Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Use the CData ODBC Driver for SingleStore in MicroStrategy
Connect to SingleStore data in MicroStrategy Developer using the CData ODBC Driver for SingleStore.
MicroStrategy is an analytics and mobility platform that enables data-driven innovation. When you pair MicroStrategy with the CData ODBC Driver for SingleStore, you gain database-like access to live SingleStore data from MicroStrategy, expanding your reporting and analytics capabilities. In this article, we walk through creating a database instance for SingleStore in MicroStrategy Developer and creating a Warehouse Catalog based on SingleStore data.
The CData ODBC Driver offers unmatched performance for interacting with live SingleStore data in MicroStrategy due to optimized data processing built into the driver. When you issue complex SQL queries from MicroStrategy to SingleStore, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to SingleStore and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations (often SQL functions and JOIN operations) client-side. With built-in dynamic metadata querying, you can visualize and analyze SingleStore data using native MicroStrategy data types.
Connect to SingleStore as an ODBC Data Source
Information for connecting to SingleStore follows, along with different instructions for configuring a DSN in Windows and Linux environments (the ODBC Driver for SingleStore must be installed on the machine hosting the connected MicroStrategy Intelligence Server).
The following connection properties are required in order to connect to data.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the SingleStore database.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the SingleStore database.
- Database (Optional): The default database to connect to when connecting to the SingleStore Server. If this is not set, tables from all databases will be returned.
Connect Using Standard Authentication
To authenticate using standard authentication, set the following:
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the SingleStore server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the SingleStore server.
Connect Using Integrated Security
As an alternative to providing the standard username and password, you can set IntegratedSecurity to True to authenticate trusted users to the server via Windows Authentication.
Connect Using SSL Authentication
You can leverage SSL authentication to connect to SingleStore data via a secure session. Configure the following connection properties to connect to data:
- SSLClientCert: Set this to the name of the certificate store for the client certificate. Used in the case of 2-way SSL, where truststore and keystore are kept on both the client and server machines.
- SSLClientCertPassword: If a client certificate store is password-protected, set this value to the store's password.
- SSLClientCertSubject: The subject of the TLS/SSL client certificate. Used to locate the certificate in the store.
- SSLClientCertType: The certificate type of the client store.
- SSLServerCert: The certificate to be accepted from the server.
Connect Using SSH Authentication
Using SSH, you can securely login to a remote machine. To access SingleStore data via SSH, configure the following connection properties:
- SSHClientCert: Set this to the name of the certificate store for the client certificate.
- SSHClientCertPassword: If a client certificate store is password-protected, set this value to the store's password.
- SSHClientCertSubject: The subject of the TLS/SSL client certificate. Used to locate the certificate in the store.
- SSHClientCertType: The certificate type of the client store.
- SSHPassword: The password that you use to authenticate with the SSH server.
- SSHPort: The port used for SSH operations.
- SSHServer: The SSH authentication server you are trying to authenticate against.
- SSHServerFingerPrint: The SSH Server fingerprint used for verification of the host you are connecting to.
- SSHUser: Set this to the username that you use to authenticate with the SSH server.
When you configure the DSN, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
Windows
If you have not already, first specify connection properties in an ODBC DSN (data source name). This is the last step of the driver installation. You can use the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure ODBC DSNs.
Linux
If you are installing the CData ODBC Driver for SingleStore in a Linux environment, the driver installation predefines a system DSN. You can modify the DSN by editing the system data sources file (/etc/odbc.ini) and defining the required connection properties.
/etc/odbc.ini
[CData SingleStore Sys]
Driver = CData ODBC Driver for SingleStore
Description = My Description
User = myUser
Password = myPassword
Database = NorthWind
Server = myServer
Port = 3306
For specific information on using these configuration files, please refer to the help documentation (installed and found online).
Create a SingleStore Database Instance in MicroStrategy Developer
You can connect to SingleStore in MicroStrategy Developer by adding a database instance based on the CData ODBC Driver for SingleStore.*
- Open MicroStrategy Developer and select a Project Source.
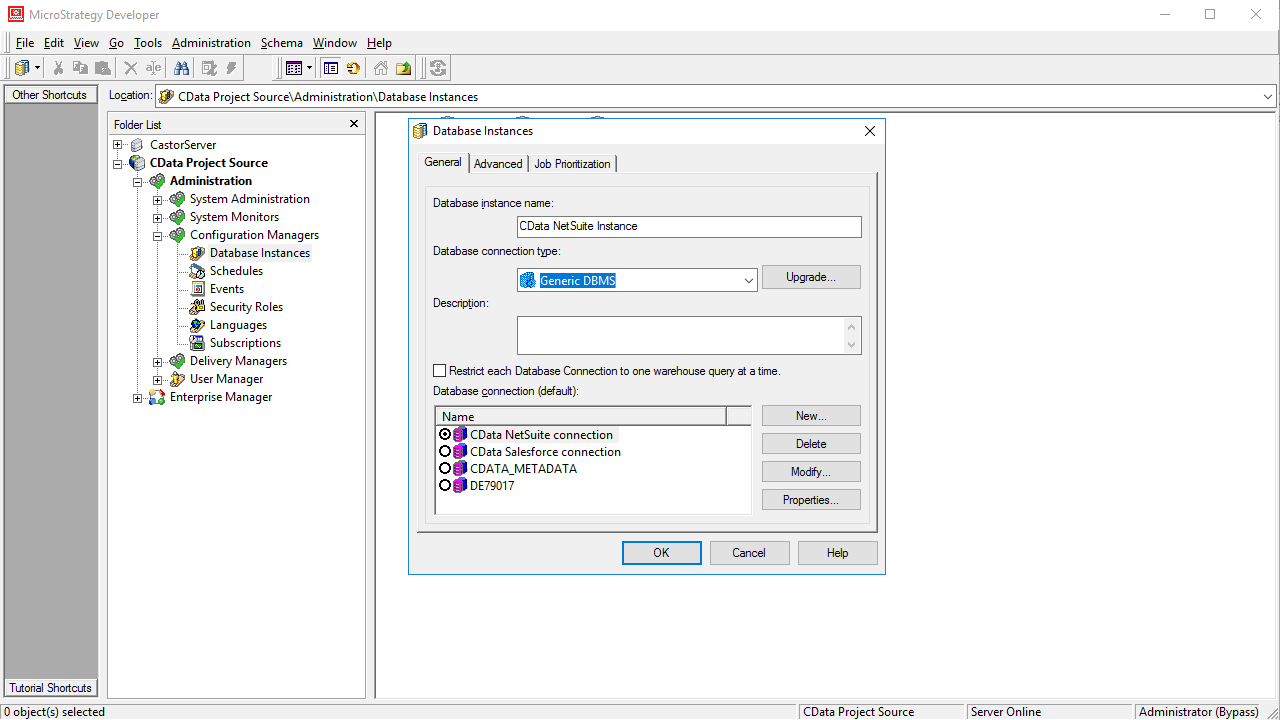
- Navigate to Administration -> Configuration Managers -> Database Instances and right-click to add a new instance.
- Name the instance, select Generic DBMS as the database connection type, and create a new database connection.
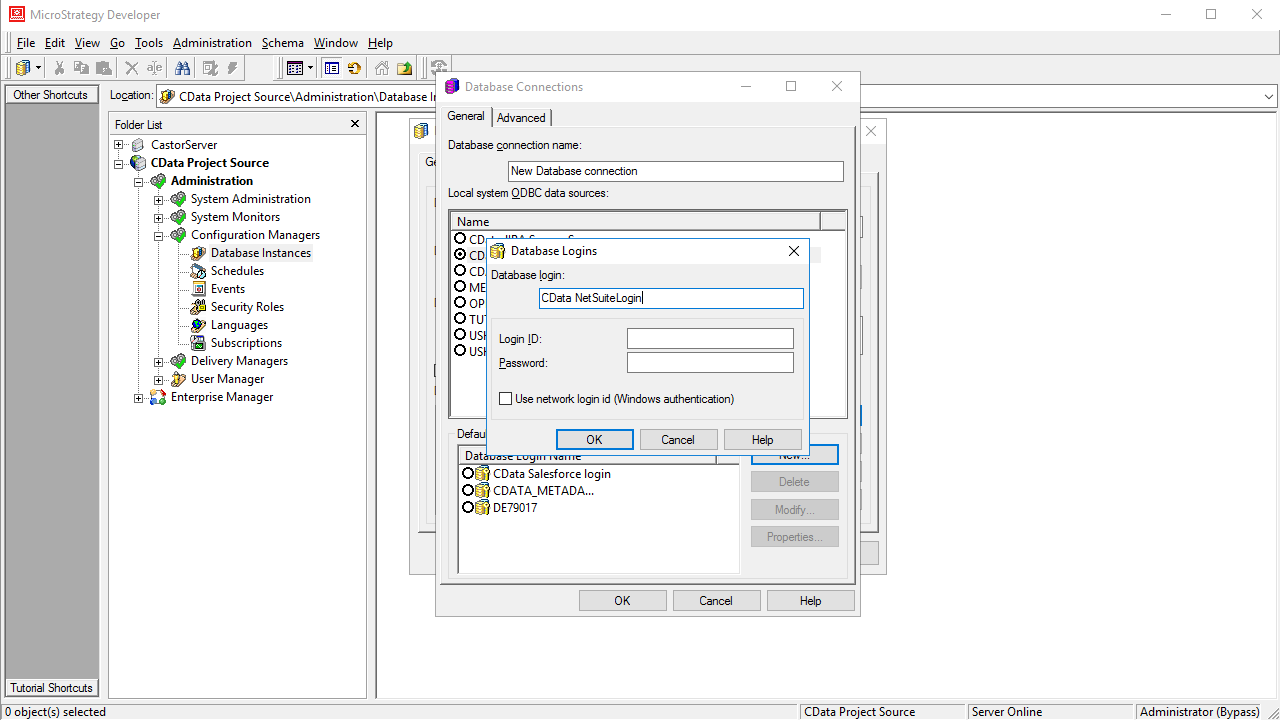
- In the database connection wizard, name the connection and create a new Database Login name, using filler values for the user and password.
![Create a new database login.]()
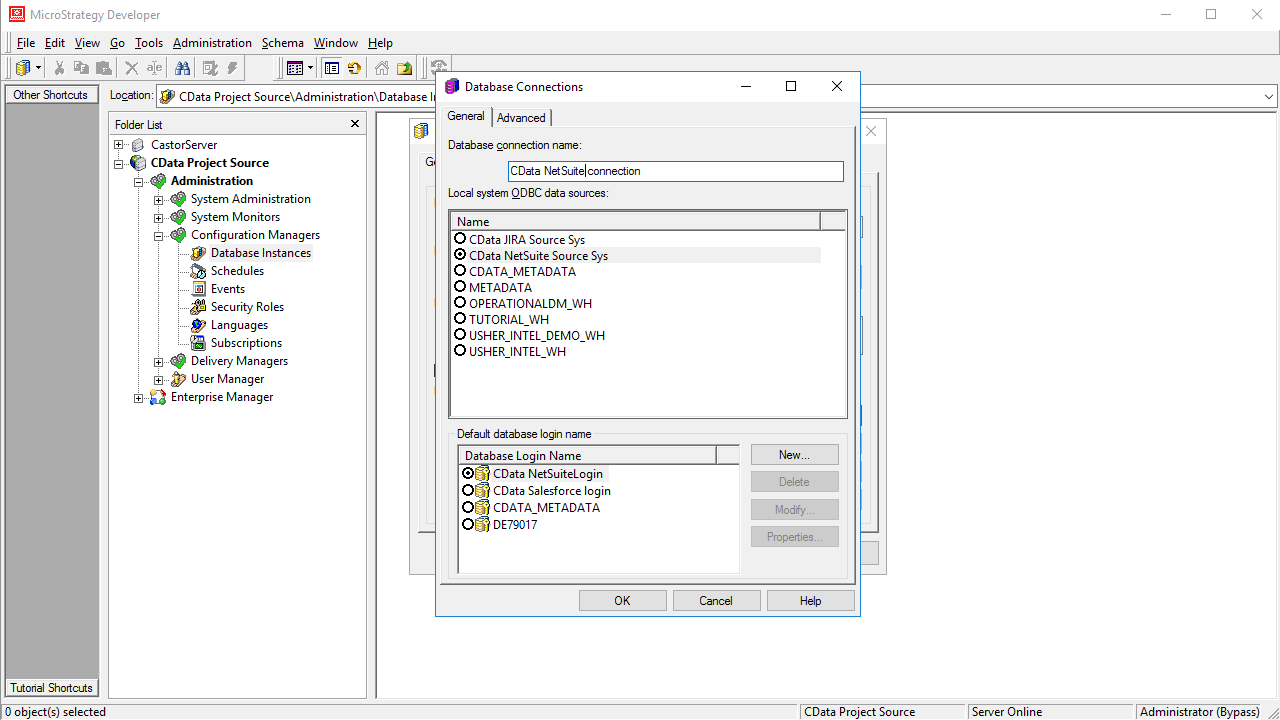
- Select the DSN that you configured earlier as the ODBC data source (i.e., CData SingleStore Sys).
![Choosing the DSN for the database connection.]()
- Select the newly created database connection.
- In the Project Source, right-click the project and open the Project configuration.
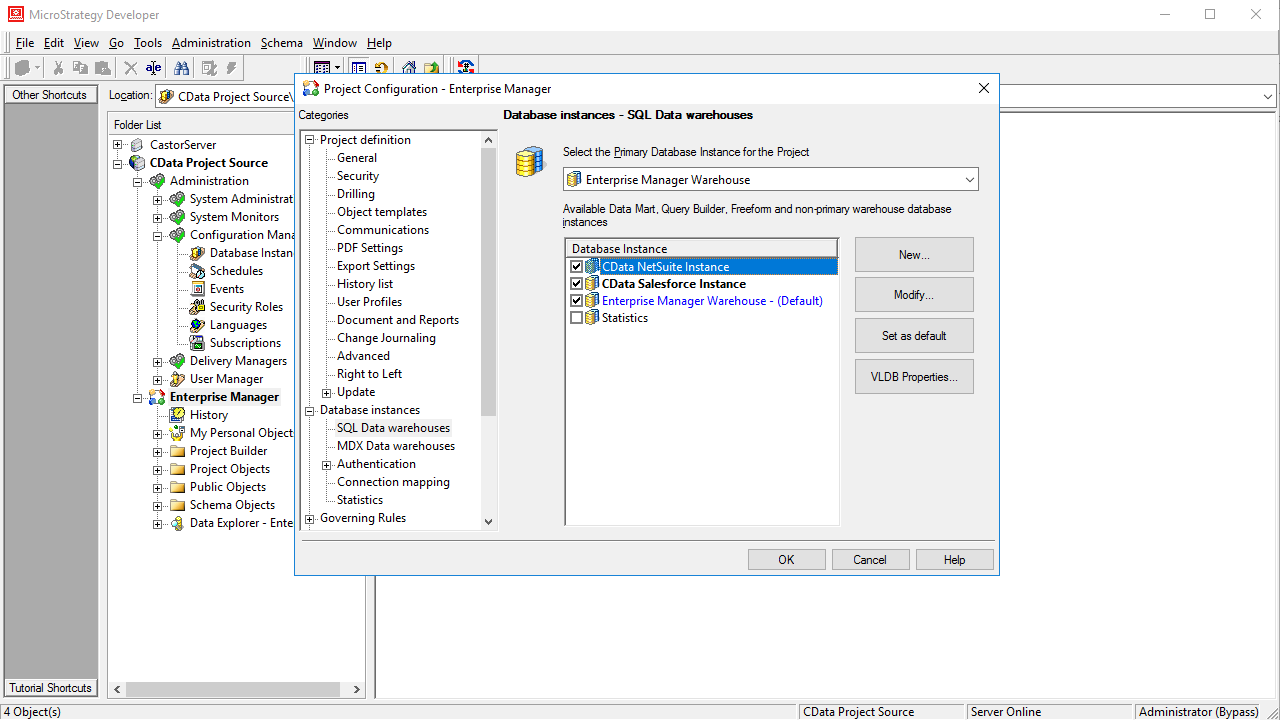
- Navigate to Database Instances and select the newly created database instance.
![Adding the new database instance to the project.]()
- Close MicroStrategy Developer and restart the connected MicroStrategy Intelligence Server to complete the database instance creation.
With the database instance configured, you will now be able to connect to SingleStore data from the Warehouse Catalog and Data Import.
Connect to SingleStore Data from the Warehouse Catalog
Once you have created a database instance based on the ODBC Driver for SingleStore, you can connect to data from the Warehouse Catalog.
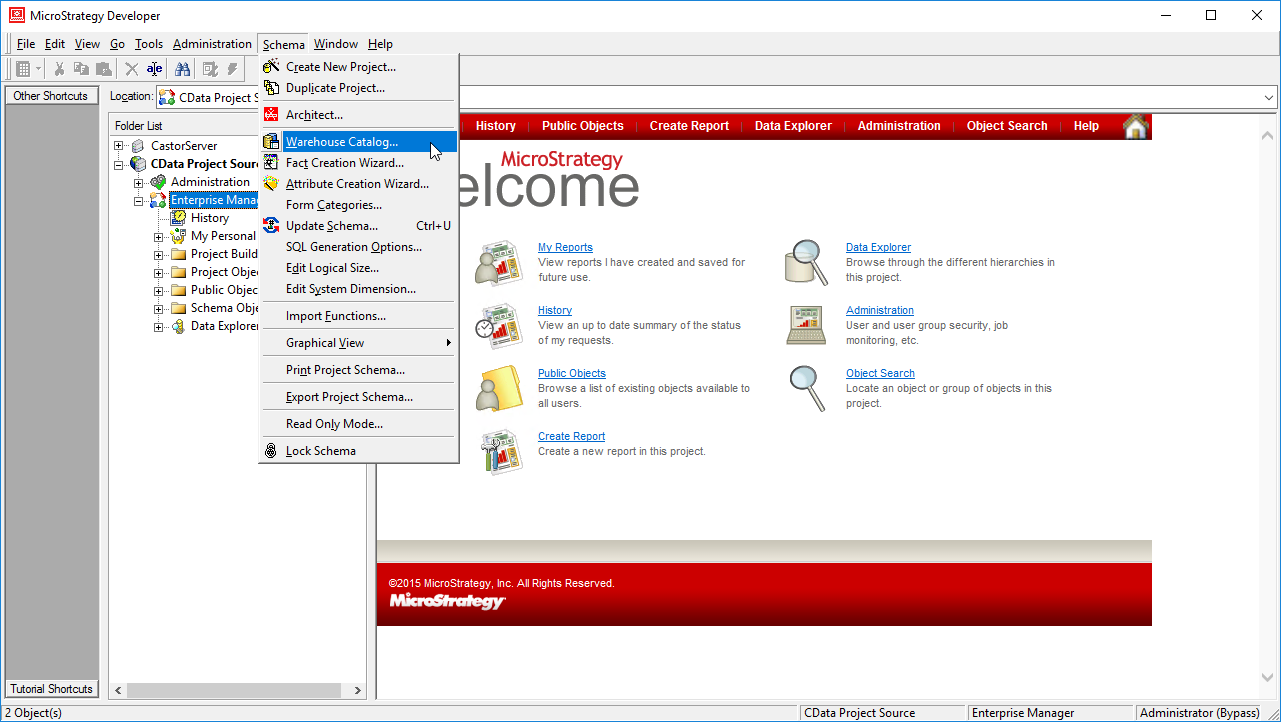
- Select your project and click Schema -> Warehouse Catalog.
![Creating the Warehouse Catalog]()
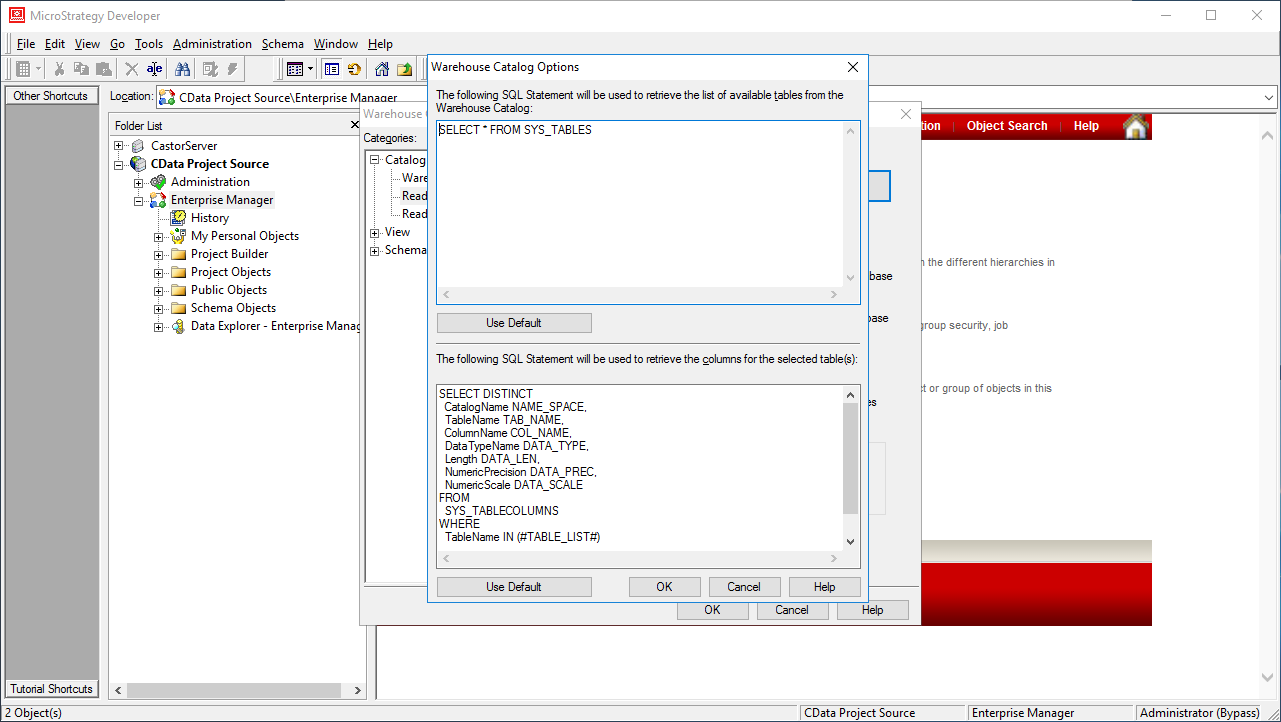
- In the Read Settings for the Catalog, click Settings and set the queries to retrieve the schema:
- To retrieve the list of tables, use the following query:
SELECT CatalogName NAME_SPACE, TableName TAB_NAME FROM SYS_TABLES - To retrieve the list of columns for selected tables, use the following query:
SELECT DISTINCT CatalogName NAME_SPACE, TableName TAB_NAME, ColumnName COL_NAME, DataTypeName DATA_TYPE, Length DATA_LEN, NumericPrecision DATA_PREC, NumericScale DATA_SCALE FROM SYS_TABLECOLUMNS WHERE TableName IN (#TABLE_LIST#) ORDER BY 1,2,3
![Custom metadata queries.]()
- To retrieve the list of tables, use the following query:
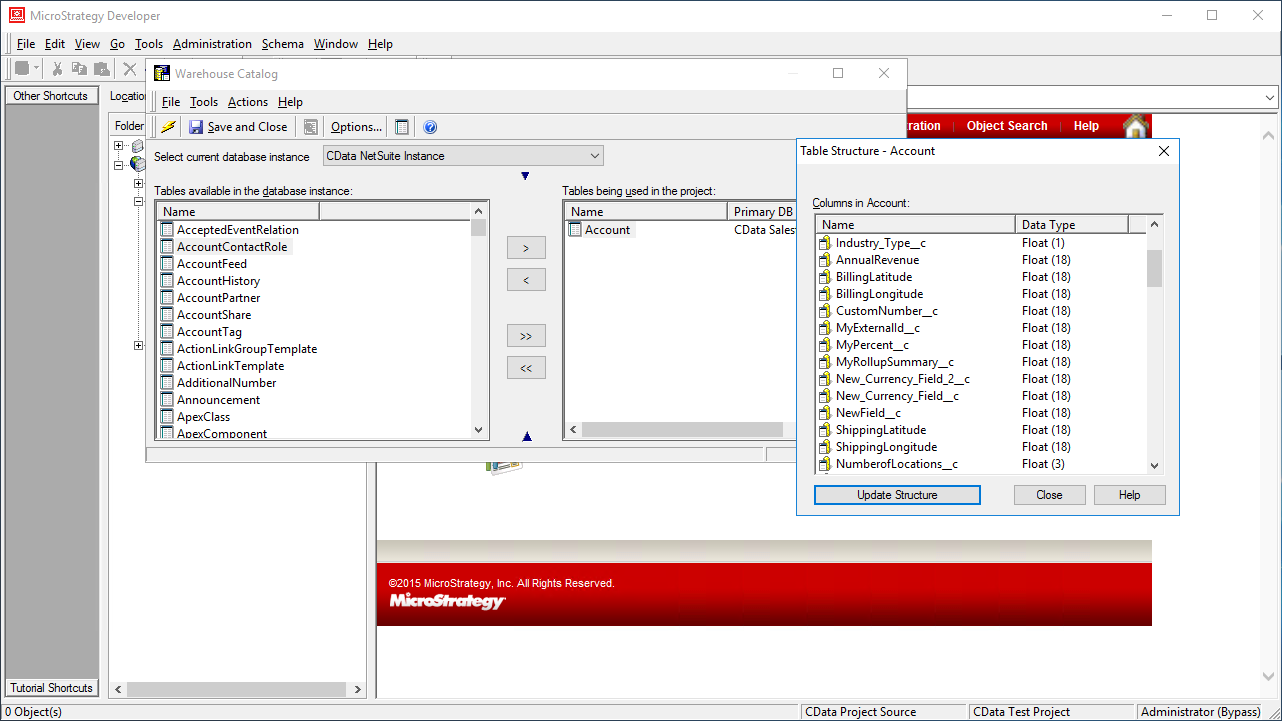
- Select tables to be used in the project.
![Selecting tables to be used in the project.]()
If you are interested in connecting to SingleStore from other MicroStrategy products, you can read about connecting from MicroStrategy Web and connecting from MicroStrategy Desktop.
Note: connecting using a ODBC driver requires a 3- or 4-tier architecture.