Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →How to connect to IBM Cloud Data Engine Data from Google Apps Script
Use CData Connect Server to access IBM Cloud Data Engine data in Google Apps Script.
Google Apps Script gives you the ability to create custom functionality within your Google documents, including Google Sheets, Google Docs, and more. With CData Connect Server, you get a SQL Server interface for any of the 200+ sources supported by CData, including IBM Cloud Data Engine. The SQL Server protocol is natively supported through the JDBC service in Google Apps Script, so by utilizing Connect Server, you gain access to live IBM Cloud Data Engine data within your Google documents.
This article shows how to create a virtual database for IBM Cloud Data Engine in Connect Server and provides sample scripting for processing IBM Cloud Data Engine data in a Google Spreadsheet.
Our script only reads data from a specified table, but you can easily extend the script to incorporate update functionality.
CData Connect Server provides a pure SQL Server interface for IBM Cloud Data Engine, allowing you to easily build reports from live IBM Cloud Data Engine data in Apps Script — without replicating the data to a natively supported database. As you build visualizations, Apps Script generates SQL queries to gather data. Using optimized data processing out of the box, CData Connect Server pushes all supported SQL operations (filters, JOINs, etc) directly to IBM Cloud Data Engine, leveraging server-side processing to quickly return the requested IBM Cloud Data Engine data.
Create a Virtual SQL Server Database for IBM Cloud Data Engine Data
CData Connect Server uses a straightforward, point-and-click interface to connect to data sources and generate APIs.
-
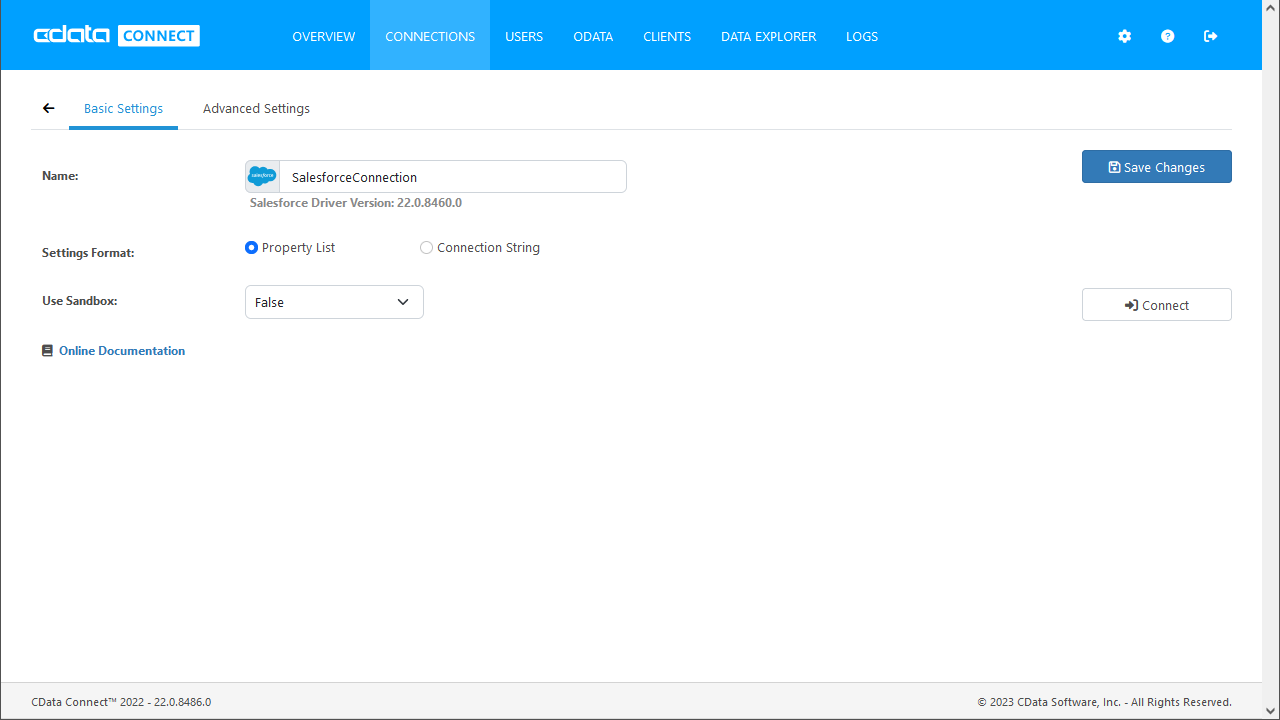
Login to Connect Server and click Connections.
![Adding a connection]()
- Select "IBM Cloud Data Engine" from Available Data Sources.
-
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to IBM Cloud Data Engine.
IBM Cloud Data Engine uses the OAuth and HMAC authentication standards. See the "Getting Started" chapter of the help documentation for a guide to using OAuth.
![Configuring a connection (SQL Server is shown).]()
- Click Save Changes
- Click Privileges -> Add and add the new user (or an existing user) with the appropriate permissions.
With the virtual database created, you are ready to connect to IBM Cloud Data Engine data from Apps Script.
Connect to IBM Cloud Data Engine Data with Apps Script
At this point, you should have configured a virtual database for IBM Cloud Data Engine in Connect Server. All that is left now is to use Google Apps Script to access Connect Server and work with your IBM Cloud Data Engine data in Google Sheets.
In this section, you will create a script (with a menu option to call the script) to populate a spreadsheet with IBM Cloud Data Engine data. We have created a sample script and explained the different parts. You can view the raw script at the end of the article.
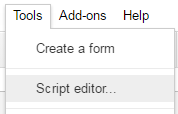
1. Create an Empty Script
To create a script for your Google Sheet, click Tools Script editor from the Google Sheets menu:
2. Declare Class Variables
Create a handful of class variables to be available for any functions created in the script.
//replace the variables in this block with real values as needed var address = 'CONNECT_SERVER_URL:port'; var user = 'CONNECT_USER'; var userPwd = 'CONNECT_PASSWORD'; var db = 'ibmclouddataenginedb'; var serverSslCert = '-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- ... -----END CERTIFICATE-----'; var clientSslCert = '-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- ... -----END CERTIFICATE-----'; var clientSslKey = '-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- ... -----END CERTIFICATE-----'; var dbUrl = 'jdbc:sqlserver://' + address + '/' + db + '?useSSL=true';
3. Add a Menu Option
This function adds a menu option to your Google Sheet, allowing you to use the UI to call your function.
function onOpen() {
var spreadsheet = SpreadsheetApp.getActive();
var menuItems = [
{name: 'Write data to a sheet', functionName: 'connectToIBMCloudDataEngineData'}
];
spreadsheet.addMenu('IBM Cloud Data Engine Data', menuItems);
}
4. Write a Helper Function
This function is used to find the first empty row in a spreadsheet.
/*
* Finds the first empty row in a spreadsheet by scanning an array of columns
* @return The row number of the first empty row.
*/
function getFirstEmptyRowByColumnArray(spreadSheet, column) {
var column = spreadSheet.getRange(column + ":" + column);
var values = column.getValues(); // get all data in one call
var ct = 0;
while ( values[ct] && values[ct][0] != "" ) {
ct++;
}
return (ct+1);
}
5. Write a Function to Write IBM Cloud Data Engine Data to a Spreadsheet
The function below writes the IBM Cloud Data Engine data, using the Google Apps Script JDBC functionality to connect to Connect Server, SELECT data, and populate a spreadsheet. When the script is run, two input boxes will appear:
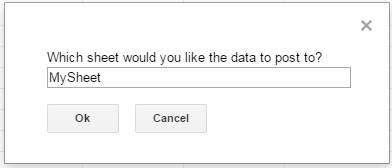
The first one asks the user to input the name of a sheet to hold the data (if the spreadsheet does not exist, the function creates it).
The second asks the user to input the name of a IBM Cloud Data Engine table to read. If an invalid table is chosen, an error message appears and the function is exited.
Note, while the function is designed for use as a menu option, you can extend it for use as a spreadsheet formula.
/*
* Reads data from a specified IBM Cloud Data Engine 'table' and writes it to the specified sheet.
* (If the specified sheet does not exist, it is created.)
*/
function connectToIBMCloudDataEngineData() {
var thisWorkbook = SpreadsheetApp.getActive();
//select a sheet and create it if it does not exist
var selectedSheet = Browser.inputBox('Which sheet would you like the data to post to?',Browser.Buttons.OK_CANCEL);
if (selectedSheet == 'cancel')
return;
if (thisWorkbook.getSheetByName(selectedSheet) == null)
thisWorkbook.insertSheet(selectedSheet);
var resultSheet = thisWorkbook.getSheetByName(selectedSheet);
var rowNum = 2;
//select a IBM Cloud Data Engine 'table'
var table = Browser.inputBox('Which table would you like to pull data from?',Browser.Buttons.OK_CANCEL);
if (table == 'cancel')
return;
var conn = Jdbc.getConnection(dbUrl, {
user: user,
password: userPwd,
_serverSslCertificate: serverSslCert,
_clientSslCertificate: clientSslCert,
_clientSslKey: clientSslKey
);
//confirm that var table is a valid table/view
var dbMetaData = conn.getMetaData();
var tableSet = dbMetaData.getTables(null, null, table, null);
var validTable = false;
while (tableSet.next()) {
var tempTable = tableSet.getString(3);
if (table.toUpperCase() == tempTable.toUpperCase()){
table = tempTable;
validTable = true;
break;
}
}
tableSet.close();
if (!validTable) {
Browser.msgBox("Invalid table name: " + table, Browser.Buttons.OK);
return;
}
var stmt = conn.createStatement();
var results = stmt.executeQuery('SELECT * FROM ' + table);
var rsmd = results.getMetaData();
var numCols = rsmd.getColumnCount();
//if the sheet is empty, populate the first row with the headers
var firstEmptyRow = getFirstEmptyRowByColumnArray(resultSheet, "A");
if (firstEmptyRow == 1) {
//collect column names
var headers = new Array(new Array(numCols));
for (var col = 0; col < numCols; col++){
headers[0][col] = rsmd.getColumnName(col+1);
}
resultSheet.getRange(1, 1, headers.length, headers[0].length).setValues(headers);
} else {
rowNum = firstEmptyRow;
}
//write rows of IBM Cloud Data Engine data to the sheet
var values = new Array(new Array(numCols));
while (results.next()) {
for (var col = 0; col < numCols; col++) {
values[0][col] = results.getString(col + 1);
}
resultSheet.getRange(rowNum, 1, 1, numCols).setValues(values);
rowNum++;
}
results.close();
stmt.close();
}
When the function is completed, you have a spreadsheet populated with your IBM Cloud Data Engine data, and you can now leverage all of the calculating, graphing, and charting functionality of Google Sheets anywhere you have access to the Internet.
Complete Google Apps Script
//replace the variables in this block with real values as needed
var address = 'CONNECT_SERVER_URL:port';
var user = 'CONNECT_USER';
var userPwd = 'CONNECT_PASSWORD';
var db = 'ibmclouddataenginedb';
var serverSslCert = '-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----';
var clientSslCert = '-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----';
var clientSslKey = '-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----';
var dbUrl = 'jdbc:sqlserver://' + address + '/' + db + '?useSSL=true';
function onOpen() {
var spreadsheet = SpreadsheetApp.getActive();
var menuItems = [
{name: 'Write table data to a sheet', functionName: 'connectToIBMCloudDataEngineData'}
];
spreadsheet.addMenu('IBM Cloud Data Engine Data', menuItems);
}
/*
* Finds the first empty row in a spreadsheet by scanning an array of columns
* @return The row number of the first empty row.
*/
function getFirstEmptyRowByColumnArray(spreadSheet, column) {
var column = spreadSheet.getRange(column + ":" + column);
var values = column.getValues(); // get all data in one call
var ct = 0;
while ( values[ct] && values[ct][0] != "" ) {
ct++;
}
return (ct+1);
}
/*
* Reads data from a specified 'table' and writes it to the specified sheet.
* (If the specified sheet does not exist, it is created.)
*/
function connectToIBMCloudDataEngineData() {
var thisWorkbook = SpreadsheetApp.getActive();
//select a sheet and create it if it does not exist
var selectedSheet = Browser.inputBox('Which sheet would you like the data to post to?',Browser.Buttons.OK_CANCEL);
if (selectedSheet == 'cancel')
return;
if (thisWorkbook.getSheetByName(selectedSheet) == null)
thisWorkbook.insertSheet(selectedSheet);
var resultSheet = thisWorkbook.getSheetByName(selectedSheet);
var rowNum = 2;
//select a IBM Cloud Data Engine 'table'
var table = Browser.inputBox('Which table would you like to pull data from?',Browser.Buttons.OK_CANCEL);
if (table == 'cancel')
return;
var conn = Jdbc.getConnection(dbUrl, {
user: user,
password: userPwd,
_serverSslCertificate: serverSslCert,
_clientSslCertificate: clientSslCert,
_clientSslKey: clientSslKey
);
//confirm that var table is a valid table/view
var dbMetaData = conn.getMetaData();
var tableSet = dbMetaData.getTables(null, null, table, null);
var validTable = false;
while (tableSet.next()) {
var tempTable = tableSet.getString(3);
if (table.toUpperCase() == tempTable.toUpperCase()){
table = tempTable;
validTable = true;
break;
}
}
tableSet.close();
if (!validTable) {
Browser.msgBox("Invalid table name: " + table, Browser.Buttons.OK);
return;
}
var stmt = conn.createStatement();
var results = stmt.executeQuery('SELECT * FROM ' + table);
var rsmd = results.getMetaData();
var numCols = rsmd.getColumnCount();
//if the sheet is empty, populate the first row with the headers
var firstEmptyRow = getFirstEmptyRowByColumnArray(resultSheet, "A");
if (firstEmptyRow == 1) {
//collect column names
var headers = new Array(new Array(numCols));
for (var col = 0; col < numCols; col++){
headers[0][col] = rsmd.getColumnName(col+1);
}
resultSheet.getRange(1, 1, headers.length, headers[0].length).setValues(headers);
} else {
rowNum = firstEmptyRow;
}
//write rows of IBM Cloud Data Engine data to the sheet
var values = new Array(new Array(numCols));
while (results.next()) {
for (var col = 0; col < numCols; col++) {
values[0][col] = results.getString(col + 1);
}
resultSheet.getRange(rowNum, 1, 1, numCols).setValues(values);
rowNum++;
}
results.close();
stmt.close();
}