Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Connect to Adobe Commerce Data from a Connection Pool in JBoss
Integrate Adobe Commerce data into Java servlets: Use the Management Console in JBoss to install the Adobe Commerce JDBC Driver.
CData JDBC drivers can be configured in JBoss by following the standard procedure for connection pooling. This article details how to access Adobe Commerce data from a connection pool in JBoss applications. This article details how to use the JBoss Management Interface to configure the CData JDBC Driver for Adobe Commerce. You will then access Adobe Commerce data from a connection pool.
Create a JDBC Data Source for Adobe Commerce from the Management Console
Follow the steps below to add the driver JAR and define required connection properties.
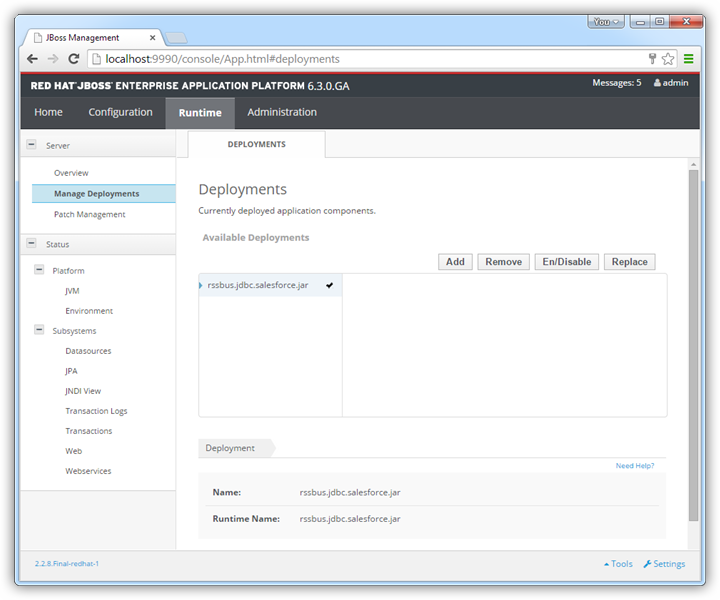
- In the Runtime menu, select the Domain or Server menu, depending on whether you are deploying to a managed domain or to a stand-alone server, and click "Manage deployments" to open the Deployments page.
- Click Add. In the resulting wizard, add the JAR file and license for the driver, located in the lib subfolder of the installation directory. Finish the wizard with the defaults, select the driver, and click Enable.
![The deployed JAR. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
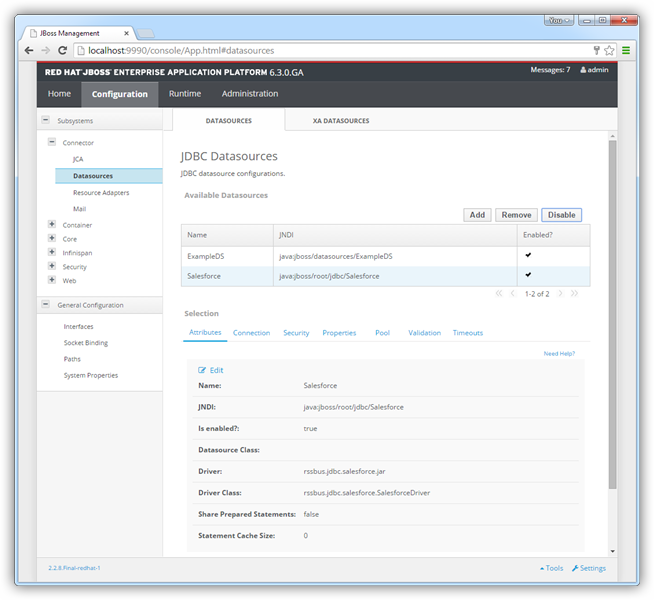
- In the Configuration menu, click Subsystems -> Connector -> Datasources. This opens the JDBC Datasources page.
- Click Add and, in the resulting wizard, enter a name for the driver and the JNDI name. For example:
java:jboss/root/jdbc/Adobe Commerce - Select the driver that you added above.
Enter the JDBC URL and the username and password. The syntax of the JDBC URL is jdbc:adobe commerce: followed by a semicolon-separated list of connection properties.
Adobe Commerce uses the OAuth 1 authentication standard. To connect to the Adobe Commerce REST API, you will need to obtain values for the OAuthClientId, OAuthClientSecret, and CallbackURL connection properties by registering an app with your Adobe Commerce system. See the "Getting Started" section in the help documentation for a guide to obtaining the OAuth values and connecting.
You will also need to provide the URL to your Adobe Commerce system. The URL depends on whether you are using the Adobe Commerce REST API as a customer or administrator.
Customer: To use Adobe Commerce as a customer, make sure you have created a customer account in the Adobe Commerce homepage. To do so, click Account -> Register. You can then set the URL connection property to the endpoint of your Adobe Commerce system.
Administrator: To access Adobe Commerce as an administrator, set CustomAdminPath instead. This value can be obtained in the Advanced settings in the Admin menu, which can be accessed by selecting System -> Configuration -> Advanced -> Admin -> Admin Base URL.
If the Use Custom Admin Path setting on this page is set to YES, the value is inside the Custom Admin Path text box; otherwise, set the CustomAdminPath connection property to the default value, which is "admin".
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Adobe Commerce JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.adobe commerce.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
A typical connection string is below:
jdbc:adobe commerce:OAuthClientId=MyConsumerKey;OAuthClientSecret=MyConsumerSecret;CallbackURL=http://127.0.0.1:33333;Url=https://myAdobe Commercehost.com;InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH- Test the connection and finish the wizard. Select the Adobe Commerce data source and click Enable.
More JBoss Integration
The steps above show how to configure the driver in a simple connection pooling scenario. For more information, refer to the Data Source Management chapter in the JBoss EAP documentation.