Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →How to connect to HDFS Data from Spring Boot
Connect to HDFS in a Spring Boot Application using CData JDBC HDFS Driver
Spring Boot is a framework that makes engineering Java web applications easier. It offers the ability to create standalone applications with minimal configuration. When paired with the CData JDBC driver for HDFS, Spring Boot can work with live HDFS data. This article shows how to configure data sources and retrieve data in your Java Spring Boot Application, using the CData JDBC Driver for HDFS.
With built-in optimized data processing, the CData JDBC Driver offers unmatched performance for interacting with live HDFS data. When you issue complex SQL queries to HDFS, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to HDFS and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations client-side (often SQL functions and JOIN operations). Its built-in dynamic metadata querying allows you to work with and analyze HDFS data using native data types.
Creating the Spring Boot Project in Java
In an IDE (in this tutorial, we use IntelliJ), choose a Maven project:
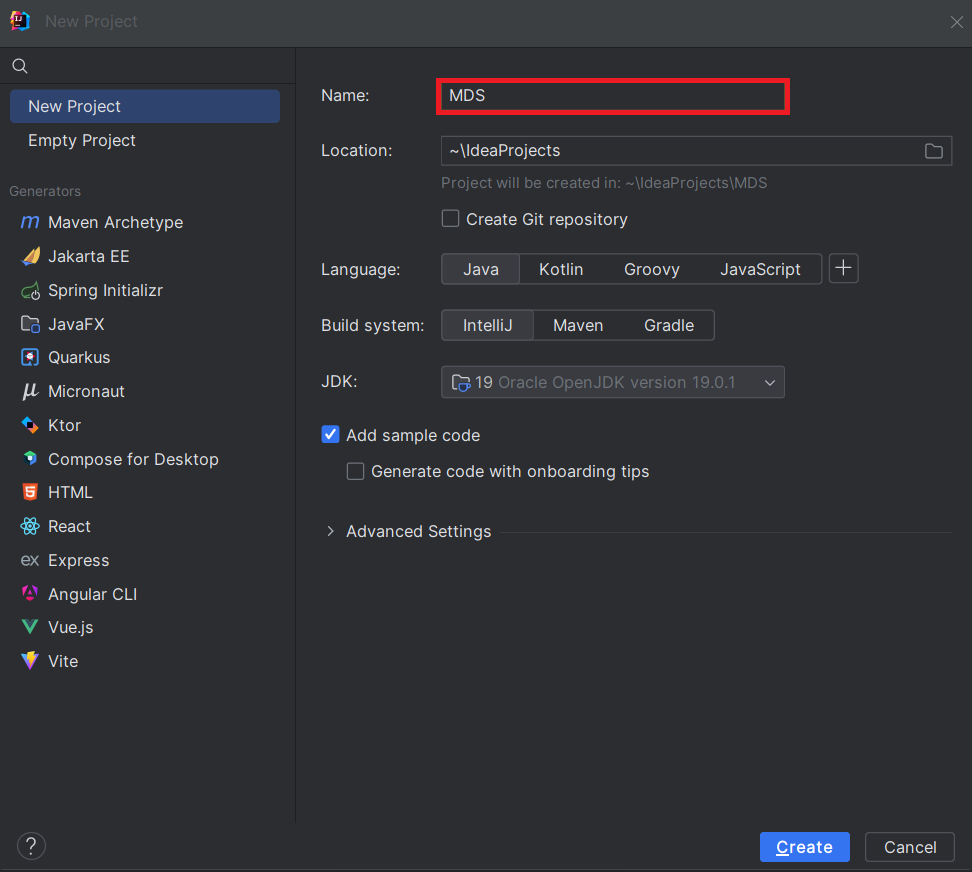 In the generated project, go to the pom.xml file, and add the required dependencies for Spring Boot:
In the generated project, go to the pom.xml file, and add the required dependencies for Spring Boot:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.2</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>demo</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-install-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.5.1</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>id.install-file</id>
<phase>clean</phase>
<goals>
<goal>install-file</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<file>C:\Program Files\CData[product_name] ####\lib\cdata.jdbc.hdfs.jar</file>
<groupId>org.cdata.connectors</groupId>
<artifactId>cdata-hdfs-connector</artifactId>
<version>23</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>2.7.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.cdata.connectors</groupId>
<artifactId>cdata-hdfs-connector</artifactId>
<version>23</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<distributionManagement>
<repository>
<uniqueVersion>false</uniqueVersion>
<id>test</id>
<name>My Repository</name>
<url>scp://repo/maven2</url>
<layout>default</layout>
</repository>
</distributionManagement>
</project>
Note: The year (####) and the version number (as seen in the provided XML script) should be adjusted according to the current version of the CData JDBC driver being utilized.
Project Structure
In the java directory, create a new package. Usually the name of the package is the name of the groupId
(com.example) followed by the artifactId (.MDS).
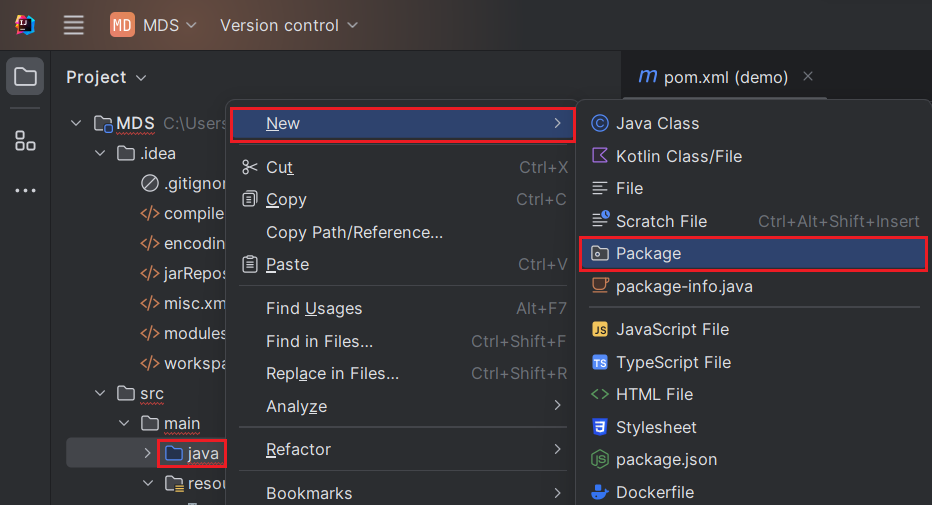
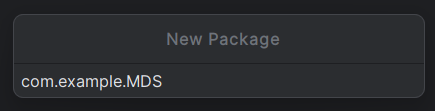
Mark the "java" directory as the "Sources Root" (denoted by a blue color). To do this, right-click the java directory and choose Mark Directory as -> Sources Root (As shown below). Additionally, mark the "resources" directory as the "Resources Root."
Store Database Connection Properties
Create an "application.properties" file to store the database connection properties. To do this, right-click on the "resources" folder, opt for New -> File, input the file name as "application.properties," and press Enter.
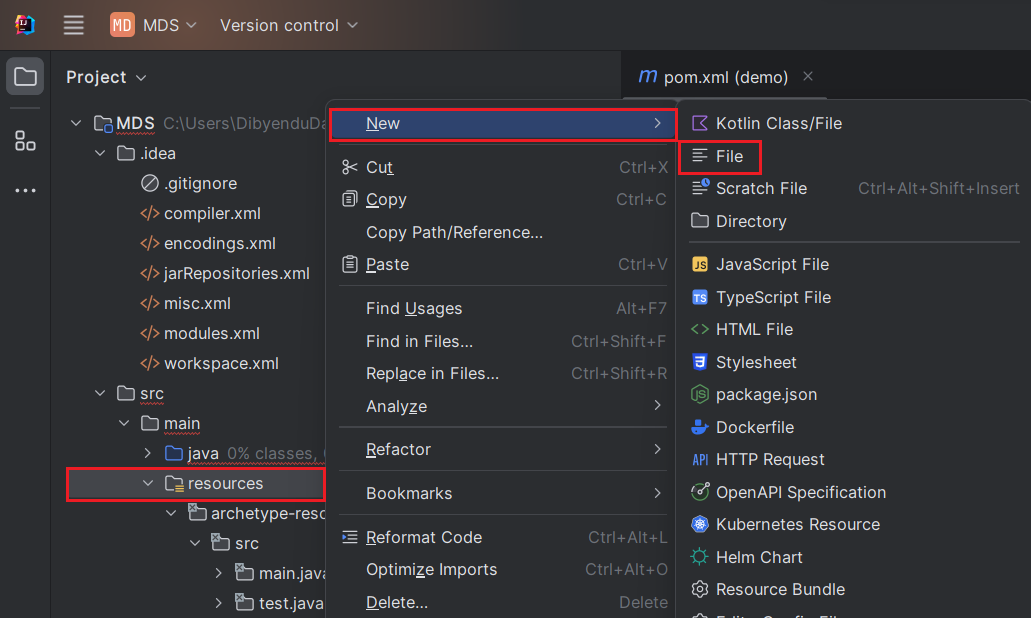
In the application.properties file, we set the configuration properties for the HDFS JDBC Driver, using the Class name and JDBC URL:
spring.datasource.driver=cdata.jdbc.hdfs.HDFSDriver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:hdfs:Host=sandbox-hdp.hortonworks.com;Port=50070;Path=/user/root;User=root;
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the HDFS JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.hdfs.jar
In order to authenticate, set the following connection properties:
- Host: Set this value to the host of your HDFS installation.
- Port: Set this value to the port of your HDFS installation. Default port: 50070

After setting the properties in the application.properties file, we now configure them.
Data Source Configuration
First, we mark the HDFS data source as our primary data source. Then, we create a Data Source Bean.
Create a DriverManagerDataSource.java file and create a Bean within it, as shown below. If @Bean gives an error, Spring Boot may not have loaded properly. To fix this, go to File -> Invalidate Caches and restart. Additionally, make sure that Maven has added the Spring Boot dependencies.
To create a data source bean, we use the DriverManagerDataSource Class. This class allows us to set
the properties of the data source. To create this Java class, right-click on "com.example.MDS" package, and choose New -> Java Class.
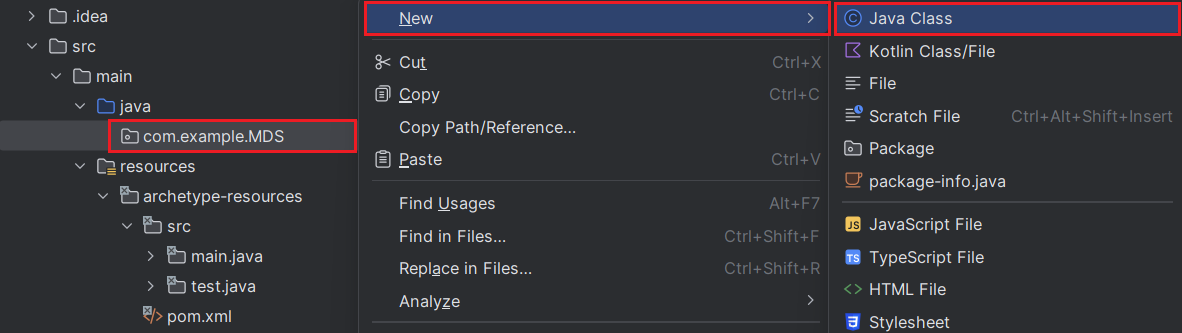
The following code shows the bean definition of our data source. Each driver should have a bean.
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
public class DriverManagerDataSource{
@Autowired
private static Environment env;
@Bean(name ="HDFS")
@Primary
public static DataSource HDFSDataSource()
{
DataSourceBuilder<?> dataSourceBuilder = DataSourceBuilder.create();
dataSourceBuilder.driverClassName("cdata.jdbc.hdfs.HDFSDriver");
dataSourceBuilder.url("jdbc:hdfs:Host=sandbox-hdp.hortonworks.com;Port=50070;Path=/user/root;User=root;");
return dataSourceBuilder.build();
}
//@Override
public void setEnvironment( final Environment environment) {
env=environment;
}
}
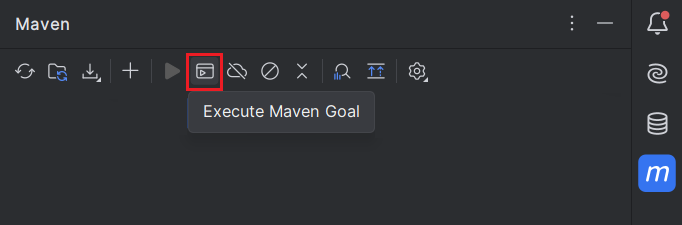
Next, move the HDFS jar file to the Documents folder (see path in command below) - The idea is to have a path without any spaces for the jar file. Then, click the
Maven icon (top right corner of IntelliJ) and click "Execute Maven Goal." Now, run the following command:

mvn install:install-file "-Dfile=C:\Program Files\CData[product_name] ####\lib\cdata.jdbc.hdfs.jar" -DgroupId=org.cdata.connectors -DartifactId=cdata-hdfs-connector -Dversion=23 -Dpackaging=jar
Follow either of the given steps to run this command:
- The "-Dfile location" can be kept as the default installation path of the CData JDBC Driver. Make sure to keep the path in quotations in this case. Also, change the year and "Dversion" based on the current version of the driver being used.
- As mentioned earlier in the article, in case you relocate the
jar file to the Documents folder, make sure to modify the path in the provided command. In such instances, avoid enclosing the Dfile location in quotations and edit "Dversion" based on the current version of the driver being used.
After pressing enter, we see the following output:
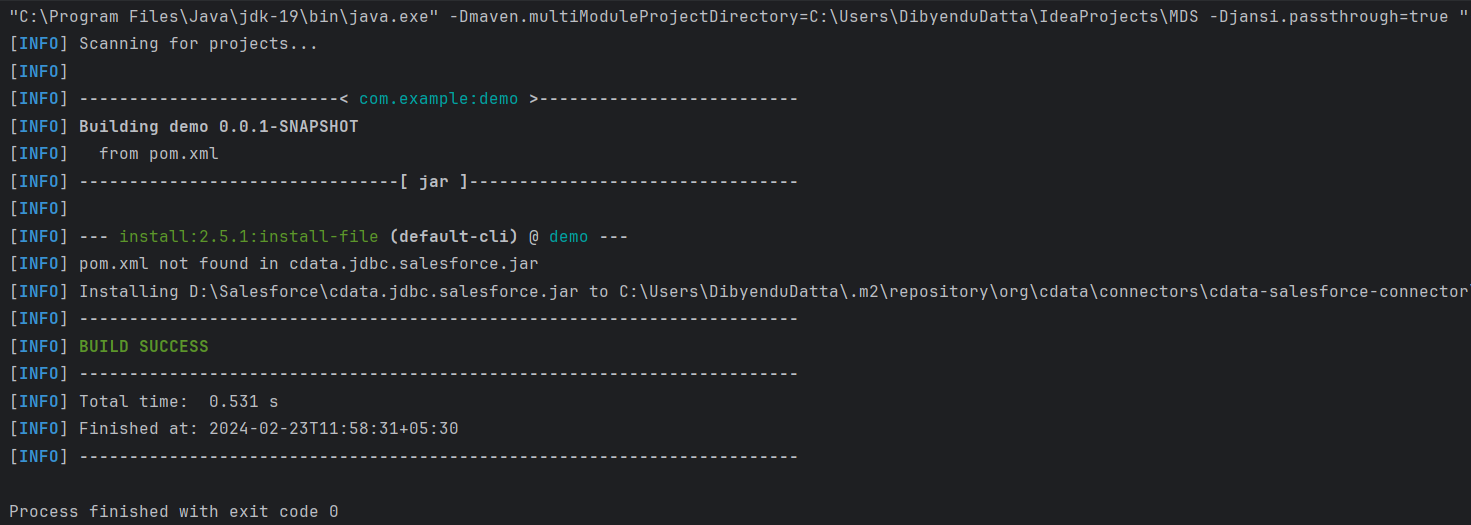
Testing the Connection
The last step is testing the connection. Create a new Java class following the format
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import static com.example.demo.DriverManagerDataSources.HDFSDataSource;
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
public class MDSApplication {
//remove the comment on the line below
public static void main (){
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
Connection conn = HDFSDataSource().getConnection();
System.out.println("Catalog: "+ conn.getCatalog());
}
}
The output generated should look like this:
Free Trial & More Information
Download a free, 30-day trial of the CData JDBC Driver for HDFS and start working with your live HDFS in Spring Boot.






