Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →How to integrate Google Cloud Storage with Apache Airflow
Access and process Google Cloud Storage data in Apache Airflow using the CData JDBC Driver.
Apache Airflow supports the creation, scheduling, and monitoring of data engineering workflows. When paired with the CData JDBC Driver for Google Cloud Storage, Airflow can work with live Google Cloud Storage data. This article describes how to connect to and query Google Cloud Storage data from an Apache Airflow instance and store the results in a CSV file.
With built-in optimized data processing, the CData JDBC Driver offers unmatched performance for interacting with live Google Cloud Storage data. When you issue complex SQL queries to Google Cloud Storage, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to Google Cloud Storage and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations client-side (often SQL functions and JOIN operations). Its built-in dynamic metadata querying allows you to work with and analyze Google Cloud Storage data using native data types.
Configuring the Connection to Google Cloud Storage
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Google Cloud Storage JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.googlecloudstorage.jar
Fill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
Authenticate with a User Account
You can connect without setting any connection properties for your user credentials. After setting InitiateOAuth to GETANDREFRESH, you are ready to connect.
When you connect, the Google Cloud Storage OAuth endpoint opens in your default browser. Log in and grant permissions, then the OAuth process completes
Authenticate with a Service Account
Service accounts have silent authentication, without user authentication in the browser. You can also use a service account to delegate enterprise-wide access scopes.
You need to create an OAuth application in this flow. See the Help documentation for more information. After setting the following connection properties, you are ready to connect:
- InitiateOAuth: Set this to GETANDREFRESH.
- OAuthJWTCertType: Set this to "PFXFILE".
- OAuthJWTCert: Set this to the path to the .p12 file you generated.
- OAuthJWTCertPassword: Set this to the password of the .p12 file.
- OAuthJWTCertSubject: Set this to "*" to pick the first certificate in the certificate store.
- OAuthJWTIssuer: In the service accounts section, click Manage Service Accounts and set this field to the email address displayed in the service account Id field.
- OAuthJWTSubject: Set this to your enterprise Id if your subject type is set to "enterprise" or your app user Id if your subject type is set to "user".
- ProjectId: Set this to the Id of the project you want to connect to.
The OAuth flow for a service account then completes.

To host the JDBC driver in clustered environments or in the cloud, you will need a license (full or trial) and a Runtime Key (RTK). For more information on obtaining this license (or a trial), contact our sales team.
The following are essential properties needed for our JDBC connection.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Database Connection URL | jdbc:googlecloudstorage:RTK=5246...;ProjectId='project1';InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH |
| Database Driver Class Name | cdata.jdbc.googlecloudstorage.GoogleCloudStorageDriver |
Establishing a JDBC Connection within Airflow
- Log into your Apache Airflow instance.
- On the navbar of your Airflow instance, hover over Admin and then click Connections.
![Clicking connections]()
- Next, click the + sign on the following screen to create a new connection.
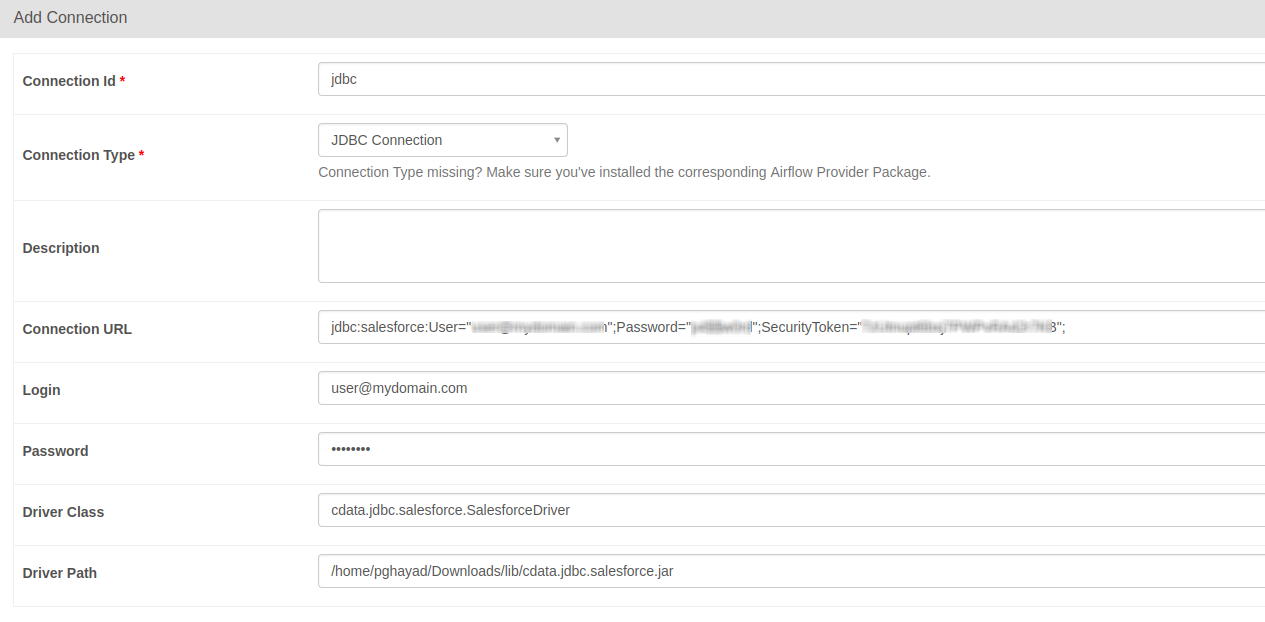
- In the Add Connection form, fill out the required connection properties:
- Connection Id: Name the connection, i.e.: googlecloudstorage_jdbc
- Connection Type: JDBC Connection
- Connection URL: The JDBC connection URL from above, i.e.: jdbc:googlecloudstorage:RTK=5246...;ProjectId='project1';InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH)
- Driver Class: cdata.jdbc.googlecloudstorage.GoogleCloudStorageDriver
- Driver Path: PATH/TO/cdata.jdbc.googlecloudstorage.jar
![Add JDBC connection form]()
- Test your new connection by clicking the Test button at the bottom of the form.
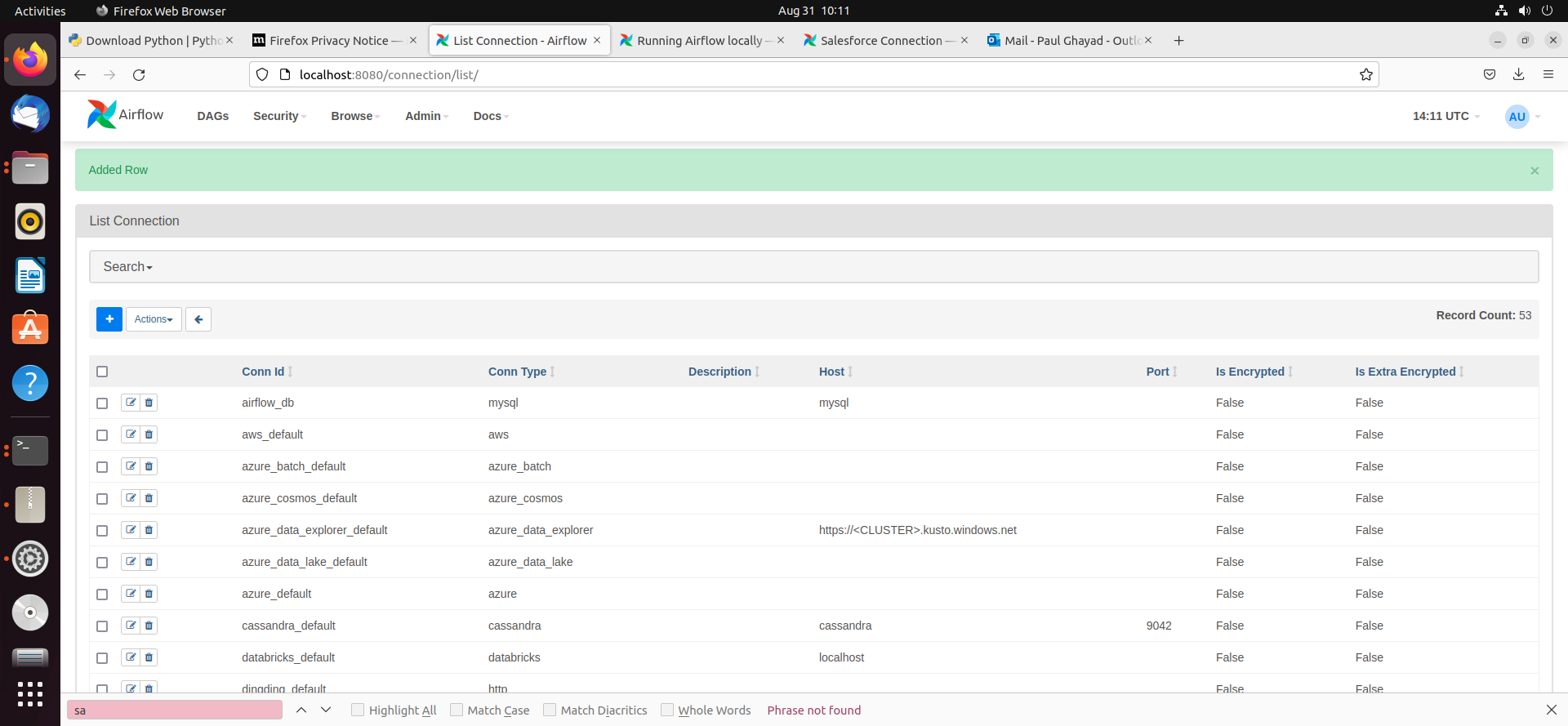
- After saving the new connection, on a new screen, you should see a green banner saying that a new row was added to the list of connections:
![New connection added]()
Creating a DAG
A DAG in Airflow is an entity that stores the processes for a workflow and can be triggered to run this workflow. Our workflow is to simply run a SQL query against Google Cloud Storage data and store the results in a CSV file.
- To get started, in the Home directory, there should be an "airflow" folder. Within there, we can create a new directory and title it "dags". In here, we store Python files that convert into Airflow DAGs shown on the UI.
- Next, create a new Python file and title it google cloud storage_hook.py. Insert the following code inside of this new file:
import time from datetime import datetime from airflow.decorators import dag, task from airflow.providers.jdbc.hooks.jdbc import JdbcHook import pandas as pd # Declare Dag @dag(dag_id="google cloud storage_hook", schedule_interval="0 10 * * *", start_date=datetime(2022,2,15), catchup=False, tags=['load_csv']) # Define Dag Function def extract_and_load(): # Define tasks @task() def jdbc_extract(): try: hook = JdbcHook(jdbc_conn_id="jdbc") sql = """ select * from Account """ df = hook.get_pandas_df(sql) df.to_csv("/{some_file_path}/{name_of_csv}.csv",header=False, index=False, quoting=1) # print(df.head()) print(df) tbl_dict = df.to_dict('dict') return tbl_dict except Exception as e: print("Data extract error: " + str(e)) jdbc_extract() sf_extract_and_load = extract_and_load() - Save this file and refresh your Airflow instance. Within the list of DAGs, you should see a new DAG titled "google cloud storage_hook".
![New DAG added]()
- Click on this DAG and, on the new screen, click on the unpause switch to make it turn blue, and then click the trigger (i.e. play) button to run the DAG. This executes the SQL query in our google cloud storage_hook.py file and export the results as a CSV to whichever file path we designated in our code.
![Run the DAG]()
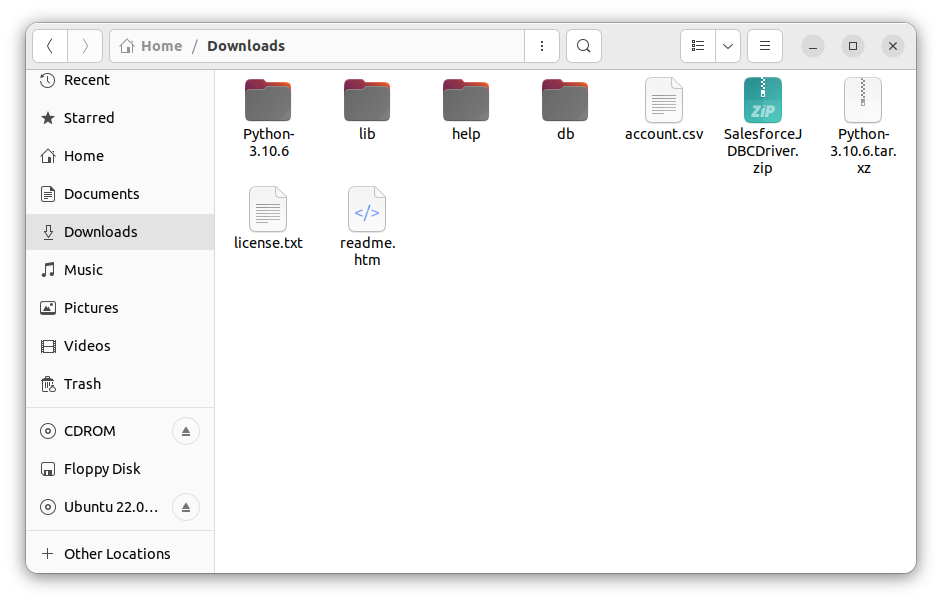
- After triggering our new DAG, we check the Downloads folder (or wherever you chose within your Python script), and see that the CSV file has been created - in this case, account.csv.
![CSV created]()
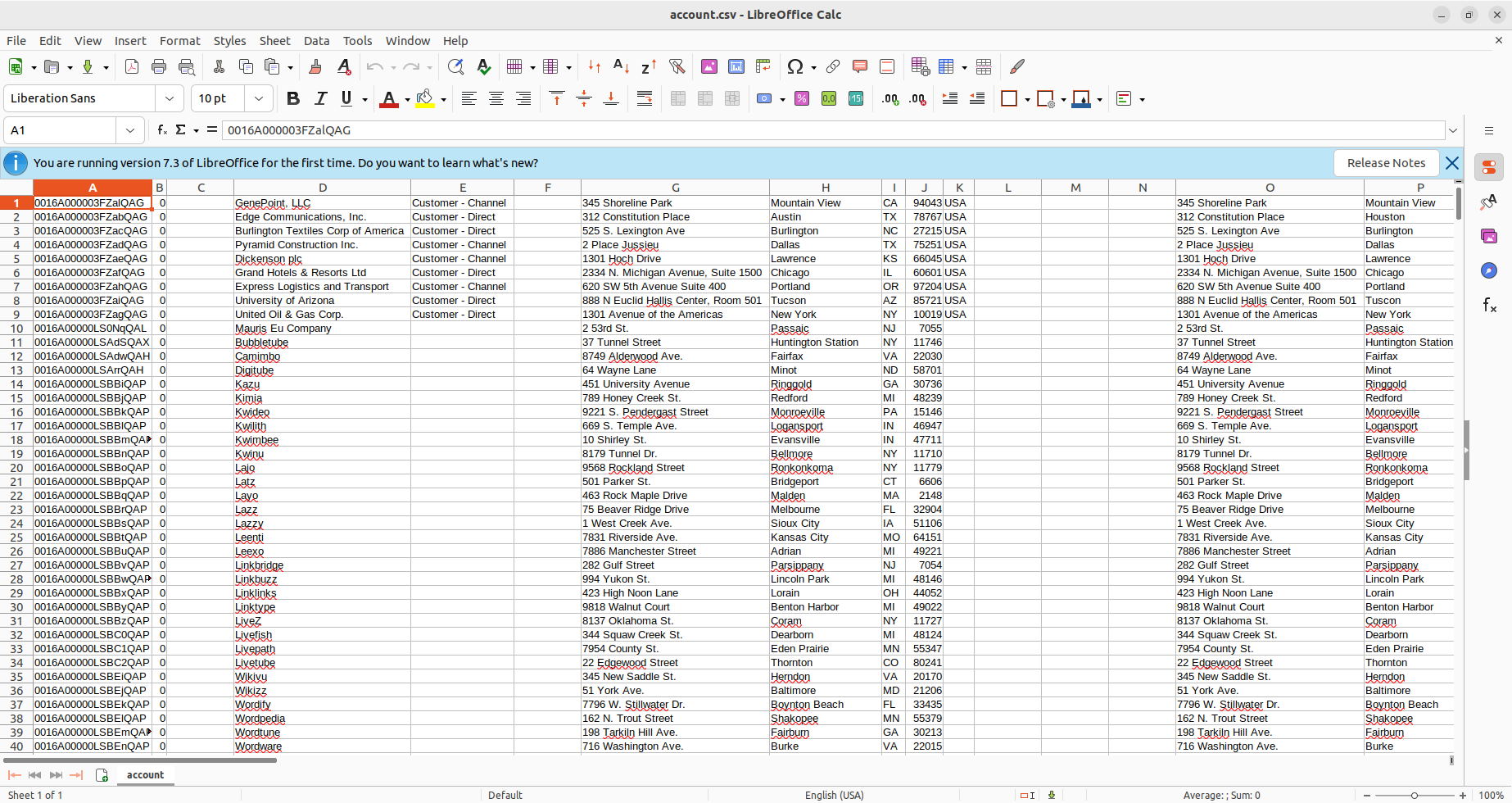
- Open the CSV file to see that your Google Cloud Storage data is now available for use in CSV format thanks to Apache Airflow.
![CSV file with Google Cloud Storage data.]()