report with any changes to the data.
At this point, you will have a Power BI report built on top of live Snowflake data. Learn more about the CData Power BI Connectors for Snowflake and download a free trial from the CData Power BI Connector for Snowflake page. Let our Support Team know if you have any questions.