Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Excel Spreadsheet Automation with the QUERY Formula
Pull data, automate spreadsheets, and more with the QUERY formula.
The CData Excel Add-In for SharePoint provides formulas that can edit, save, and delete SharePoint data. The following three steps show how you can automate the following task: Search SharePoint data for a user-specified value and then organize the results into an Excel spreadsheet.
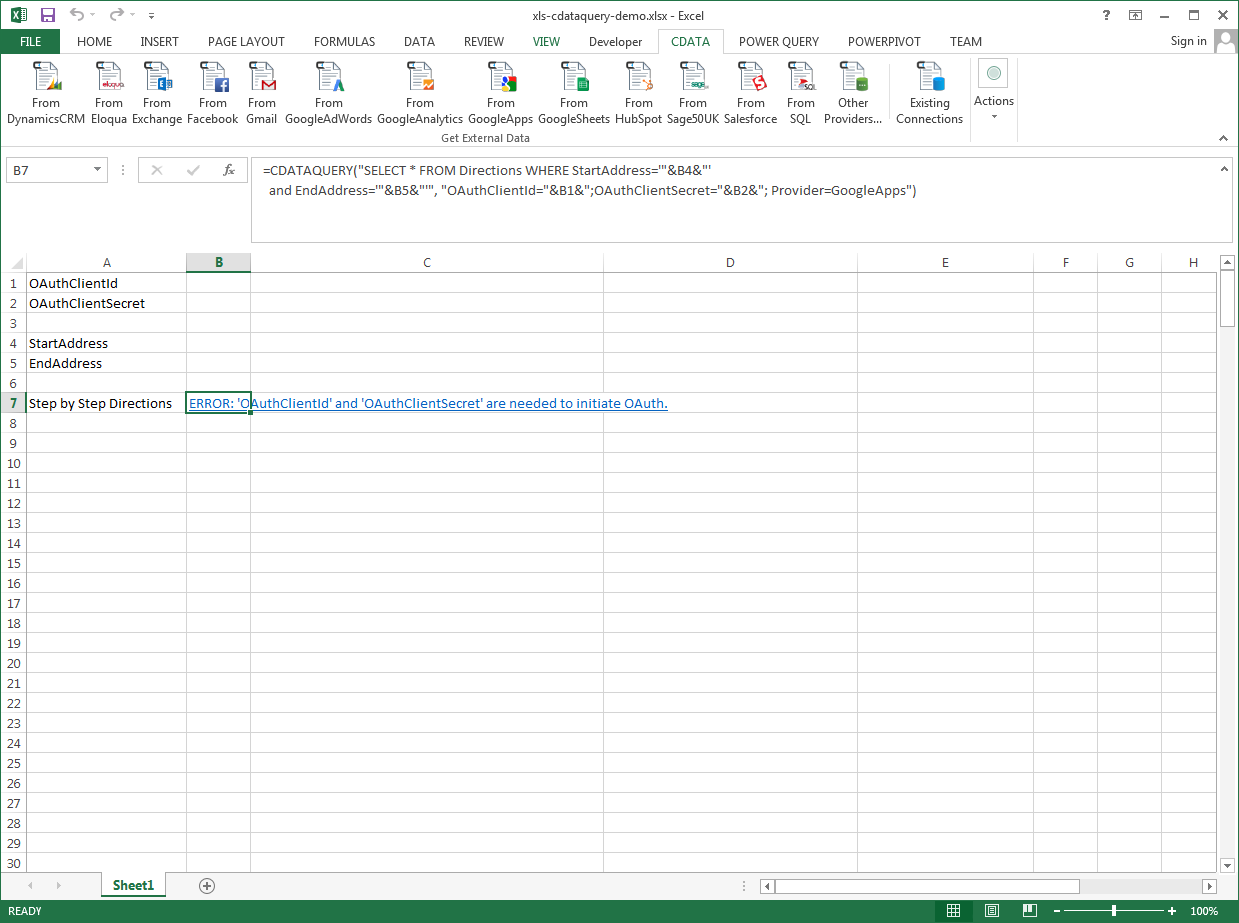
The syntax of the CDATAQUERY formula is the following:
=CDATAQUERY(Query, [Connection], [Parameters], [ResultLocation]);
This formula requires three inputs:
- Query: The declaration of the SharePoint data records you want to retrieve or the modifications to be made, written in standard SQL.
Connection: Either the connection name, such as SharePointConnection1, or a connection string. The connection string consists of the required properties for connecting to SharePoint data, separated by semicolons.
Set the URL property to the base SharePoint site or to a sub-site. This allows you to query any lists and other SharePoint entities defined for the site or sub-site.
The User and Password properties, under the Authentication section, must be set to valid SharePoint user credentials when using SharePoint On-Premise.
If you are connecting to SharePoint Online, set the SharePointEdition to SHAREPOINTONLINE along with the User and Password connection string properties. For more details on connecting to SharePoint Online, see the "Getting Started" chapter of the help documentation
- ResultLocation: The cell that the output of results should start from.
Pass Spreadsheet Cells as Inputs to the Query
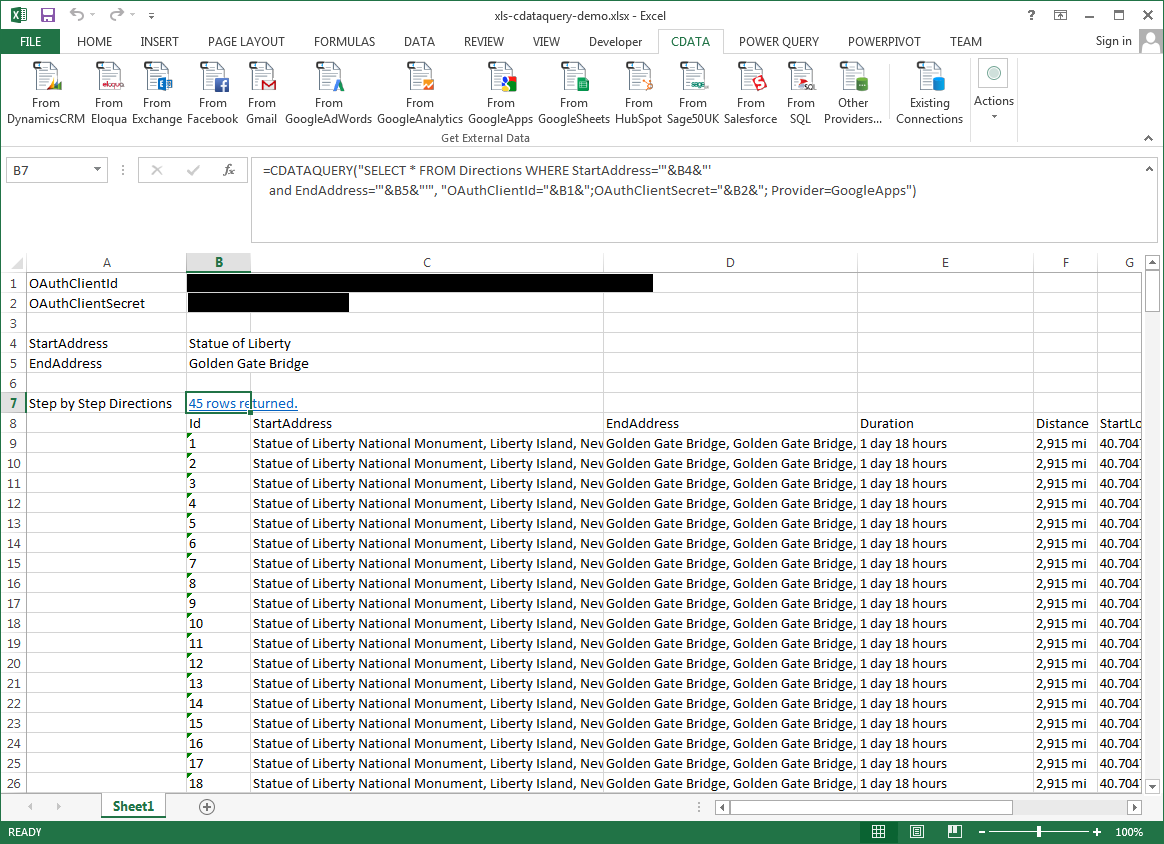
The procedure below results in a spreadsheet that organizes all the formula inputs in the first column.
- Define cells for the formula inputs. In addition to the connection inputs, add another input to define a criterion for a filter to be used to search SharePoint data, such as Location.
- In another cell, write the formula, referencing the cell values from the user input cells defined above. Single quotes are used to enclose values such as addresses that may contain spaces.
- Change the filter to change the data.
![The outputs of the formula. (Google Apps is shown.)]()
=CDATAQUERY("SELECT * FROM MyCustomList WHERE Location = '"&B6&"'","User="&B1&";Password="&B2&";Auth Scheme="&B3&";URL="&B4&";SharePointEdition="&B5&";Provider=SharePoint",B7)