Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →How to Connect to & Open SAP Ariba Source Data in Microsoft Excel
This article uses the CData ODBC driver for SAP Ariba Source to import data in Excel with Microsoft Query. This article also demonstrates how to use parameters with Microsoft Query.
The CData ODBC driver for SAP Ariba Source uses the standard ODBC interface to link SAP Ariba Source data with applications like Microsoft Access and Excel. Follow the steps below to use Microsoft Query to import SAP Ariba Source data into a spreadsheet and provide values to a parameterized query from cells in a spreadsheet.
If you have not already, first specify connection properties in an ODBC DSN (data source name). This is the last step of the driver installation. You can use the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure ODBC DSNs.
In order to connect with SAP Ariba Source, set the following:
- API: Specify which API you would like the provider to retrieve SAP Ariba data from. Select the Supplier, Sourcing Project Management, or Contract API based on your business role (possible values are SupplierDataAPIWithPaginationV4, SourcingProjectManagementAPIV2, or ContractAPIV1).
- DataCenter: The data center where your account's data is hosted.
- Realm: The name of the site you want to access.
- Environment: Indicate whether you are connecting to a test or production environment (possible values are TEST or PRODUCTION).
If you are connecting to the Supplier Data API or the Contract API, additionally set the following:
- User: Id of the user on whose behalf API calls are invoked.
- PasswordAdapter: The password associated with the authenticating User.
If you're connecting to the Supplier API, set ProjectId to the Id of the sourcing project you want to retrieve data from.
Authenticating with OAuth
After setting connection properties, you need to configure OAuth connectivity to authenticate.
- Set AuthScheme to OAuthClient.
- Register an application with the service to obtain the APIKey, OAuthClientId and OAuthClientSecret.
For more information on creating an OAuth application, refer to the Help documentation.
Automatic OAuth
After setting the following, you are ready to connect:
-
APIKey: The Application key in your app settings.
OAuthClientId: The OAuth Client Id in your app settings.
OAuthClientSecret: The OAuth Secret in your app settings.
When you connect, the provider automatically completes the OAuth process:
- The provider obtains an access token from SAP Ariba and uses it to request data.
- The provider refreshes the access token automatically when it expires.
- The OAuth values are saved in memory relative to the location specified in OAuthSettingsLocation.
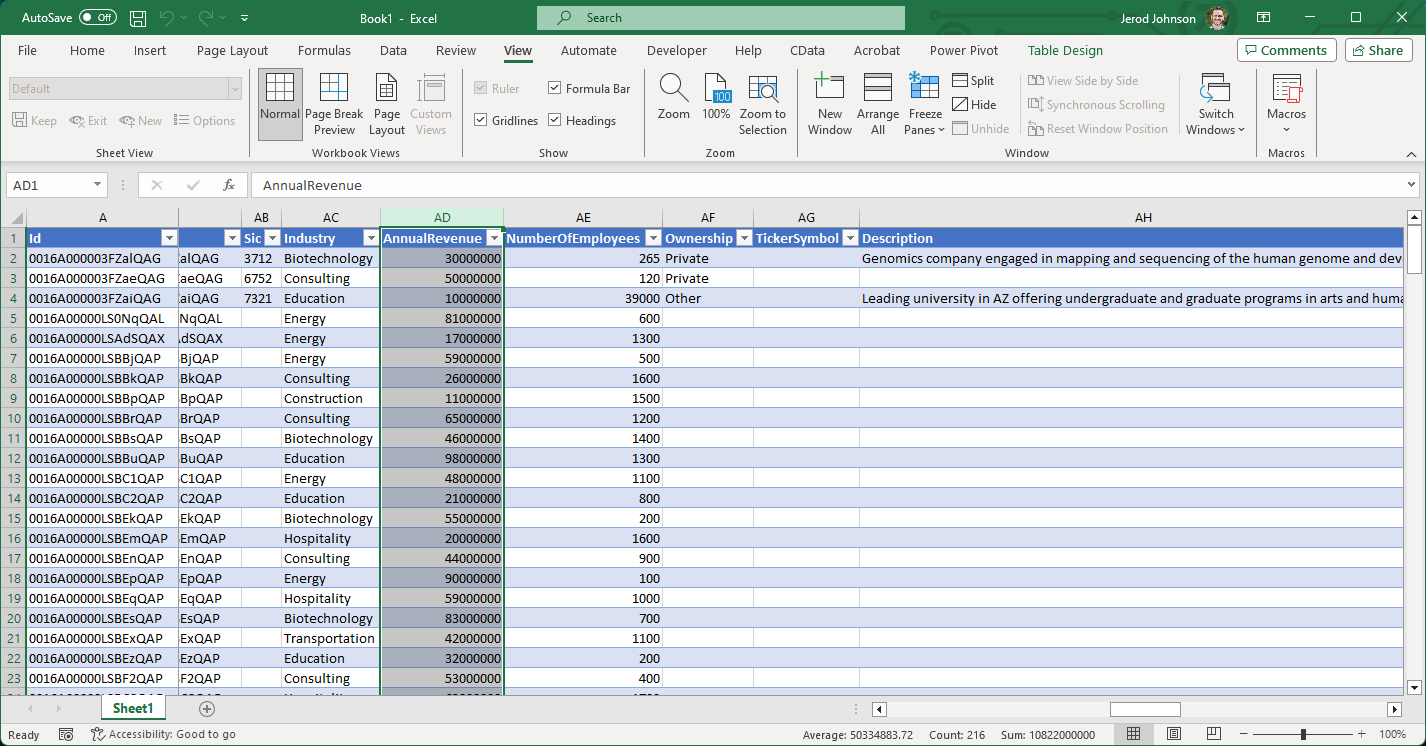
You can then work with live SAP Ariba Source data in Excel.
- In Excel, open the Data tab and choose Get Data -> From Other Sources -> From Microsoft Query.
![Open Microsoft Query from the Data tab.]()
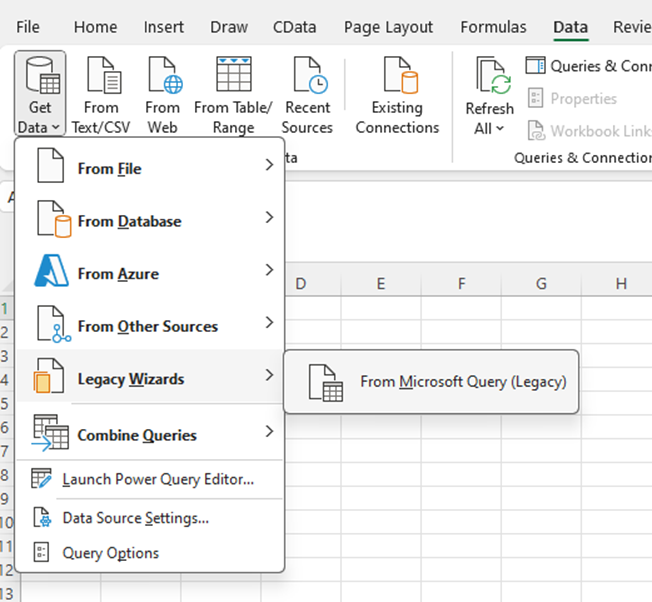
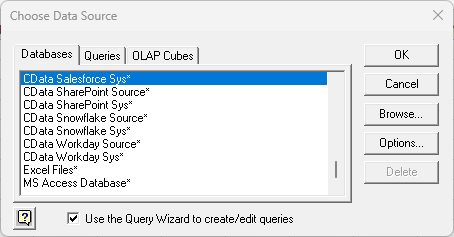
- Choose the SAPAribaSource DSN. Select the option to use Query Wizard to create/edit queries.
![The list of available ODBC DSNs in the Choose Data Source dialog.]()
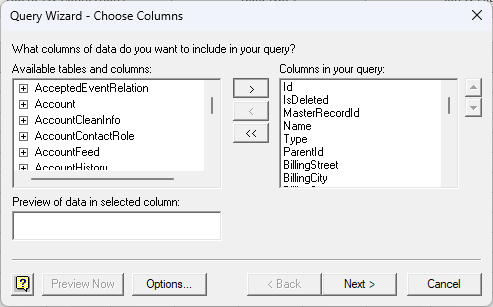
- In the Query Wizard, expand the node for the table you would like to import into your spreadsheet. Select the columns you want to import and click the arrow to add them to your query. Alternatively, select the table name to add all columns for that table.
![Available tables and columns in the Choose Columns step of the Query Wizard. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
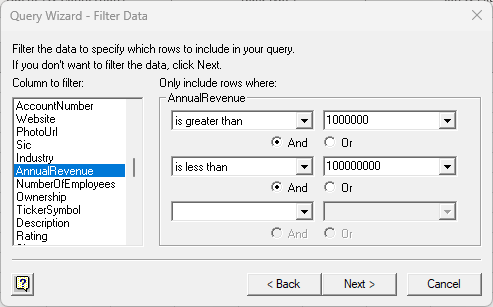
- The Filter Data page allows you to specify criteria. For example, you can limit results by setting a date range.
![The Filter Data step of the Query Wizard. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
- If you want to use parameters in your query, select the option to edit the query in Microsoft Query.
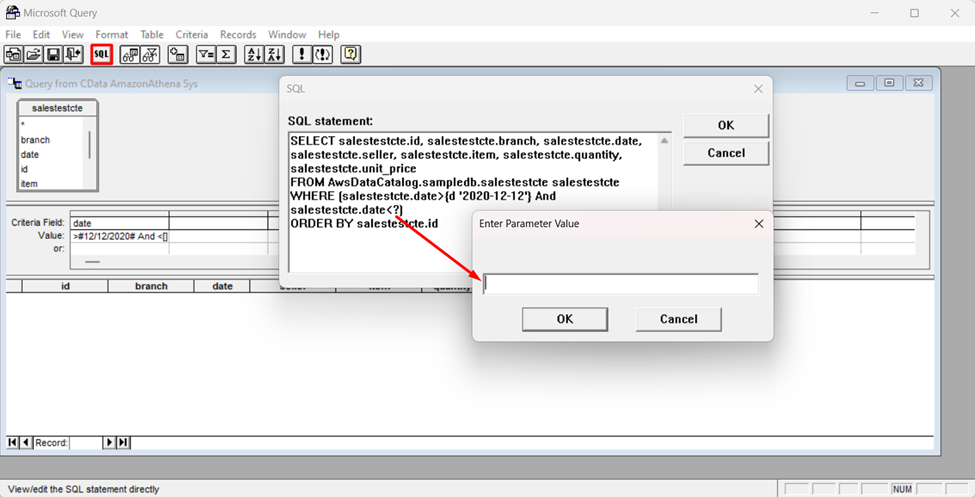
To set a parameter in the query, you will need to modify the SQL statement directly. To do this, click the SQL button in the Query Editor. If you set filter criteria earlier, you should have a WHERE clause already in the query.
To use a parameter, use a "?" character as the wildcard character for a field's value in the WHERE clause. For example, if you are importing the Vendors, you can set "Region=?".
- Close the SQL dialog when you are finished editing the SQL statement. You will be prompted to enter a parameter value. In the next step, you will select a cell to provide this value. So, leave the box in the dialog blank.
![The generated SQL statement. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
-
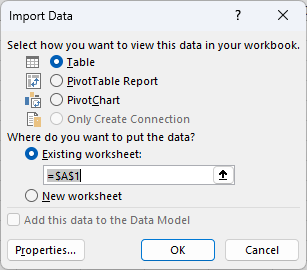
Click File -> Return Data to Microsoft Excel. The Import Data dialog is displayed. Enter a cell where results should be imported.
![The Import Data dialog.]()
- Close the Import Data dialog. You will be prompted to enter a parameter value. Click the button next to the parameter box to select a cell. Select the option to automatically refresh the spreadsheet when the value changes.