Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Visualize XML Data from Tableau
Use the Tableau Desktop business intelligence tool to connect to XML data.
With CData Drivers for XML, you can use data access standards to unlock connectivity to business intelligence tools like Tableau. The CData JDBC Driver for XML allows you to connect from Tableau on Windows and macOS. This article covers how to discover schemas and query XML data data in real-time.
NOTE: If you are using Tableau 2020.3 or higher, you can use the CData JDBC Driver for XML. If you wish to connect to XML data in Tableau Cloud, you will need to use CData Connect.
Connect to XML in Tableau
Before starting Tableau, make sure you've placed the .jar file in the correct folder:
- Windows: C:\Program Files\Tableau\Drivers
- MacOS: ~/Library/Tableau/Drivers
Once your .jar file is in place, establishing a connection is straightforward.
- Start Tableau.
- Under To a Server, select More.
- Select Other Databases (JDBC)
- Enter the JDBC connection string in the URL field.
- Document (default): Model a top-level, document view of your XML data. The data provider returns nested elements as aggregates of data.
- FlattenedDocuments: Implicitly join nested documents and their parents into a single table.
- Relational: Return individual, related tables from hierarchical data. The tables contain a primary key and a foreign key that links to the parent document.
- Select Sign in.
See the Getting Started chapter in the data provider documentation to authenticate to your data source: The data provider models XML APIs as bidirectional database tables and XML files as read-only views (local files, files stored on popular cloud services, and FTP servers). The major authentication schemes are supported, including HTTP Basic, Digest, NTLM, OAuth, and FTP. See the Getting Started chapter in the data provider documentation for authentication guides.
After setting the URI and providing any authentication values, set DataModel to more closely match the data representation to the structure of your data.
The DataModel property is the controlling property over how your data is represented into tables and toggles the following basic configurations.
See the Modeling XML Data chapter for more information on configuring the relational representation. You will also find the sample data used in the following examples. The data includes entries for people, the cars they own, and various maintenance services performed on those cars.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the XML JDBC Driver. Either double-click the .jar file or execute the .jar file from the command-line.
From Windows:
java -jar 'C:\Program Files\CData[product_name]\lib\cdata.jdbc.xml.jar'
From MacOS:
java -jar cdata.jdbc.xml.jar
Fill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.

When you configure the JDBC URL, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
The following is a sample URL created in the designer:
jdbc:xml:URI=C:/people.xml;DataModel=Relational;
Discover Schemas and Query Data
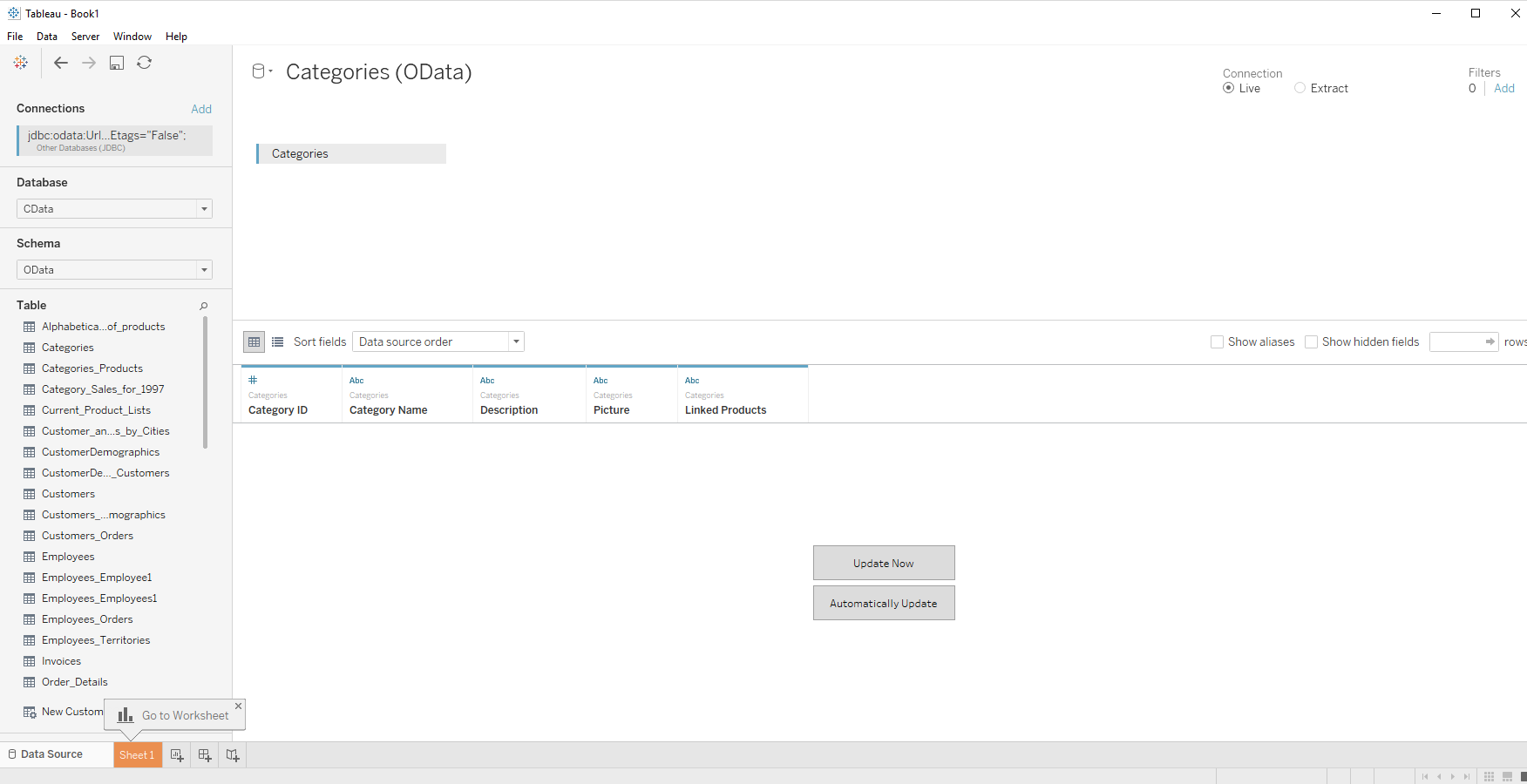
- Select CData from the Database pull-down menu.
- Select CData from the Schema pull-down menu.
- Drag the table onto the join area. You can include multiple tables.
- Select Update Now or Automatically Update. Update Now lets you preview the first 10,000 rows of the data source (or enter the number of rows you want to see in the Rows text box). Automatically Update automatically reflects the changes in the preview area.
- In the Connection menu, select the Live option, so that you skip loading a copy of the data into Tableau and instead work on real-time data.
- Click the tab for your worksheet. Columns are listed as Dimensions and Measures, depending on the data type. The CData Driver discovers data types automatically, allowing you to leverage the powerful data processing and visualization features of Tableau.
- Click and drag a field from the Dimensions or Measures area to Rows or Columns. Tableau creates column or row headers.
- Select one of the chart types from the Show Me tab. Tableau displays the chart type that you selected.
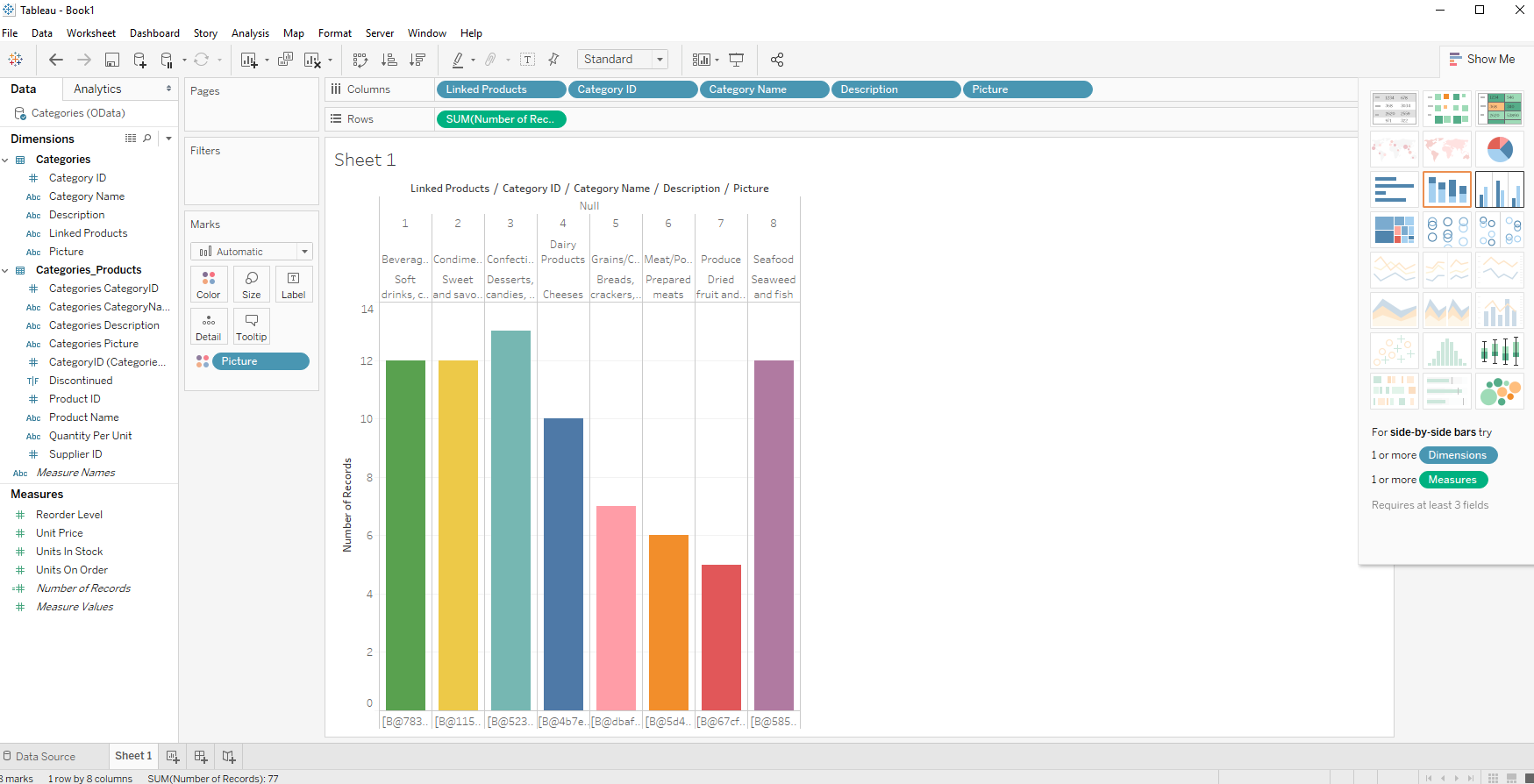
Using the CData JDBC Driver for XML with Tableau, you can easily create robust visualizations and reports on XML data. Download a free, 30-day trial and get started today.






