Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →LINQ to Microsoft Exchange Data
LINQ offers versatile querying capabilities within the .NET Framework (v3.0+), offering a straightforward method for programmatic data access through CData ADO.NET Data Providers. In this article, we demonstrate the use of LINQ to retrieve information from the Microsoft Exchange Data Provider.
This article illustrates using LINQ to access tables within the Microsoft Exchange via the CData ADO.NET Data Provider for Microsoft Exchange. To achieve this, we will use LINQ to Entity Framework, which facilitates the generation of connections and can be seamlessly employed with any CData ADO.NET Data Providers to access data through LINQ.
See the help documentation for a guide to setting up an EF 6 project to use the provider.
- In a new project in Visual Studio, right-click on the project and choose to add a new item. Add an ADO.NET Entity Data Model.
- Choose EF Designer from Database and click Next.
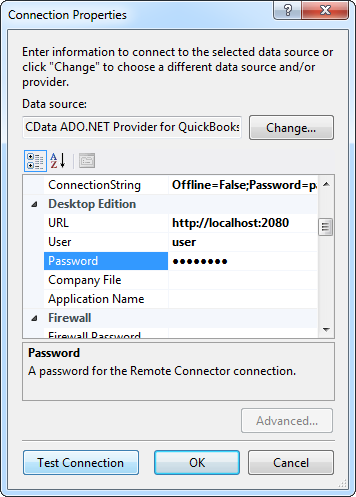
- Add a new Data Connection, and change your data source type to "CData Microsoft Exchange Data Source".
Enter your data source connection information.
Specify the User and Password to connect to Exchange. Additionally, specify the address of the Exchange server you are connecting to and the Platform associated with the server.
Below is a typical connection string:
User='myUser@mydomain.onmicrosoft.com';Password='myPassword';Server='https://outlook.office365.com/EWS/Exchange.asmx';Platform='Exchange_Online';- If saving your entity connection to App.Config, set an entity name. In this example we are setting ExchangeEntities as our entity connection in App.Config.
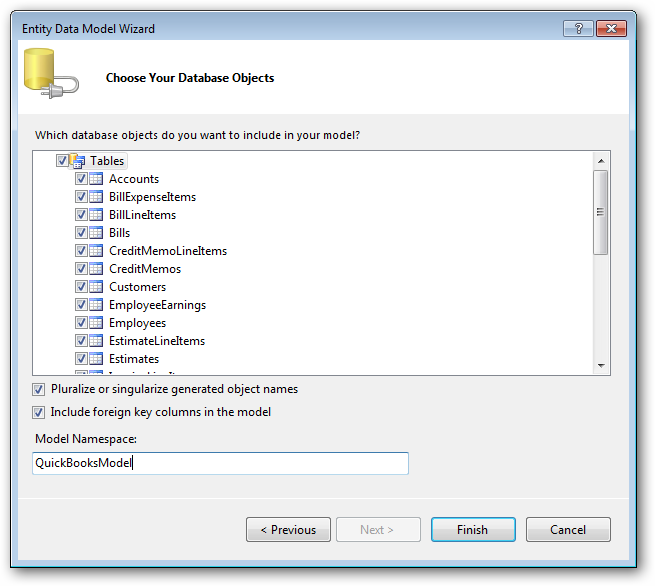
- Enter a model name and select any tables or views you would like to include in the model.
Using the entity you created, you can now perform select , update, delete, and insert commands. For example:
ExchangeEntities context = new ExchangeEntities();
var contactsQuery = from contacts in context.Contacts
select contacts;
foreach (var result in contactsQuery) {
Console.WriteLine("{0} {1} ", result.Id, result.GivenName);
}
See "LINQ and Entity Framework" chapter in the help documentation for example queries of the supported LINQ.






