Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Replicate SAP ByDesign Data to Multiple Databases
Replicate SAP ByDesign data to disparate databases with a point-and-click configuration.
Always-on applications rely on automatic failover capabilities and real-time access to data. CData Sync integrates live SAP ByDesign data into your mirrored databases, always-on cloud databases, and other databases such as your reporting server: Automatically synchronize with remote SAP ByDesign data from Windows.
Configure Replication Destinations
Using CData Sync, you can replicate SAP ByDesign data to any number of databases, both cloud-based and on-premises. To add a replication destination, navigate to the Connections tab.
For each destination database:
- Click Add Connection.
- Select a destination. In this article, we use SQLite.
![Configure a Destination connection.]()
- Enter the necessary connection properties. To replicate SAP ByDesign to a SQLite database, enter a file path in the Data Source box.
- Click Test Connection to ensure that the connection is configured properly.
![Configure a Destination connection (SQLite is shown).]()
- Click Save Changes.
Configure the SAP ByDesign Connection
You can configure a connection to SAP ByDesign from the Connections tab. To add a connection to your SAP ByDesign account, navigate to the Connections tab.
- Click Add Connection.
- Select a source (SAP ByDesign).
- Configure the connection properties.
Set the following connection properties to connect to SAP ByDesign.
- Url: Set this to the Url of your SAP ByDesign site. For example, https://test.sapbydesign.com
- User: Set this to the username of your account.
- Password: Set this to the password of your account.
- CustomService or AnalyticsService: Only one of these must be specified. If you have a custom service you want to retrieve data from, specify CustomService. If you want to retrieve the reports of a analytical service, specify AnalyticsService.
If neither is specified, 'cc_home_analytics.svc' will used as a default for the AnalyticsService property. If you are not sure what service to specify, you can always query the Services view to list available services.
![Configure a Source connection (Salesforce is shown).]()
- Click Connect to ensure that the connection is configured properly.
- Click Save Changes.
Configure Replication Queries
CData Sync enables you to control replication with a point-and-click interface and with SQL queries. For each replication you wish to configure, navigate to the Jobs tab and click Add Job. Select the Source and Destination for your replication.
Replicate Entire Tables
To replicate an entire table, click Add Tables in the Tables section, choose the table(s) you wish to replicate, and click Add Selected Tables.
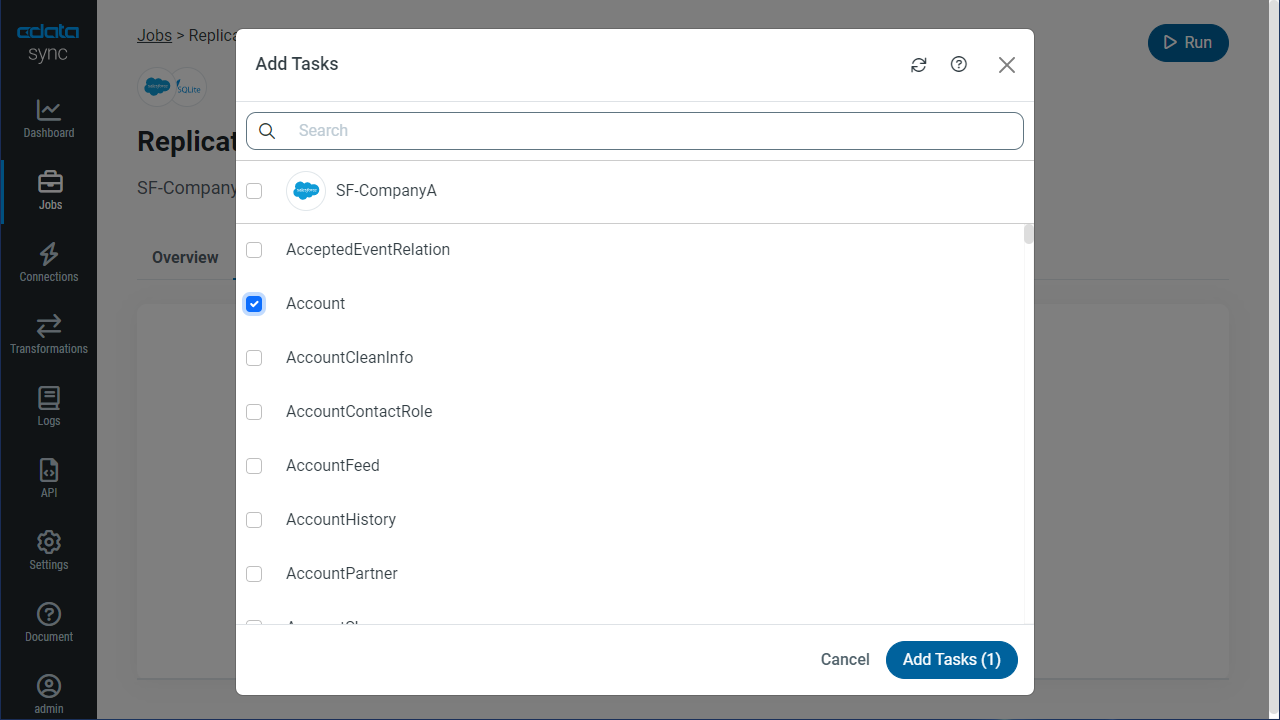
Customize Your Replication
You can use a SQL query to customize your replication. The REPLICATE statement is a high-level command that caches and maintains a table in your database. You can define any SELECT query supported by the SAP ByDesign API. To customize your replication, click Add Custom Query in the Tables section and define the Query Statement.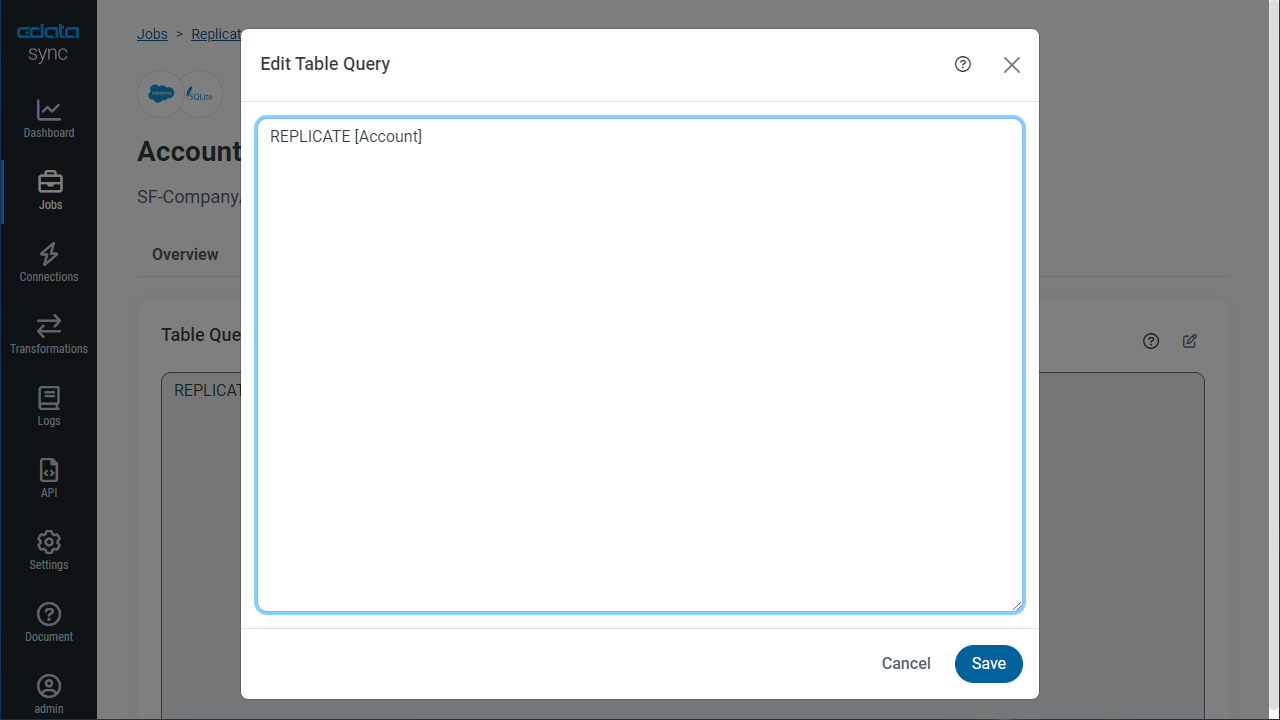
The statement below caches and incrementally updates a table of SAP ByDesign data:
REPLICATE [Inventory Balance];
You can specify a file containing the replication queries you want to use to update a particular database. Separate replication statements with semicolons. The following options are useful if you are replicating multiple SAP ByDesign accounts into the same database:
-
Use a different table prefix in the REPLICATE SELECT statement:
REPLICATE PROD_[Inventory Balance] SELECT * FROM [Inventory Balance]; -
Alternatively, use a different schema:
REPLICATE PROD.[Inventory Balance] SELECT * FROM [Inventory Balance];
Schedule Your Replication
In the Schedule section, you can schedule a job to run automatically, configuring the job to run after specified intervals ranging from once every 10 minutes to once every month.
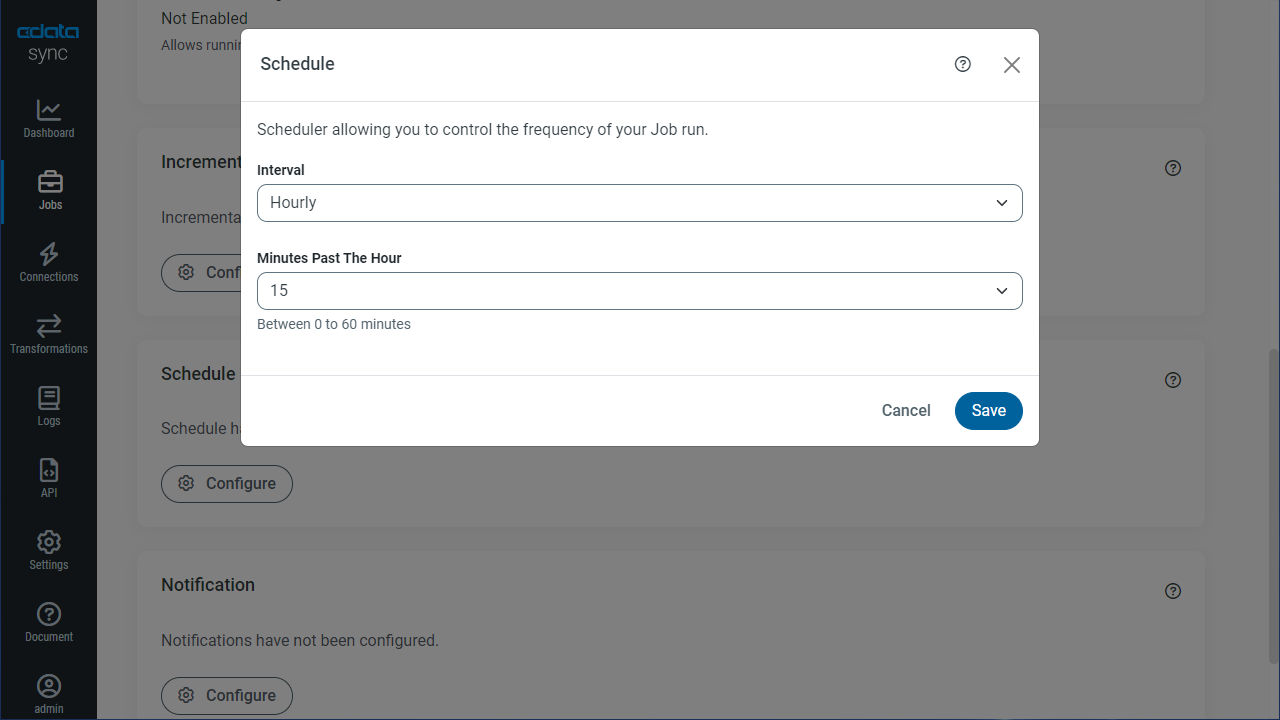
Once you have configured the replication job, click Save Changes. You can configure any number of jobs to manage the replication of your SAP ByDesign data to disparate on-premises, cloud-based, and other databases.