Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Import Real-Time Cloudant Data in ColdFusion to Build Applications
Use CData JDBC drivers to import and use Cloudant data in ColdFusion.
Adobe ColdFusion is a web and mobile application development platform. It uses its own scripting language, ColdFusion Markup Language (CFML), to create data-driven websites as well as generate remote services, such as REST.
When ColdFusion is paired with the CData JDBC Driver for IBM Cloudant, you can link your ColdFusion web and mobile applications to operational Cloudant data. This allows for your applications to be more robust and complete. This article details how to use the JDBC driver to create a table populated with Cloudant data from within a ColdFusion markup file.
With built-in optimized data processing, the CData JDBC Driver offers unmatched performance for interacting with live Cloudant data. When you issue complex SQL queries to Cloudant, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to Cloudant and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations client-side (often SQL functions and JOIN operations). Its built-in dynamic metadata querying allows you to work with and analyze Cloudant data using native data types.
Configuring the Connection to Cloudant
You will need a JDBC connection string to establish a connection between Coldfusion and Cloudant.
Set the following connection properties to connect to Cloudant:
- User: Set this to your username.
- Password: Set this to your password.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Cloudant JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.cloudant.jar

Adding a Data Source and Creating a Table
After configuring the connection, follow the steps below to add the CData JDBC Driver to ColdFusion's lib directory, add a new data source, test the connection, create a ColdFusion markup file, and, finally, make a real-time connection with Cloudant data and display it in a table written in the ColdFusion Markup Language, or CFML:
-
Copy the JDBC Driver for Cloudant and lic file from "C:\Program Files\CData[product_name]\lib" to
"C:\ColdFusion2021\cfusion\wwwroot\WEB-INF\lib".
cdata.jdbc.cloudant.jar cdata.jdbc.cloudant.licNote: If you do not copy the .lic file with the jar, you will see a licensing error that indicates you do not have a valid license installed. This is true for both the trial and full versions.
-
From the ColdFusion administrator interface, choose Data & Services.
![Selecting Data & Services]()
-
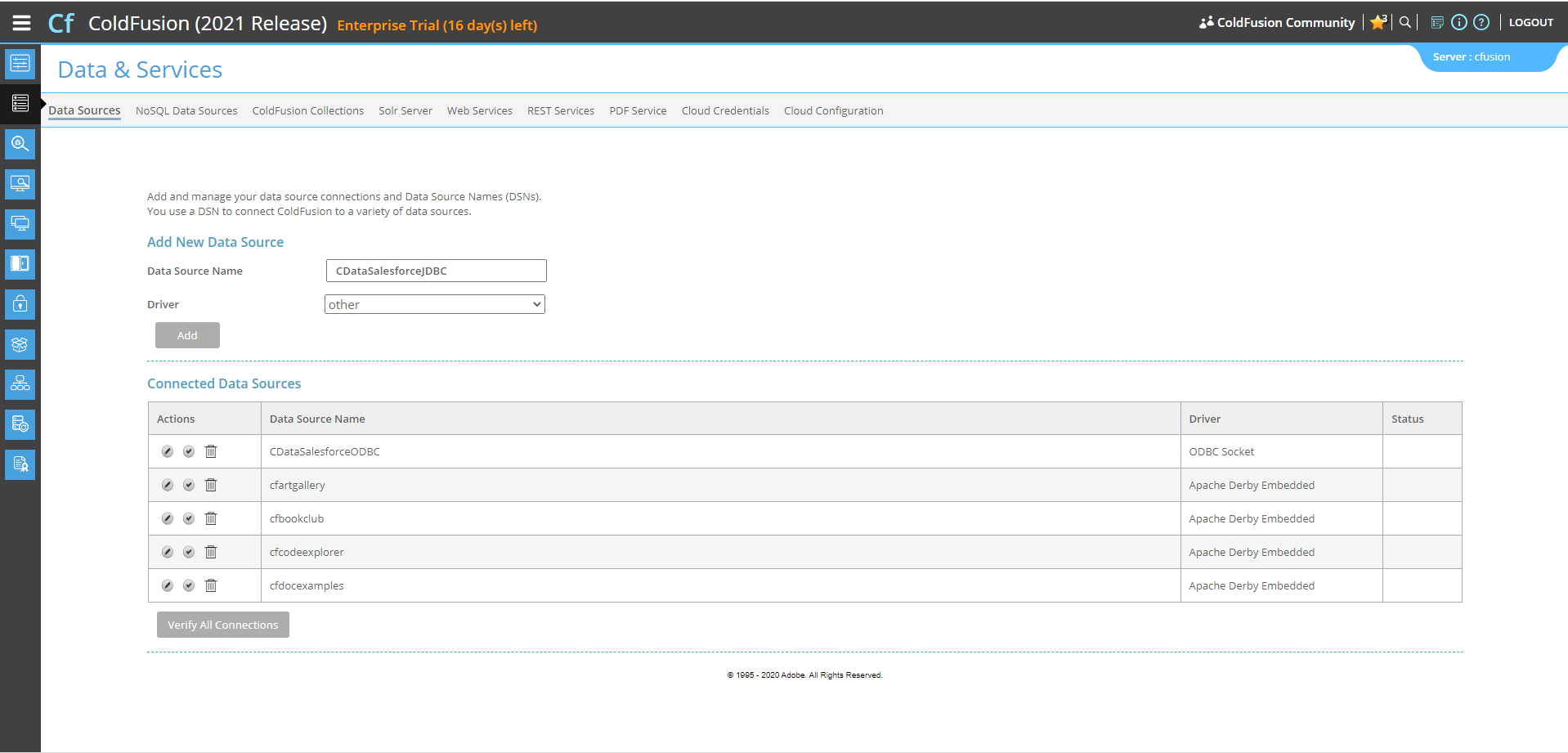
Here, we can "Add New Data Source". The data source name can be any name, provided it conforms to the ColdFusion
variable naming conventions. For our JDBC driver, choose "other", then click the "Add" button.
![Adding Data Source Name]()
-
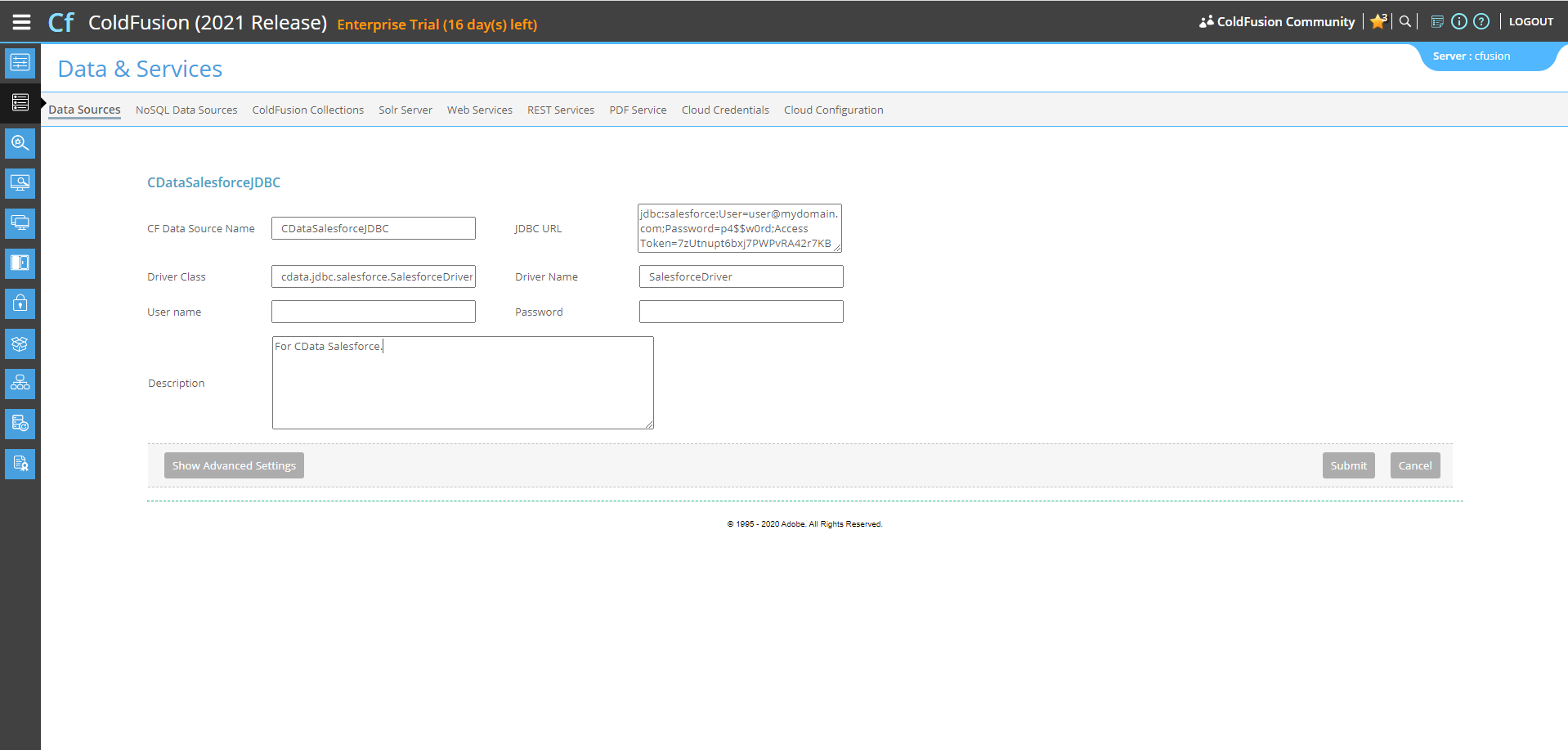
Next, populate the driver properties.
- JDBC URL will need to be in the format: jdbc:cloudant:|connectionString|.
- A typical connection string looks like this:
jdbc:cloudant:User=abc123; Password=abcdef;
- The Driver Class is: cdata.jdbc.cloudant.CloudantDriver
- The Driver Name is arbitrary and simply used to recognize the data source in the ColdFusion administration console.
![Populating driver properties]()
-
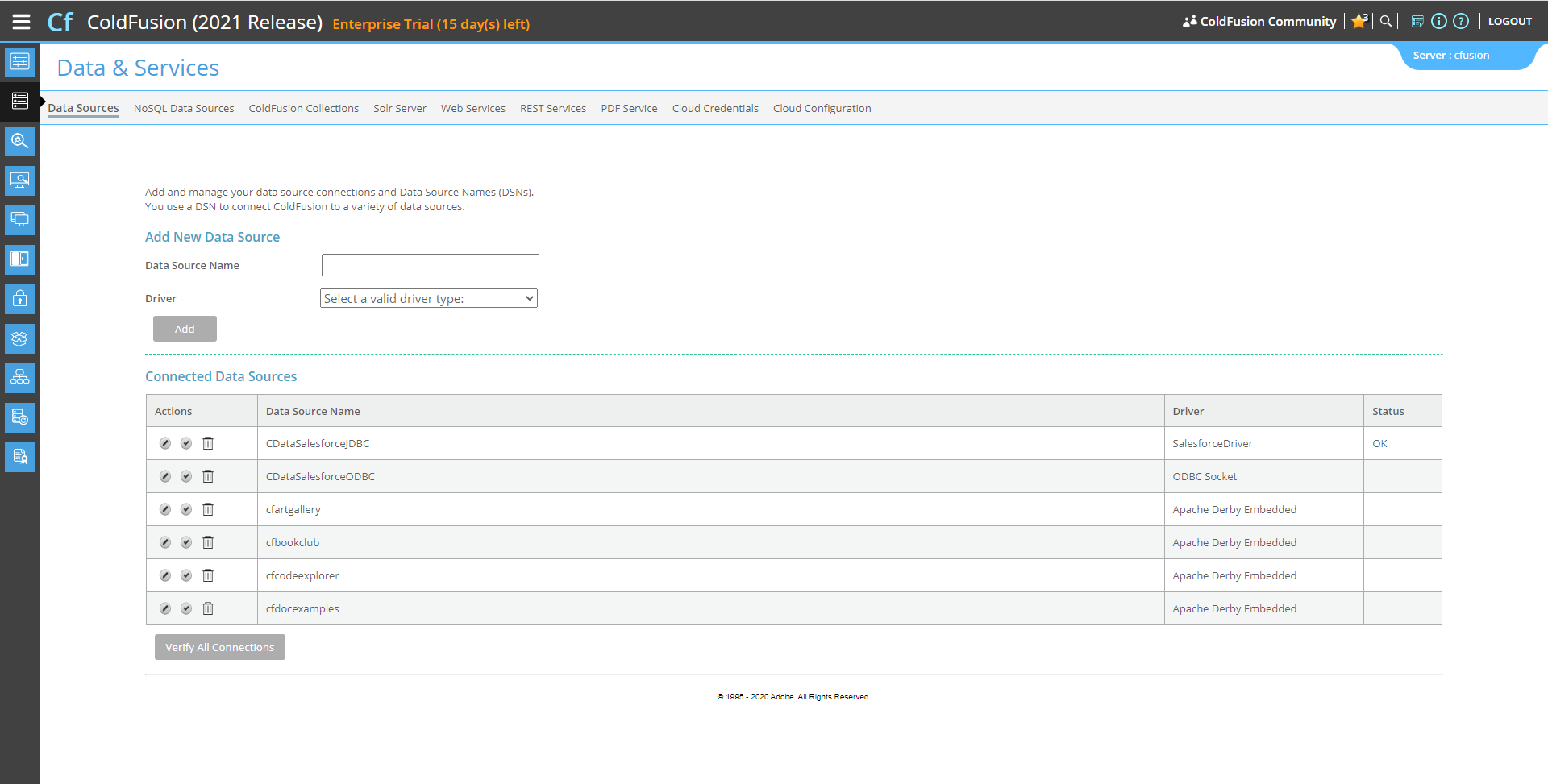
Now, test the connection by clicking the check mark to the left of the CDataCloudantJDBC data source you just created.
When the data source reports an "OK" status, it is ready for use.
![Testing the connection]()
-
Next, create a new ColdFusion Markup file (.cfm) and place it in the wwwroot directory ("C:\ColdFusion2021\cfusion\wwwroot")
for ColdFusion.
The following code queries the data source:
<cfquery name="CloudantQuery" dataSource="CDataCloudantJDBC"> SELECT * FROM Movies </cfquery>And a CFTable can be used to quickly output the table in HTML:<cftable query = "CloudantQuery" border = "1" colHeaders colSpacing = "2" headerLines = "2" HTMLTable maxRows = "500" startRow = "1"> <cfcol header="<b>MovieRuntime</b>" align="Left" width=2 text="MovieRuntime"/> <cfcol header="<b>MovieRating</b>" align="Left" width=15 text="MovieRating"/> ... </cftable>Full code, including the HTML portion is available below:<html> <head><title>CData Software | Cloudant Movies Table Demo </title></head> <body> <cfoutput>#ucase("Cloudant Movies Table Demo")#</cfoutput> <cfquery name="CloudantQuery" dataSource="CDataCloudantJDBC"> SELECT * FROM Movies </cfquery> <cftable query = "CloudantQuery" border = "1" colHeaders colSpacing = "2" headerLines = "2" HTMLTable maxRows = "500" startRow = "1"> <cfcol header="<b>MovieRuntime</b>" align="Left" width=2 text="MovieRuntime"/> <cfcol header="<b>MovieRating</b>" align="Left" width=15 text="MovieRating"/> ... </cftable> </body> </html> -
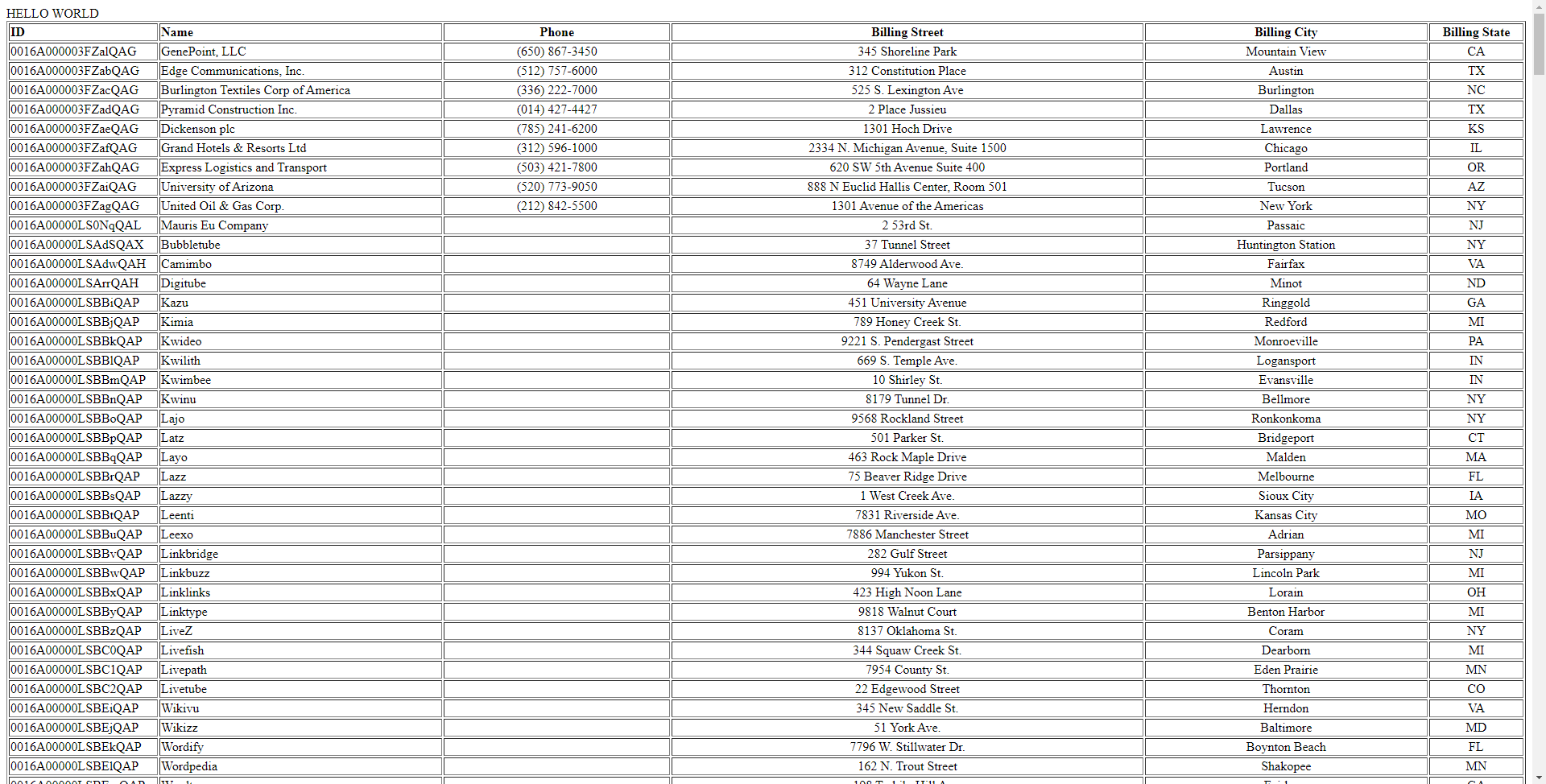
Finally, run the code locally in a browser at the default port of 8500. It produces a table populated with Cloudant data!
![Running the code]()
As a note, the CData JDBC Drivers also support parameterized queries using the cfqueryparam element.
For example:
SELECT * FROM Account WHERE name =
Get Started Today
Download a free, 30-day trial of the CData JDBC Driver for Cloudant and start building Cloudant-connected applications with Adobe ColdFusion. Reach out to our Support Team if you have any questions.