Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Create AlloyDB Reports on JasperReports Server
Deploy the CData JDBC Driver on JasperReports Server to provide real-time AlloyDB data access from reports, embedded analytics, and more.
The CData JDBC Driver for AlloyDB enables you to provide access to AlloyDB data across the enterprise. This article shows how to deploy the driver on JasperReports server and create a simple report based on a reporting domain, a business view of AlloyDB data.
Deploy the Driver JAR
Follow the steps below to deploy the driver JAR on JasperReports Server. The instructions below contain specifics for AlloyDB and the Tomcat server bundled with JasperReports Server. If you are using JBoss AS 7 instead of Tomcat, you can follow the standard process to deploy the AlloyDB JDBC Driver on JBoss.
- Copy the driver JAR and .lic file, located in the lib subfolder of the installation directory, to the lib subfolder of the apache-tomcat folder, located in the JasperReports Server installation directory.
-
Navigate to apache-tomcat -> webapps -> jasperserver-pro -> META-INF and add the following resource entry to the context.xml file:
<Resource name="jdbc/alloydb" auth="Container" type="javax.sql.DataSource" driverClassName="cdata.jdbc.alloydb.AlloyDBDriver" url="jdbc:alloydb:User=alloydb;Password=admin;Database=alloydb;Server=127.0.0.1;Port=5432" maxActive="20" maxIdle="10" maxWait="-1" factory="com.jaspersoft.jasperserver.tomcat.jndi.JSCommonsBasicDataSourceFactory"/>Specify the required connection properties in the JDBC URL -- the url attribute.
The following connection properties are usually required in order to connect to AlloyDB.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the AlloyDB database.
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
You can also optionally set the following:
- Database: The database to connect to when connecting to the AlloyDB Server. If this is not set, the user's default database will be used.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the AlloyDB database. This property is set to 5432 by default.
Authenticating with Standard Authentication
Standard authentication (using the user/password combination supplied earlier) is the default form of authentication.
No further action is required to leverage Standard Authentication to connect.
Authenticating with pg_hba.conf Auth Schemes
There are additional methods of authentication available which must be enabled in the pg_hba.conf file on the AlloyDB server.
Find instructions about authentication setup on the AlloyDB Server here.
Authenticating with MD5 Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to md5.
Authenticating with SASL Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to scram-sha-256.
Authenticating with Kerberos
The authentication with Kerberos is initiated by AlloyDB Server when the ∏ is trying to connect to it. You should set up Kerberos on the AlloyDB Server to activate this authentication method. Once you have Kerberos authentication set up on the AlloyDB Server, see the Kerberos section of the help documentation for details on how to authenticate with Kerberos.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the AlloyDB JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.alloydb.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
When you configure the JDBC URL, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
-
Navigate to jasperserver-pro -> WEB-INF and add the following reference to the web.xml file:
AlloyDB data JSP jdbc/alloydb javax.sql.DataSource Container - Restart the server.
Create the AlloyDB JDBC Data Source
Follow the steps below to map the AlloyDB JDBC driver to a JDBC data source:
- Log into JasperReports Server and click Create -> Data Source.
- In the Type menu, select JNDI Data Source.
- In the Service Name box, enter the JDNI lookup defined in the resource definition in the web.xml file. In the example, the lookup is "jdbc/alloydb".
- Click Save to create the Data Source.
Create a Domain
A domain is a metadata and access-control layer that surfaces a relevant business view to report creators. Follow the steps below to select AlloyDB columns, apply filters, and execute SQL to create a domain.
- Click Create -> Domain. Enter an Id for the domain and select a save location.
- Click Browse in the Data Source section and select the AlloyDB data source you created.
- In the Domain Design section, click Create with Domain Designer.
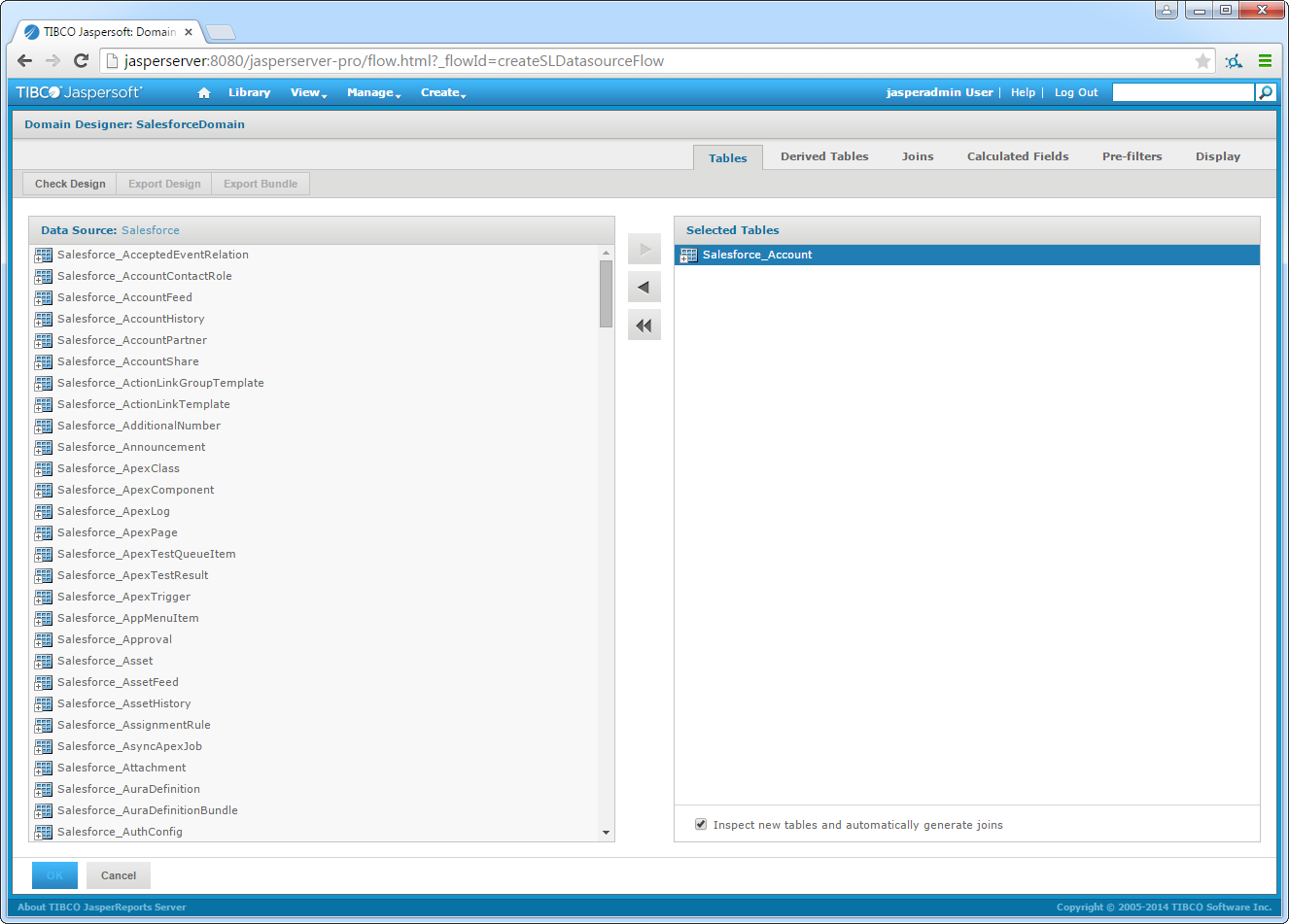
- Select the schema containing your tables.
- On the Tables tab, select a table in the Data Source pane and then click the arrow to add them to the Selected Tables pane.
![Tables to add on the Tables tab in the Domain Designer. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
- On the Derived Tables tab, you can define domains based on SQL queries. For example,
SELECT ShipName, ShipCity FROM Orders WHERE ShipCountry = 'USA'
- On the Joins tab, you can join tables by selecting the columns you want to build the join condition and selecting the join type.
- On the Pre-Filters tab, drag and drop columns to define search criteria that filters the data exposed through the domain.
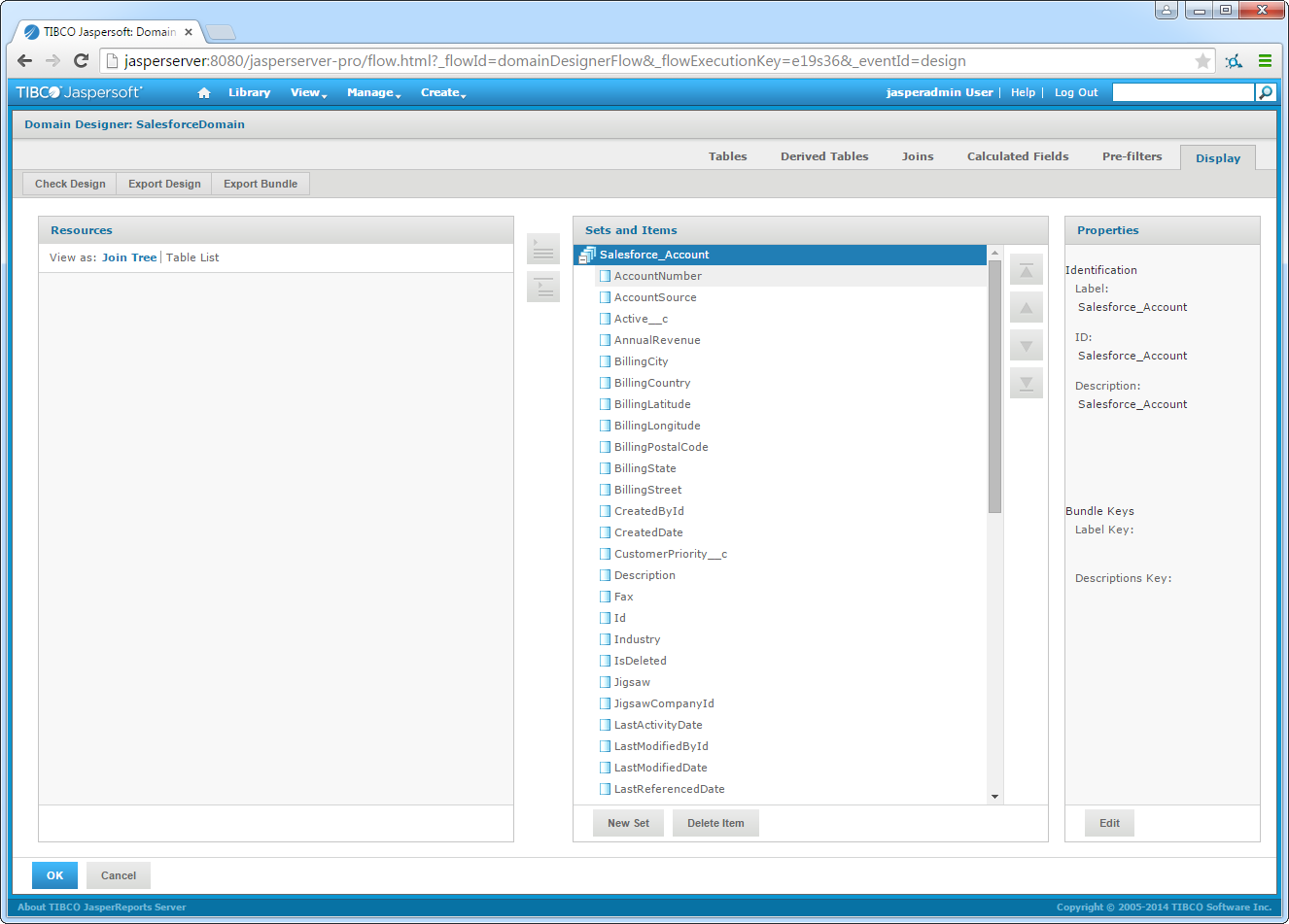
- On the Display tab, select AlloyDB data into the data sets presented to the user.
![Resources to add on the Display tab in the Domain Designer. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
- Click OK to accept your changes and click Submit to create the domain.
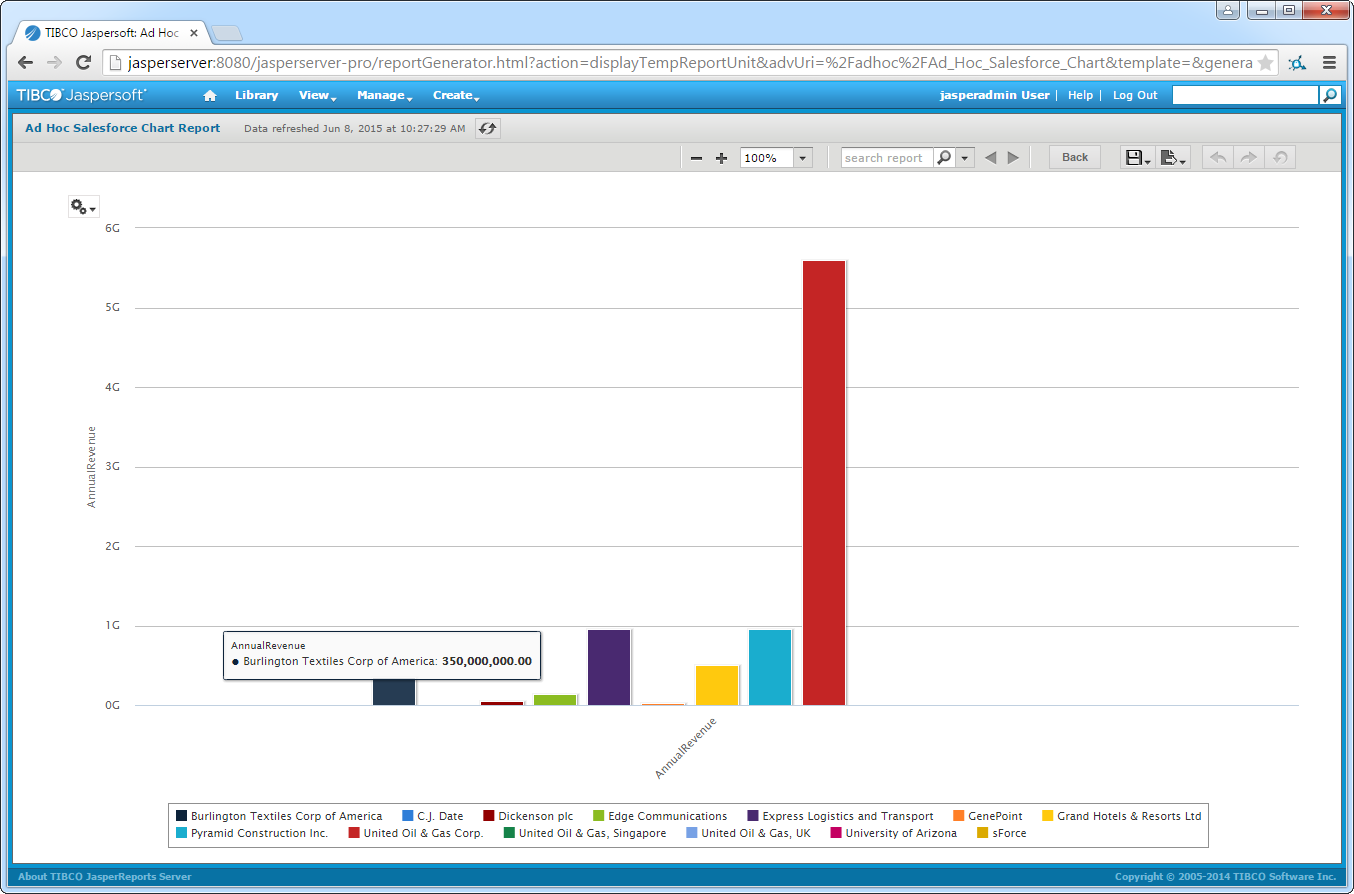
Explore Data in Real Time
After you have created a domain, you are ready to connect to data. Follow the steps below to create an Ad Hoc View in the Ad Hoc Editor.
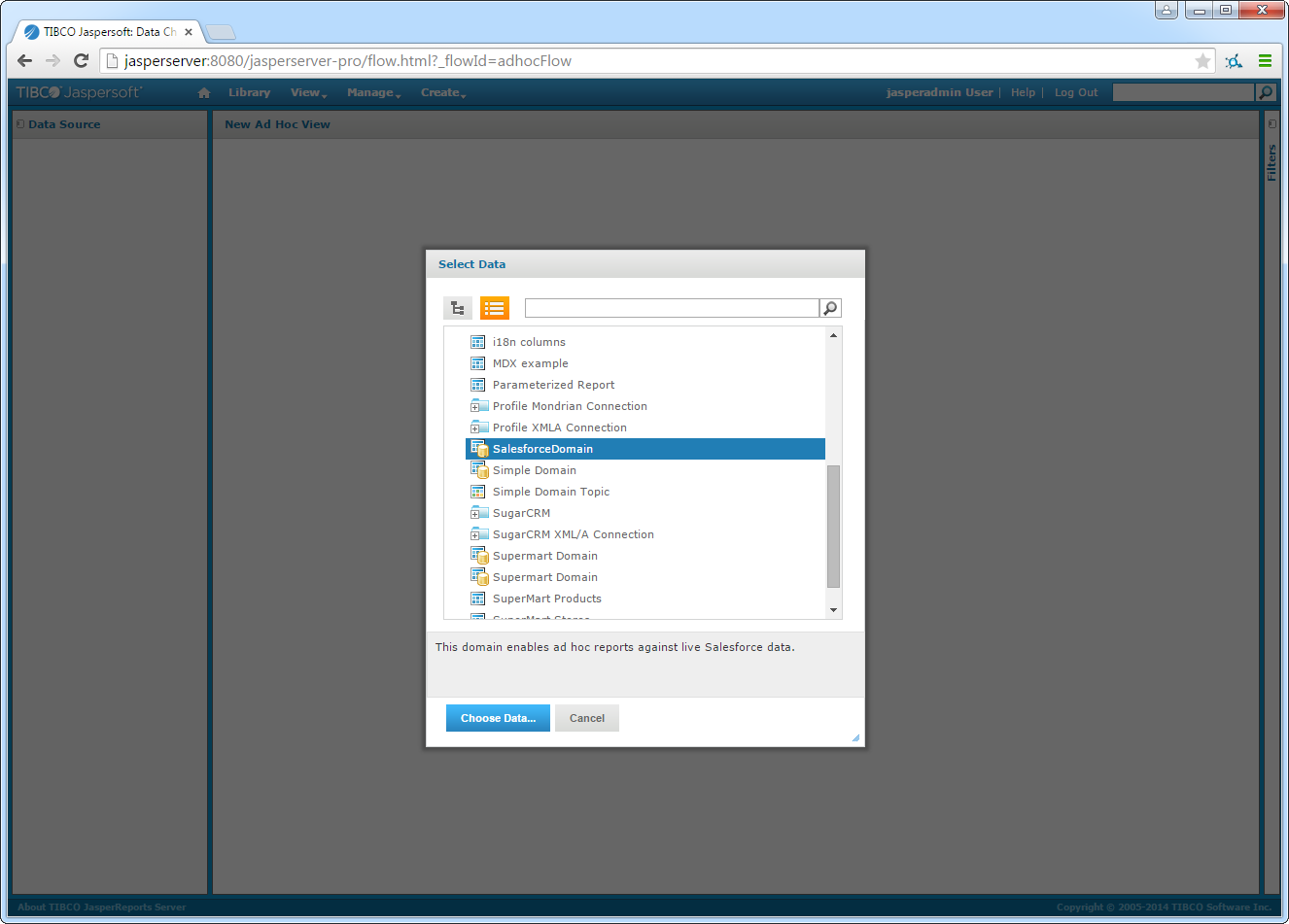
- Click Create -> Ad Hoc View.
-
In the resulting dialog, select the AlloyDB domain you created.
![The domain to be used for the view. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
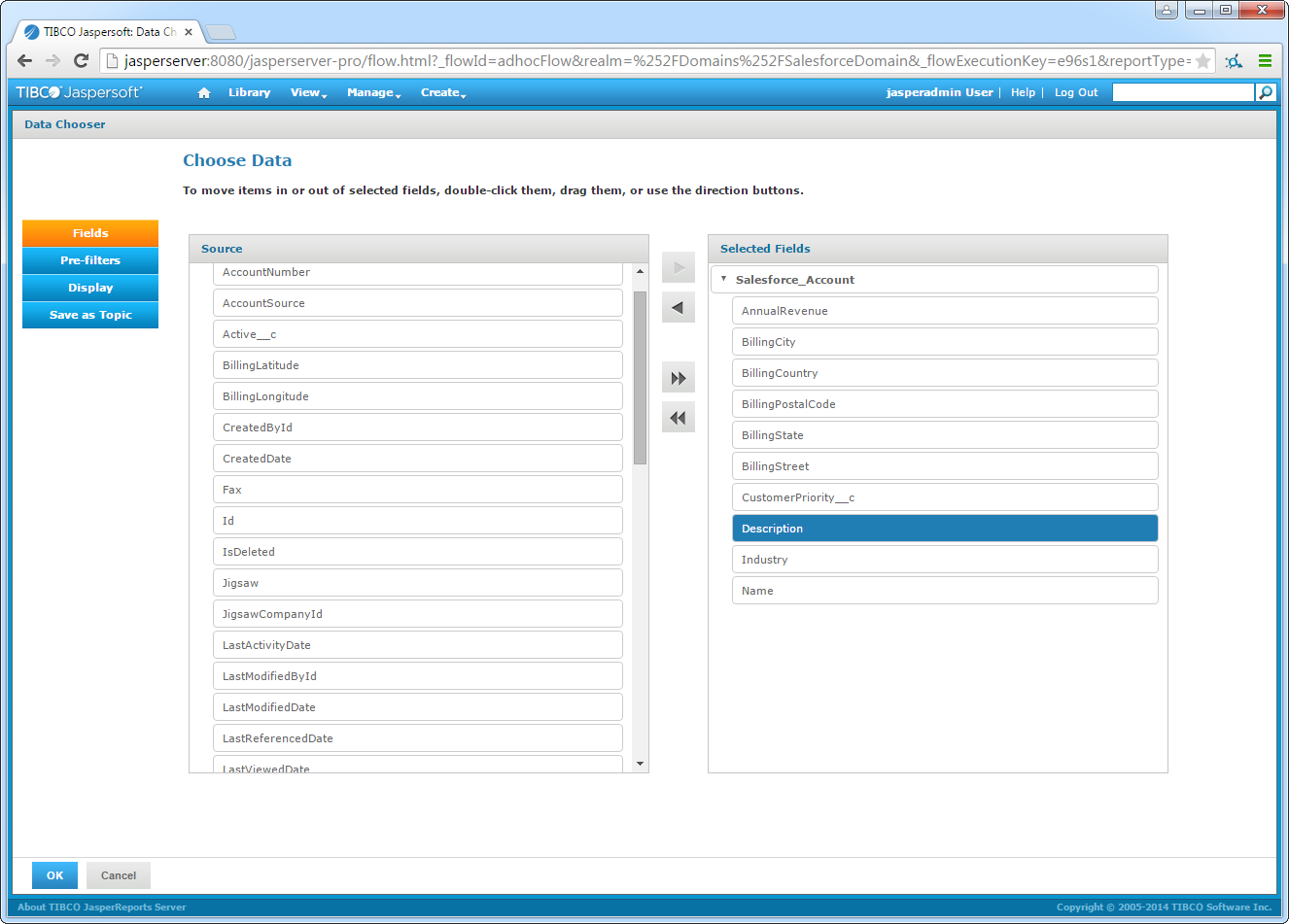
-
On the Choose Data page, select columns that you want to use in the view. In the Pre-Filters section, you can create filters based on the selected fields. In the Display section, you can modify column information as presented by the domain.
![The columns to be used in the report. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
- After completing the wizard, select the view type and add columns to the view. JasperSoft uses the metadata of the driver to detect the available dimensions and measures, based on the data type. Drag dimensions and measures onto the Columns and Rows boxes. Right-click a measure to change the summary calculation. Drag the Columns slider to the the desired data level in the Filters section.
- To access updates to the data as you design the view, change the menu selection from Sample Data to Full Data in the design mode toolbar. As you make changes, JasperSoft Server executes the underlying SQL queries to the driver.
- Save the view.
Create a Real-Time Report
You can now create reports hosted on JasperSoft Server. To do so from the Ad Hoc Editor, click Save Ad Hoc View and click Create Report.